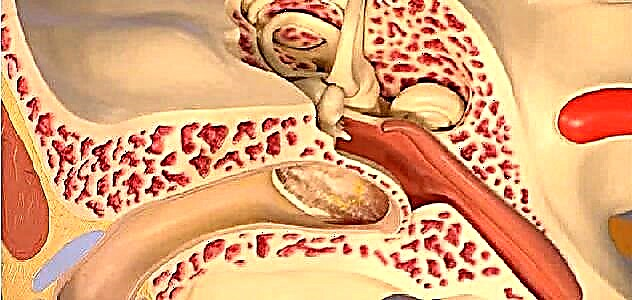
Stenosing laryngitis (false croup) often develops as a complication of a viral disease that affects the organs of the nasopharynx. Due to the resulting inflammation, edema appears and a significant increase in the amount of secretion produced. During the process of the disease, a significant narrowing of the lumen in the larynx (stenosis) occurs, which can lead to breathing difficulties and even suffocation. If false croup is diagnosed, treatment should be comprehensive and based not only on the use of medications, but also on ensuring optimal climatic conditions in the room, balanced diet, and sufficient fluid intake.
Causes
 Stenosing laryngitis occurs mainly in children in the period from half a year to six years. The main reason for false croup is considered to be the structural features of the larynx in a child in the first years of life. Due to the extremely small lumen in the child's larynx, even slight swelling can cause breathing difficulties.
Stenosing laryngitis occurs mainly in children in the period from half a year to six years. The main reason for false croup is considered to be the structural features of the larynx in a child in the first years of life. Due to the extremely small lumen in the child's larynx, even slight swelling can cause breathing difficulties.
The structure of the larynx creates favorable conditions for the development of stenosis before the age of six:
- elastic cartilaginous skeleton;
- narrow and short vestibule of the pharynx;
- highly located vocal cords;
- a large number of cellular elements and blood vessels in the pharyngeal mucosa.
Important! The younger the child who has fallen ill with false croup, the more serious the consequences can be caused by the disease.
The risk group for the development of stenosis includes children with a predisposition to allergies, low immunity, increased emotional excitability. It is also known that boys are more likely to have croup than girls. After the age of six years, croup is extremely rare, this is due to a significant increase in the lumen in the larynx, which becomes wider, therefore, edema with laryngitis is no longer life-threatening.
False croup in children most often appears as a complication as a result of exposure to the body of an infectious disease, often caused by a virus (parainfluenza, influenza, herpes). Much less often, stenosing laryngitis occurs when bacteria (haemophilus influenzae, staphylococcus) are exposed to the body. False croup of a bacterial nature is more complicated.
There are several reasons for the development of edema with stenosing laryngitis:
- a significant decrease in the opening in the larynx due to the occurrence of edema;
- involuntary spasm of the laryngeal muscles, which significantly aggravates the manifestation of stenosis;
- increased production of viscous secretion due to the overly active work of the glands of the nasopharynx, which becomes the cause of obstruction of the reduced lumen of the larynx.
Warm and very dry air, improper diet, insufficient fluid intake - all this can cause stenosis against the background of an existing infection.
Symptoms
Signs of stenosing laryngitis often develop on the second or third day after the onset of the underlying disease. Doctors identify certain symptoms that indicate that the child is beginning to have a false croup:
- barking, dry, annoying cough;
- burning and sore throat;
- rapid, noisy breathing, accompanied by shortness of breath.
These symptoms occur against a background of hyperthermia (body temperature is more often above 38 degrees), overexcitation, an increase in the size of the cervical lymph nodes, wheezing, audible when inhaling.
Important! Symptoms of false croup can change during the day, a worsening of the patient's condition often occurs during a night's sleep, it is then that asthma attacks occur.
An exacerbation of croup symptoms during a night's sleep is associated with several factors:
- a significant increase in the tone of the parasympathetic nervous system at night, which increases the secretion and contractile activity of the muscles of the trachea;
- horizontal position during sleep, which significantly impairs the drainage function of the lungs.
Experts distinguish several stages of the development of the disease, each of which corresponds to certain symptoms.
- The first stage is the initial stage of stenosis development. The disease is accompanied by shortness of breath, shortness of breath, which are manifested solely as a result of physical exertion. On examination by a doctor, increased inhalation and dry wheezing may be heard.
- The second stage of the disease is characterized by the appearance of shortness of breath even in the absence of physical activity. Breathing becomes difficult, inhalation is accompanied by the confluence of the intercostal spaces. Oxygen deficiency increases, the condition is accompanied by pallor of the skin, cyanosis of the nasolabial triangle. At this stage, agitation increases significantly, the child cannot sleep.
- The third stage requires urgent help from specialists. The shortness of breath becomes worse, the cough becomes more painful. The compensatory functions of the body are not enough, the stenosis is aggravated, the cyanosis extends all over the skin. The pulse quickens, the child becomes lethargic.
- The fourth stage of the development of the disease carries a real threat to life, due to the occurrence of asphyxia. At this stage, cough and shortness of breath, characteristic of stenosing laryngitis, practically disappear, breathing becomes shallow, arrhythmia occurs. Vital signs (pressure and heart rate) are reduced, and the condition may be accompanied by seizures.
Treatment
Treatment of false croup in children should primarily be aimed at preventing and quickly stopping attacks of stenosis, as well as reducing inflammation and reducing swelling.
As a prophylaxis for croup attacks, it is necessary:
 ventilate the room where the sick child is;
ventilate the room where the sick child is;- provide a sufficient amount of liquid, it is better if the drink is alkaline;
- exclude irritating food (hot, cold, spicy, salty, smoked, solid), give preference to warm, fortified, mushy food;
- to relieve sore throat, you can use special lozenges, lozenges, sprays (Strepsils, Doctor Mom, Ingalipt, Septefril).
