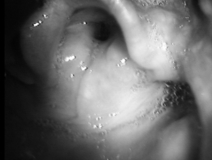
The paranasal sinuses in adverse conditions or when exposed to pathogenic microorganisms tend to become inflamed. Sinusitis is one of the most common problems people go to see an otolaryngologist. It is much more difficult to cure inflammation that has affected the maxillary or frontal sinuses than ordinary rhinitis. If, moreover, immunity is reduced and a person often suffers from ARVI, sinusitis becomes chronic.
Chronic sinusitis in adults occurs "due to" infection with an infection, changes in the sinus mucosa (polyposis) or a sharp decrease in local immunity.
Causes of occurrence
 The fact that sinusitis is chronic can be said when it is impossible to cope with it for 3 weeks. This is also evidenced by repeated relapses, repeated after the onset of recovery. Chronic sinusitis can last for several months. One of the most common types of this disease is sinusitis - the inflammatory process with this ailment is concentrated exclusively in the maxillary sinuses.
The fact that sinusitis is chronic can be said when it is impossible to cope with it for 3 weeks. This is also evidenced by repeated relapses, repeated after the onset of recovery. Chronic sinusitis can last for several months. One of the most common types of this disease is sinusitis - the inflammatory process with this ailment is concentrated exclusively in the maxillary sinuses.
Chronic sinusitis is not an independent disease that occurs immediately and on its own. Most often it develops due to:
- not completely treated diseases of the nasopharynx or illiterate antibiotic therapy;
- violations of the patency of the nasal cavity: the appearance of neoplasms, stuck foreign bodies, changes in the shape of the septum, and so on;
- overgrowth of the adenoids (often recorded in children);
- the formation of polyps that grow on the mucous membrane and block the nasal passages (in this case, we are talking about chronic polyposis sinusitis);
- allergies, accompanied by edema of the nasal mucosa;
- facial injuries (a fracture of one of the facial bones may be the cause of the development of obstruction of the nasal cavity);
- disorders of the immune system, in particular - congenital immunodeficiency.
In addition to all of the above, the risk of chronic sinusitis increases significantly if a person is under prolonged exposure to tobacco smoke and any toxic substances.
The risk group also includes those who have individual hypersensitivity to aspirin, suffer from bronchial asthma, chronic lung disease, AIDS, complicated by cystic fibrosis, and so on.
Signs of the disease
Chronic sinusitis manifests itself in many different ways. Two people with this condition may have very different symptoms. How this ailment will manifest itself depends directly on the nature of its course and the area affected by inflammation.
So, chronic sinusitis is usually characterized by:
 a protracted, long-lasting rhinitis, which is often accompanied by green or yellow discharge with purulent contents, in some cases with blood clots;
a protracted, long-lasting rhinitis, which is often accompanied by green or yellow discharge with purulent contents, in some cases with blood clots;- constantly stuffy nose (however, the nostrils in turn can periodically "break through");
- severe bouts of dry cough in the evening and at night (if, apart from this symptom, nothing else bothers you, most likely it is bronchitis);
- copious mucous mucus in the morning, combined with dryness of the nasopharynx;
- subfebrile temperature (constantly held at around 37 degrees or so);
- loss of smell - partially or completely;
- rapid fatigue, general malaise, lack of appetite and other signs indicating intoxication;
- swelling of the face, which is especially pronounced in the area of the inflamed sinuses;
- high sensitivity in the facial area of the head;
- headache concentrated at the base of the nose and in the area under the eyes (with sinusitis), above the bridge of the nose and in the frontal region (with frontal sinusitis), on the very bridge of the nose, on the frontal zone and behind the eyeballs (with ethmoiditis), on the upper part of the forehead and on the occipital part of the head (with sphenoiditis).
The pain increases if you tilt your head in different directions and forward, as well as during physical exercises of medium to high difficulty level. At the same time, its localization is lost.
Note that the difference between chronic sinusitis and acute sinusitis lies in the mild severity of symptoms and a longer duration. In addition, its signs can almost completely disappear for some time, after which they can resume again.
