Hemophilic infection affects all human organs, including the nervous and respiratory systems, provoking inflammation or suppuration. Especially often, the epiglottis cartilage is at risk of infection with a hemophilic bacillus, which causes epiglottis syndrome, abscess and epiglottitis, which are classified as acute pathologies requiring compulsory treatment.
The usual structure of the airways and esophagus directly depends on the epiglottis cartilage, which is involved in carrying food and oxygen further into the body. Therefore, it is very important to protect this organ from various inflammatory processes. Inflammation of the epiglottis most often affects children from 3 to 5 years old, as a rule, they suffer the disease in acute forms due to weak immunity.
The structure and meaning of the epiglottis
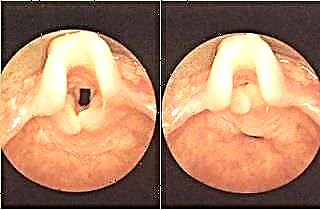
 The epiglottis is an elastic leaf-shaped cartilage located at the beginning of the tracheal tube, below the root of the tongue. The organ has two muscles - the scoop and the scutellum. When they contract, the swallowing function is triggered, and the epiglottis descends, closing the passage to the trachea for food to pass into the esophagus. This is the main task of the body.
The epiglottis is an elastic leaf-shaped cartilage located at the beginning of the tracheal tube, below the root of the tongue. The organ has two muscles - the scoop and the scutellum. When they contract, the swallowing function is triggered, and the epiglottis descends, closing the passage to the trachea for food to pass into the esophagus. This is the main task of the body.
The epiglottis cartilage is covered with pits that contain mucous glands. They are connected by nerves with the laryngeal mucosa and the root of the tongue, as well as vessels with the inferior laryngeal nerve. The glands consist of three layers, each of which is responsible for specific functions:
- Mucous membrane - it is located on the surface and moisturizes the cartilage to reduce friction with other organs and foreign objects.
- The epithelium of the mucous membrane is the part of the membrane that contains elements for purifying the air.
- The lamina of the mucosa is the tissue that contains the nerves, laryngeal glands, and blood vessels.
In some people, individual features of the location of the organ are observed, in which the sheet of the anterior surface of the epiglottis folds in half, which blocks the path to the larynx and complicates the examination using indirect laryngoscopy.
Diseases and their causes
 In the depressions of the epiglottis, inflammatory processes can occur, the cause of which is the hemophilic bacillus - an infection that affects the oral cavity. Transmission routes are organs that are the gateway for oxygen (nose and mouth). Other predisposing factors can also provoke inflammation:
In the depressions of the epiglottis, inflammatory processes can occur, the cause of which is the hemophilic bacillus - an infection that affects the oral cavity. Transmission routes are organs that are the gateway for oxygen (nose and mouth). Other predisposing factors can also provoke inflammation:
- throat damage on impact;
- burn after consuming hot meals or drinks;
- the effect of smoking and alcoholic beverages.
With inflammation, the organ enlarges, and the functions of the epiglottis are disrupted, which prevents the airways from carrying oxygen to the lungs. Bacterial agents affect the respiratory system, thereby inhibiting the antigens of the immune system in the oral cavity, as a result of which inflammatory processes occur. Further, the organ changes shape, which can provoke airway stenosis and cause death of the patient.
Who is at risk:
- people suffering from allergic reactions;
- babies aged three to five years - in children, due to weak immunity, there is a danger of infection;
- people who have had spleen surgery;
 male representatives;
male representatives;- people with malfunctioning immune systems.
There are several pathologies of the epiglottis, one of which is the penetration of bacterial agents, and the second is age-related complications, because it manifests itself after the age of 30 (the cartilage is deformed and sinks, thereby making breathing difficult).
Epiglottitis is a complex form of infection with Haemophilus influenzae. The danger of the disease lies in the sudden onset of symptoms, which consists in difficulty breathing in and out, which can lead to respiratory arrest and death.
With timely treatment, inflammation can be successfully treated, but with complications, the disease is divided into several stages, depending on the clinical picture.
Stages of development of the disease
- The initial stage of the disease is manifested by non-characteristic symptoms in the form of a cold.
 At the second stage, the symptoms become sharply more complicated, causing painful sensations in the throat, an increase in temperature indicators and difficulty in respiratory function.
At the second stage, the symptoms become sharply more complicated, causing painful sensations in the throat, an increase in temperature indicators and difficulty in respiratory function.- The third stage is the appearance of complications, which are characterized by cyanosis of the lower and upper extremities due to lack of oxygen, excessive salivation and bloating of the nose. This clinical picture requires immediate hospitalization of the patient, otherwise the chances of saving a person are significantly reduced.