False croup is often accompanied by a dry, irritating cough. In this case, you can use antitussive drugs (Sinekod, Codelac). However, the use of these drugs should be made only after consulting a doctor, and only in situations where false croup is not accompanied by the formation of a large amount of viscous secretion. If a large amount of secretion is produced with false croup, it is advisable to use expectorant and mucolytic agents (Lazolvan, Erespal).
Complex treatment of stenosis in children should include the use of antiallergic drugs to reduce tissue edema, for example, Diazolin, Suprastin, Loratadin.
In the later stages of croup development, it is advisable to use:
- for the rapid removal of puffiness, glucocorticoid drugs are recommended (Dexamethasone, Prednisolone);
- sedatives to relieve laryngeal spasm, reduce muscle tone (Novo-Passit, Barboval, Valerian);
- anti-inflammatory drugs that reduce swelling and normalize body temperature (ibuprofen);
Important! In the complex treatment of inflammatory processes in children, the use of such an anti-inflammatory agent as Aspirin is contraindicated due to the risk of Reye's syndrome.
- with the viral nature of false croup, antiviral drugs (Groprinosin, Arbidol) are used in complex treatment;
- with the bacterial nature of false croup, treatment is carried out using antibacterial therapy (Sumamed, Augmentin).
The use of diuretics helps to remove excess fluid from the body, which helps to reduce the severity of edema. For this, special diuretic drugs are used, for example, Arifon, Lasix, Diuver.
 Croup attacks are often accompanied by a reflex spasm of the laryngeal muscles. In order to reduce the symptom, it is necessary to induce the opposite reflex, for example, induce vomiting by pressing on the tongue, or try to induce a sneeze by tickling the nose.
Croup attacks are often accompanied by a reflex spasm of the laryngeal muscles. In order to reduce the symptom, it is necessary to induce the opposite reflex, for example, induce vomiting by pressing on the tongue, or try to induce a sneeze by tickling the nose.
Hot foot baths are used as a distracting non-drug procedure. In this case, blood rushes to the extremities, reducing swelling. Warming up the chest and larynx area with warm compresses will help reduce muscle tone and relax the muscles.
Inhalation is an effective means of reducing the severity of stenosis. With false croup, inhalations are shown using alkaline solutions, for example, Borjomi, Polyana Kvasova. You can prepare such a solution yourself, at the rate of one teaspoon of baking soda per liter of warm boiled water.
First aid
Along with drug treatment, it is important to know the basic principles and methods of providing first aid to a patient with stenosing laryngitis, because without timely measures, the disease will develop and can cause death. Therefore, a common viral infection in a child is accompanied by shortness of breath and other symptoms characteristic of stenosing laryngitis, it follows:
- call a doctor;
- raise the patient's upper body by placing an additional pillow;
- try to calm the patient down, as anxiety can only aggravate the signs of laryngeal spasm;
- provide an influx of fresh air (open the window), make breathing easier (take off tight clothes);
- it is imperative to observe the optimal climatic conditions in the room: humidity not lower than 50% (with cereals about 70%), temperature not higher than 18-20 degrees;
- give the child a large amount of warm liquid, it is better to just water or herbal decoction (chamomile, sage), excluding juices, carbonated drinks;
- before the arrival of an ambulance, you can use the antihistamines described above, antispasmodics (Drotaverin, Papaverine).
Further therapy should be carried out exclusively in a medical institution and carried out under the supervision of a specialist.
Important! In the later stages of the development of stenosis, surgical intervention may be required: intubation (insertion of a special tube into the trachea) or tracheostomy (insertion of a cannula into the trachea or suturing the tracheal wall to the skin).
Inhalation
Inhalation is a simple and effective way to provide first aid and treatment for stenosing laryngitis in children and adults.
- The easiest way to inhale with a nebulizer is to use alkaline mineral waters. 2-4 ml of liquid is poured into the device, the procedure is carried out for ten minutes, repeated three to five times throughout the day. If the necessary device is not available, then the soda can be dissolved in warm water and let the child breathe alkaline air.
- Inhalation with a nebulizer with a solution of Berodual, Euphyllin or Salbutamol is also indicated for the development of stenosis. In this case, the drug in the appropriate age concentration is diluted with 2 ml of saline, inhalations are carried out 2-3 times a day as prescribed by the doctor.
- The use of hormonal antiallergic drugs by inhalation also has a higher efficiency in comparison with oral administration. With stenosing laryngitis, the use of Dexamethasone, Pulmicort, Cromohexal is indicated.
Prophylaxis
In order to reduce the likelihood of stenosing laryngitis in a child, it is important to prevent the occurrence of respiratory diseases and treat acute forms of diseases in time.
- Throat hardening. This is a simple procedure that needs to be done regularly. The child should gargle with water, using room temperature water first. Gradually, over several months, the water temperature should decrease, reaching about five degrees. The main thing is not to rush, lowering the temperature by one or two degrees a week, because otherwise the child may get sick.
- Proper nutrition. The child's daily diet should be balanced and rich in vitamins, trace elements that help in the formation of immunity and resist viral infections. It should also be borne in mind that the cause of false croup is often allergic reactions to certain foods.
- Compliance with the regime of work and rest. Adequate sleep is especially important in childhood, as it helps the body to recuperate and resist the development of infections.
- To reduce the likelihood of developing stenosing laryngitis, which has arisen against the background of viral infections, it is necessary to monitor the cleanliness, temperature and humidity of the air in the apartment where the child lives. So, dusty, too warm and dry air can cause drying of the nasopharyngeal mucosa and the development of complications.

 ventilate the room where the sick child is;
ventilate the room where the sick child is;