How does it manifest in children
In children, the above signs of "adult" sinusitis are more pronounced. The final formation of the maxillary sinuses in a child is completed only by the age of 9. And before that, the radius of the anastomosis located between the separately located sinuses remains very small. This leads to their regular clogging.
If acute respiratory infections or a common rhinitis are not completely cured, the channels of the cavities are guaranteed to be blocked. As a result, there is a violation of the full removal of mucus, and the first signs of sinusitis appear.
In addition to the main symptoms indicating the development of this disease, parents should pay attention to:
- lethargy and quickly approaching fatigue;
- blanching of the skin;
- blue circles under the eyes;
- weight loss;
- loss of appetite.

In toddlers at an early age, chronic sinusitis can be suspected if a dry cough develops that bothers the child at night. And also if pus from the nasal passages continues to stand out for more than 10 days.
Most often, both adults and children have sinusitis. This is a type of chronic sinusitis that affects the maxillary sinus. This disease is characterized by all of the above symptoms. Additionally, soreness in the upper jaw area should be noted, which intensifies if you press on it where the incisors are located.
Since the immune system of 8-9-year-old children does not always function smoothly and stably, the temperature may not rise. First of all, parents should be alerted by the discharge of pus from the nose and attacks of dry cough that has come out of nowhere, annoying the child in the evenings and nights. With sinusitis and other types of chronic sinusitis, they last more than 10 days.
If the child begins to complain of a headache, and he has symptoms of intoxication, you should immediately contact a pediatric otolaryngologist. The sooner adequate treatment is prescribed, the lower the risk of complications.
Types and forms of chronic sinusitis
- Sinusitis - this type of sinusitis involves inflammation of the sinuses located in the upper jaw (one or two at once). With sinusitis, as a rule, the temples, the forehead and the front wall of the affected sinus hurt, there is a heaviness in the head, purulent discharge and unilateral nasal congestion are disturbed.
- Maxillary. Already from the very name of the disease, it is clear that inflammation affects only the maxillary sinuses. It should be noted that this is a rather complex type of chronic sinusitis. Its danger lies in the fact that after a certain time it can turn into an oncological disease.
 Frontal. A characteristic feature of this ailment is pain syndrome of moderate intensity, concentrated in the area of the frontal sinuses. Nasal discharge has a specific, unpleasant odor. Their abundance is significantly increased. As for body temperature, it is kept at a subfebrile level.
Frontal. A characteristic feature of this ailment is pain syndrome of moderate intensity, concentrated in the area of the frontal sinuses. Nasal discharge has a specific, unpleasant odor. Their abundance is significantly increased. As for body temperature, it is kept at a subfebrile level.- Sphenoid. With this disease, the sphenoid sinuses of the nasal cavity become inflamed. The main symptom is pain concentrated in the head.Occipital soreness and soreness. In this case, no discharge from the nose is observed. Although his congestion still remains.
- Ethmoidal. Soreness in this type of sinusitis is concentrated in the area of the bridge of the nose and in the place where the base of the nose is located. When the ailment is just beginning to develop, the nasal discharge becomes clear and flowing. The snot then thickens and causes permanent nasal congestion. As a result, there is a violation of full breathing through the nose.
- Polypoid sinusitis is an ailment in which the mucous membranes of the nose become inflamed. It is not uncommon. Its main symptom is the presence of polyps. They are edematous tissue infiltrated with eosinophils. If the disease progresses, new polyps appear, and old ones increase in size.
Depending on the nature of the inflammatory process, sinusitis is:
- edematous-catarrhal - when the disease affects only the mucous membrane of the paranasal sinuses (this form can be recognized by serous nasal discharge);
- purulent - when the deep layers of tissues in the paranasal sinuses become inflamed (it can be determined by nasal discharge with pus);
- mixed - the symptoms of edematous-catarrhal and purulent forms of the disease are combined.
Odontogenic sinusitis
What is odontogenic sinusitis? Many people probably hear such a phrase for the first time. This is a chronic disease in which the mucous membrane of the maxillary sinus becomes inflamed. It can begin to develop if there is a focus of chronic inflammation in the area of the 4th, 5th or 6th upper teeth, and the infection spreads from it. The main reason for this trouble is the unsatisfactory or untimely sanitation of the oral cavity. In second place among the reasons are the anatomical features of the process of the upper jaw. If there are signs of developing caries on the surface of the tooth, it is logical to assume that the very focus of infection is located in it, which is gradually transferred to the maxillary sinus - or rather, to its mucous membrane.