Also, epiglottitis is divided into an edematous (excessively high pain threshold is observed) form, abscessed and infiltrative (seizures are characteristic, temperature indicators rise to 38 degrees and a plaque appears on the tongue).
Epiglottis syndrome - characterized by a feeling of a lump in the throat and makes breathing a little difficult. In this case, it is important to try as little as possible to make swallowing movements so as not to irritate the cartilage when it is raised.
If the pain intensifies, you should contact the attending specialist for X-ray diagnostic measures. This will help determine the presence of a tumor and establish an accurate diagnosis. Women are at risk.
The clinical picture in children and adults
 Symptoms of inflammation or epiglottis syndrome begin as a simple cold, accompanied by fever, painful sneezing, and a runny nose. But then the symptomatology manifests itself depending on the type, form and type of complication.
Symptoms of inflammation or epiglottis syndrome begin as a simple cold, accompanied by fever, painful sneezing, and a runny nose. But then the symptomatology manifests itself depending on the type, form and type of complication.
The clinical picture differs in children and adults due to differences in the development of protective systems. So, the most complex manifestation and severe course of pathology is observed in children.
The onset of acute epiglottitis is characterized by sore throat, soreness when swallowing (dysphagia), hoarseness (dysphonia), and increased body temperature.
To relieve pain, it is recommended to stretch your neck, open your mouth, and stick out your tongue.
Complications of inflammatory processes
Complications of diseases of the epiglottis are very dangerous and, if ignored or self-medicated, lead to death. Basically, due to epiglottitis, a form of abscess occurs - an acute complication that causes purulent processes in the oral cavity and an increase in the epiglottis cartilage.
There are more serious consequences of complications leading to death, especially in children - acute respiratory failure, aspiration of vomit, hypoxic coma.
Diagnostic measures
 Due to the severity of symptoms in pathological processes, the patient does not need a special diagnosis. However, at the initial stage of the disease, the specialist prescribes diagnostic measures, consisting in examination and X-ray examination.
Due to the severity of symptoms in pathological processes, the patient does not need a special diagnosis. However, at the initial stage of the disease, the specialist prescribes diagnostic measures, consisting in examination and X-ray examination.
In order to find out the cause and degree of swelling, a blood test and taking a smear from the oral cavity are prescribed. For some patients, a procedure is performed with the introduction of an endotracheal tube - it does not obstruct breathing and helps to accurately determine the disease.
Treatment activities
Initially, the treatment of pathologies of the epiglottis takes place in the hospital, in order to use a plastic tube that normalizes breathing. Next, a recovery course is carried out, fed through the drains, and nutrients are injected into the blood.
After discharge, a course of treatment with drugs, rinsing and the use of herbal decoctions is prescribed. With therapeutic actions aimed at combating purulent inflammation, drugs are needed to resolve abscesses, but if such treatment is ineffective, they are excised under anesthesia using specialized instruments.
If the diagnosis is not determined, doctors prescribe massages, inhalations, gargles, or tranquilizers.
Sometimes cryotherapy is used - a procedure using cold. It is also safe for people with increased sensitivity, because it does not load the thermoregulatory system, does not stress the body. With the pathology of the epiglottis, local therapy is performed.
Prevention
 After treatment, especially in children, prophylaxis is important to protect the affected organ and restore the immune system as soon as possible. For this, drugs are prescribed, the course of which lasts 1-2 weeks. The prophylactic vaccine is given to children under 5 years of age.
After treatment, especially in children, prophylaxis is important to protect the affected organ and restore the immune system as soon as possible. For this, drugs are prescribed, the course of which lasts 1-2 weeks. The prophylactic vaccine is given to children under 5 years of age.
During the recovery period, folk remedies are widely used, but after consultation with the attending specialist and only with his permission. Rosehip oil is a good remedy and during the main course you can instill or drink oil 2 times a week. The use of alcoholic beverages and smoking should be avoided.
Conclusion
The role of the epiglottis is very important in the vital processes of the body, therefore, at the first signs of organ diseases, you should seek qualified help, otherwise the person will simply suffocate. It is important to adhere to recommendations for treatment and prevention to reduce the risk of complications of inflammatory processes.

 male representatives;
male representatives; At the second stage, the symptoms become sharply more complicated, causing painful sensations in the throat, an increase in temperature indicators and difficulty in respiratory function.
At the second stage, the symptoms become sharply more complicated, causing painful sensations in the throat, an increase in temperature indicators and difficulty in respiratory function.

