Sinusitis is inflammation of the paranasal sinuses (sinuses). It can be localized in one sinus, or it can affect several sinuses at the same time. In some cases, such a disease acts as an independent one. In others, it is a complication of an incompletely cured cold, flu, tonsillitis and some other seasonal infectious ailments.
The symptoms of sinusitis vary depending on the specific form of the disease. For example, in an acute form, the patient's temperature rises rapidly, and nasal congestion appears. Acute sinusitis lasts on average up to two months. In the absence of adequate treatment (or with self-medication), the acute form is easily transformed into a chronic one. She has similar symptoms, although they will be less severe.
Reasons for the appearance
 According to doctors, in about half of all clinical cases, the inflammatory process is caused by bacterial agents - pneumococci and Pfeifer's bacillus. Slightly less often, the cause of sinusitis is Staphylococcus aureus, Moraxela, anaerobic, viral and fungal pathogens.
According to doctors, in about half of all clinical cases, the inflammatory process is caused by bacterial agents - pneumococci and Pfeifer's bacillus. Slightly less often, the cause of sinusitis is Staphylococcus aureus, Moraxela, anaerobic, viral and fungal pathogens.
The risk group includes people with congenital or acquired anomalies in the structure of the nasal cavity. Curvature of the nasal septum, polyps, adenoids - this and much more often provokes the appearance of sinusitis in children and adults. For example, pathological changes in the sinuses can occur after an incorrect operation. Mechanical trauma to the face also contributes to the appearance of an inflammatory process within one, two or more sinuses.
Often, the symptoms of sinusitis manifest themselves after diagnostic and therapeutic procedures that lead to blockage of the anastomosis (it connects the nasal cavity and sinuses). We are talking about nasotracheal intubation, intubation and even tamponade of the nose.
Slightly less often, the main cause of sinusitis is the so-called sensitization of the body, when the sensitivity to external as well as internal unfavorable factors increases.
As for the fungal infection, it appears as a direct consequence of the unjustified or improper use of antibacterial and some other drugs. In most cases, this significantly reduces immunity, and bacterial ones attach to the fungal agents.
In addition, one should not forget about the risk factors that greatly increase the likelihood of inflammation of the paranasal sinuses:
- cystic fibrosis (high viscosity of mucus);
- diseases of the teeth of the upper jaw;
- diabetes;
- hypothyroidism;
- diathesis of an allergic type and so on.
Varieties of the disease
 What is sinusitis and how does it manifest itself? To answer this question, we recommend that you familiarize yourself with the classification of such an ailment. It is based on the place of localization of the inflammatory process. Pathological changes can occur in all seven paranasal sinuses. With this in mind, sinusitis can be divided into 4 types:
What is sinusitis and how does it manifest itself? To answer this question, we recommend that you familiarize yourself with the classification of such an ailment. It is based on the place of localization of the inflammatory process. Pathological changes can occur in all seven paranasal sinuses. With this in mind, sinusitis can be divided into 4 types:
- Sinusitis is an inflammatory process that occurs within the maxillary sinus of the nose. In most cases, this ailment is a complication of acute rhinitis (rhinitis), flu, measles, scarlet fever and some other infectious diseases.
- Front. In this case, the inflammation is localized in the frontal sinus (one or two). This is the most dangerous type of sinusitis. If left untreated, serious orbital and intracranial complications can develop. This is due to the proximity of the frontal sinuses to the brain and organs of vision.
- Ethmoiditis - the inflammatory process affects the cells of the ethmoid labyrinth.
- Sphenoiditis is the least common and involves inflammation of the sphenoid sinus.
Sinusitis, the symptoms of which are quite extensive, always begins with prolonged rhinitis (it lasts more than a week). In this case, the patient notes abundant nasal discharge. At first, the mucus is transparent, but as the pathogenic microflora develops, bacteria penetrate into it and begin to actively multiply. For this reason, mucus from ordinary serous quickly turns into purulent.
Sinusitis can be unilateral, as well as bilateral, that is, simultaneously affect the sinuses on both sides.
Symptoms
Signs of sinusitis in adults will entirely depend on which sinus is the inflammatory process. However, one can single out general symptoms characteristic of all varieties of such ailment. In patients, due to nasal congestion, normal breathing through the nose is disrupted. The sinuses are involved in the formation of the voice (act as resonators). If they are blocked by serous or purulent fluid, the vocal timbre changes, and nasalness appears.