 The course of odontogenic sinusitis, as a rule, is not accompanied by any pronounced clinical symptoms. Often, patients with this diagnosis suffer from:
The course of odontogenic sinusitis, as a rule, is not accompanied by any pronounced clinical symptoms. Often, patients with this diagnosis suffer from:
- nasal congestion (as a rule, only one nasal passage is clogged);
- discharge of purulent contents from the nasal cavity;
- unpleasant odor coming from the nose;
- intermittent painful sensations over the inflamed sinus;
- pain in the area where 4, 5 or 6 upper molars are located (if they were previously removed, this does not mean that sinusitis cannot be; teeth may be missing - but the pain will still annoy).
The severity of the disease
Depending on how chronic sinusitis proceeds, 3 degrees are distinguished: mild, moderate and severe.
- Lightweight. The disease is easily tolerated by humans. The temperature is within normal limits. Typically, this sinusitis is of viral origin.
- Average. This severity suggests an increase in body temperature to about 38 degrees. Among other symptoms, severe headache and unpleasant sensations in the area of the paranasal sinuses (pressure or distention) are most pronounced.
- Heavy. If this ailment is severe, discharge from the nasal passages contains impurities of pus. As for the body temperature, it can rise to 39 degrees - and this is not the limit. The person suffers from an almost constant headache and a feeling of weakness.
Sometimes people mistakenly believe that a mild form of chronic sinusitis and the absence of unpleasant symptoms guarantee the safety of this disease. However, a permanently blocked nose is not only a functional inconvenience. The inability to fully breathe through the nose has an extremely negative effect on the work of the respiratory system.
As a result, shortness of breath occurs, and the amount of oxygen that enters the blood is reduced. This has an extremely unfavorable effect on the condition of all internal organs. And for pregnant women, this ailment is completely dangerous, since the child is in utero experiencing oxygen starvation.
Possible complications
When the chronic form of sinusitis slowly progresses, the inflammatory process sometimes involves not only the paranasal sinuses, but also other structures located inside the skull. Thus, certain complications arise. Most often, chronic sinusitis is complicated by:
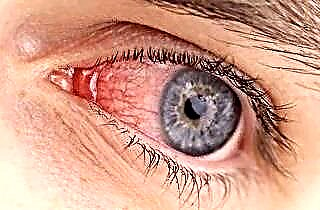 Otitis media of the middle ear. The nasal cavity communicates with the middle ear through the maxillary sinus. Since it is infected, harmful microorganisms enter the ear cavity from there. As a result, unpleasant symptoms such as congestion and pain appear. Due to edema of the ear canal, hearing acuity decreases. With an unfavorable development of the disease, pathogenic microbes enter the inner ear through the tympanic membrane. In this case, we are talking about a labyrinth. In addition to ear pain, the functions of the vestibular apparatus are disturbed in a person: he is dizzy, he loses balance and spatial orientation.
Otitis media of the middle ear. The nasal cavity communicates with the middle ear through the maxillary sinus. Since it is infected, harmful microorganisms enter the ear cavity from there. As a result, unpleasant symptoms such as congestion and pain appear. Due to edema of the ear canal, hearing acuity decreases. With an unfavorable development of the disease, pathogenic microbes enter the inner ear through the tympanic membrane. In this case, we are talking about a labyrinth. In addition to ear pain, the functions of the vestibular apparatus are disturbed in a person: he is dizzy, he loses balance and spatial orientation.- Conjunctivitis. If the organs of vision are affected by the inflammatory process, pressure on the eyeballs will cause pain in the person. In this case, there is swelling and redness of the eyelids, as well as increased tearing. In addition, sinusitis can be complicated by purulent inflammation of the soft tissues of the eye, necrosis and thrombosis of the eye veins.
- Trinity neuritis. One of the most dangerous complications, since it is extremely difficult to treat it. The main symptom is very severe pain. The inflammatory process can move along the endings of the nerves in any direction.