Painful sensations are localized on the sides of the nose and in the region of the brow ridges. The body temperature rises (up to a maximum of 39 degrees). The acuity of smell is noticeably reduced. Moreover, the patient may completely cease to distinguish between smells. Severe headaches appear that do not go away even after taking strong analgesics.
 To understand what sinusitis is, let's look at the symptoms that are specific to each type of sinusitis:
To understand what sinusitis is, let's look at the symptoms that are specific to each type of sinusitis:
- With sinusitis, the inflammatory process manifests itself very quickly and quite sharply. In addition to an increase in body temperature to 38-39 degrees, the patient is worried about unpleasant sensations in the cheekbones, forehead and root of the nose. Congestion is noted, abundant mucus appears - first serous, then greenish with an unpleasant odor. The blockage of the lacrimal canal causes frequent bouts of lacrimation.
- Sinusitis, the symptoms of which in the acute form will be bright and expressive, also manifest themselves in the form of frontal sinusitis. In this case, the pains are concentrated in the frontal region and above the eyebrows, and are aggravated by palpation (feeling) and tilting the head. The sinuses fill with mucus and are completely blocked. The active reproduction of pathogenic microflora leads to an increase in temperature up to 39 degrees. Headaches are aching and pressing in nature, often worse in the morning after a night's sleep.
- In most cases, the development of ethmoiditis is complicated by sinusitis and frontal sinusitis. Clinical symptoms appear quickly - these are headaches, discomfort in the area of the bridge of the nose and the root of the nose. If children are sick with ethmoiditis, the disease is often complemented by eye inflammations and, in particular, conjunctivitis. There is an increased body temperature, the mucus very quickly becomes purulent. The active development of the inflammatory process often leads to exophthalmos (forward displacement of the eyeball).
- Sphenoiditis - what is it? The key symptom of sphenoid sinus inflammation is pain in the parietal and occipital regions. Often, patients are diagnosed with swelling of the fornix and posterior wall of the nasopharynx. The inflammatory process causes an increase in temperature. Sphenoiditis (in the absence of therapy) quickly develops into dangerous ocular and intracranial complications, for example, retrobulbar neuritis (inflammation of the optic nerve).
Symptoms of acute and chronic sinusitis differ from each other only in the intensity of manifestation. In the chronic form, the symptoms will be somewhat blurred and muted (especially during the period of remission). But with an exacerbation, they manifest themselves quite clearly.
Diagnostic measures
 Before starting treatment for sinusitis, you need to see a doctor. Only he is able to accurately diagnose and choose the optimal rehabilitation course. In the acute form of the disease with pronounced symptoms, it is not difficult to determine the type of ailment. The chronic form is more difficult to diagnose.This is done after taking anamnesis (interviewing the patient), analyzing all clinical manifestations, instrumental and laboratory diagnostics.
Before starting treatment for sinusitis, you need to see a doctor. Only he is able to accurately diagnose and choose the optimal rehabilitation course. In the acute form of the disease with pronounced symptoms, it is not difficult to determine the type of ailment. The chronic form is more difficult to diagnose.This is done after taking anamnesis (interviewing the patient), analyzing all clinical manifestations, instrumental and laboratory diagnostics.
As effective instrumental methods are rhinoscopic examination, ultrasound of the paranasal sinuses, diaphanoscopy, radiography, computed tomography of the sinuses (and if complications are suspected, and CT of the brain), and so on.
In addition, blood tests and bacteriological analysis of nasal secretions cannot be dispensed with. The last diagnostic method makes it possible to recognize the type of pathogen and determine its resistance (sensitivity) to one or another active component of the antibiotic. After all the diagnostic measures have been completed, the optimal treatment strategy is selected.
Drug therapy
In this case, the key task of treatment is to eliminate the inflammatory process and the infectious focus, to organize the drainage of the affected sinus (cleaning) and the removal of pathological contents from the sinus. If sinusitis is caused by bacterial agents, your doctor will prescribe antibiotics to which the pathogenic flora is sensitive. As a rule, drugs from the group of penicillins "Augmentin", "Amoxicillin" and some others are used to treat sinusitis.
 But do not forget that the root cause of the disease can be not only bacterial, but also infectious pathogens. In this case, the use of antibiotics is considered unreasonable and even harmful. Their use can lead to the bacteria becoming resistant to the active substances of the drug, which will negatively affect the overall clinical picture.
But do not forget that the root cause of the disease can be not only bacterial, but also infectious pathogens. In this case, the use of antibiotics is considered unreasonable and even harmful. Their use can lead to the bacteria becoming resistant to the active substances of the drug, which will negatively affect the overall clinical picture.
For this reason, the doctor prescribes corticosteroids. These are nasal aerosols (sprays) of local action. These drugs include Beclomethasone, Triamcinolone, Fluticasone and others.
Sinusitis can be caused by an allergy to some type of irritant (pet hair, pollen, dust, etc.). In this case, antibiotics are also ineffective. Antihistamines come to the rescue, blocking the production of histamine by the body - "Tavegil", "Claritin", "Zirtek", "Klarotadin" and others. However, these medications should only be taken under the direction and permission of your healthcare professional. Wrong reception can provoke thickening of the mucous membrane, its swelling, or impaired drainage of the paranasal sinuses.
Also, do not forget about medicines for vasoconstriction. They quickly relieve puffiness, normalize the condition of the mucous membrane and nasal breathing. Such drugs are available in the form of tablets, but most often they are represented by nasal drops and aerosols (Galazolin, Naftizin, Sanorin, and so on). Be careful with such drugs, as their prolonged use is addictive and fraught with the appearance of excessive dryness of the mucous membrane and fragility of blood vessels.
Prophylaxis and other therapeutic methods
In addition to medication for sinusitis, a surgical method is often used. This is the most radical, but in some cases the only correct solution. Surgical intervention allows you to quickly unblock the affected sinus, organize its ventilation and drainage. Also, the surgical method is indicated in identifying complications of sinusitis. The most popular and effective methods are:
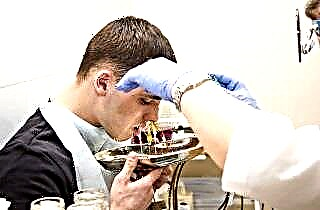 puncture (puncture) of the paranasal sinus;
puncture (puncture) of the paranasal sinus;- balloon synoplasty;
- endoscopic method.
The most commonly used sinus puncture. We are talking about a puncture of the sinus wall, washing it and pumping out purulent masses.
As for balloon synoplasty, it is an artificial expansion of the narrowed nasal passage using a catheter. This operation allows you to unblock the sinus and provide fresh air. In endoscopy, the affected sinus is affected by a coagulator or laser.
Now a few words must be said about prevention. Like any disease, sinusitis is always easier to prevent than to cure. The cornerstone of prevention should be timely and high-quality treatment of infectious ailments - rhinitis, colds, flu, and so on. Most often, sinusitis develops against their background or becomes a direct result of self-medication.
Believe me, it is better to cure a cold at home than to get rid of sinusitis for weeks in a hospital.
In addition, we recommend listening to the following helpful tips:
- Dental diseases are one of the main factors that provoke the appearance of sinusitis. Therefore, it makes sense to regularly (at least once every six months) undergo a preventive examination by a dentist.
- We remind you once again - completely exclude self-medication. This is dangerous and will only aggravate the clinical picture. If your runny nose persists within 3-4 days, see your doctor. It is quite possible that the cause of poor health is not rhinitis at all, but an inflamed paranasal sinus.
 Introduce healthy foods with a lot of vitamins and minerals into your diet. This is especially true in the autumn-winter period - the time of SARS and influenza epidemics. Give up semi-finished products completely, give preference to natural food.
Introduce healthy foods with a lot of vitamins and minerals into your diet. This is especially true in the autumn-winter period - the time of SARS and influenza epidemics. Give up semi-finished products completely, give preference to natural food.- Start boosting your immunity. It has been noticed that sinusitis develops more actively in a weakened body, so we advise you to start hardening the body. It is not at all necessary to swim in cold water; it is enough to take contrasting douches every day. This will help to activate the defenses. As a result, the body will be able to cope with some infectious ailments on its own - without the use of medications.
Do not let the disease take its course. If you find the first signs of sinusitis, see your doctor immediately. This will save not only your health, but, possibly, your life. Be healthy, live happily ever after!

 puncture (puncture) of the paranasal sinus;
puncture (puncture) of the paranasal sinus; Introduce healthy foods with a lot of vitamins and minerals into your diet. This is especially true in the autumn-winter period - the time of SARS and influenza epidemics. Give up semi-finished products completely, give preference to natural food.
Introduce healthy foods with a lot of vitamins and minerals into your diet. This is especially true in the autumn-winter period - the time of SARS and influenza epidemics. Give up semi-finished products completely, give preference to natural food.