- Osteoperiostitis. This disease occurs when the infection has spread deep into the tissues and affects the bones of the skull and periosteum. Urgent hospitalization is required. Oral and maxillofacial surgeons are involved in the treatment of this ailment.
- Meningitis. The meninges are also directly connected to the sinuses. This means that in order for meningitis to occur, as they say, much is not needed. If a person has reduced immunity to everything, there is a risk of death.
When to see a doctor
Before a person develops a chronic form of sinusitis, he or she may well endure this disease in an acute form several times. Each of these individual outbreaks typically lasts up to 4 weeks.
To make the diagnosis as accurate as possible, the therapist (family doctor) refers the patient who has complained to the otolaryngologist or allergist. These specialists, after a detailed history collection, examination and a series of examinations, will make an accurate diagnosis and prescribe a course of treatment. You should not refuse visits to them and from a broader examination. After all, it is in your interests to quickly get rid of this trouble and, finally, recover.
 So, it is imperative to consult a doctor if:
So, it is imperative to consult a doctor if:
- the sinusitis was transferred several times, and the prescribed treatment did not help;
- the duration of the illness is more than 7 days;
- after medical advice and compliance with the recommendations issued by the doctor, the condition did not improve;
- there is swelling and soreness in the forehead and around the eyes;
- annoying headaches;
- consciousness becomes confused;
- begins to see double or vision impairment in some other way;
- the tone of the muscles of the occiput has sharply increased;
- shortness of breath appeared.
Let's summarize
With chronic sinusitis, symptoms may increase over time and then decrease again. But this will not yet indicate recovery. After the next exacerbation, the symptomatology, as a rule, gradually smoothes out. Only the so-called background symptoms remain.
For example, the nose may be permanently blocked.Moreover, complete congestion is periodically replaced by partial. Also, the person experiences slight discomfort. The next exacerbation again gives the symptoms severity and sometimes complicates the course of the disease.
Let us emphasize that sinusitis can be considered chronic when its signs do not disappear for more than 3 months in a row.
If you ignore the need for treatment for chronic sinusitis, symptoms will worsen over time. In addition, inflammation can affect nearby areas - the adjacent bones, ears, eyes, and even the brain. And this is already dangerous to health and life.

 a protracted, long-lasting rhinitis, which is often accompanied by green or yellow discharge with purulent contents, in some cases with blood clots;
a protracted, long-lasting rhinitis, which is often accompanied by green or yellow discharge with purulent contents, in some cases with blood clots; Frontal. A characteristic feature of this ailment is pain syndrome of moderate intensity, concentrated in the area of the frontal sinuses. Nasal discharge has a specific, unpleasant odor. Their abundance is significantly increased. As for body temperature, it is kept at a subfebrile level.
Frontal. A characteristic feature of this ailment is pain syndrome of moderate intensity, concentrated in the area of the frontal sinuses. Nasal discharge has a specific, unpleasant odor. Their abundance is significantly increased. As for body temperature, it is kept at a subfebrile level. Otitis media of the middle ear. The nasal cavity communicates with the middle ear through the maxillary sinus. Since it is infected, harmful microorganisms enter the ear cavity from there. As a result, unpleasant symptoms such as congestion and pain appear. Due to edema of the ear canal, hearing acuity decreases. With an unfavorable development of the disease, pathogenic microbes enter the inner ear through the tympanic membrane. In this case, we are talking about a labyrinth. In addition to ear pain, the functions of the vestibular apparatus are disturbed in a person: he is dizzy, he loses balance and spatial orientation.
Otitis media of the middle ear. The nasal cavity communicates with the middle ear through the maxillary sinus. Since it is infected, harmful microorganisms enter the ear cavity from there. As a result, unpleasant symptoms such as congestion and pain appear. Due to edema of the ear canal, hearing acuity decreases. With an unfavorable development of the disease, pathogenic microbes enter the inner ear through the tympanic membrane. In this case, we are talking about a labyrinth. In addition to ear pain, the functions of the vestibular apparatus are disturbed in a person: he is dizzy, he loses balance and spatial orientation.