The choice of modern hearing aids is so wide that it is even difficult to categorize them unambiguously. Manufacturers are trying to combine several technologies so that the device becomes as convenient, compact and functional as possible. That is why it is difficult for users to navigate the market and choose the right hearing aid for themselves. Experienced audiologists will come to the rescue here. But in order to speak the same language with them, it is better to have at least a superficial understanding of how different types of hearing aids differ.
Principle of operation
The principle of operation of all devices is the same. The device needs:
- catch the sound coming from the environment;
- convert it into electrical impulses;
- cleanse and amplify extraneous noise;
- transfer to the phone, which again translates it into sound waves.
But how the whole cycle of these operations is carried out directly depends on the internal structure and design features of the hearing aid.
They can also be attached to the body in a variety of ways. There are removable devices and implants that are implanted into the patient's body.
And although at first glance, implants have undeniable advantages, this is not always the case. Moreover, there are more contraindications to their use than to circuit hearing aids.
Types and categories
 All hearing aids can be classified according to the following criteria:
All hearing aids can be classified according to the following criteria:
- By the way of conducting the sound:
- air - the sound is transmitted through the receiver, which is installed in the ear canal;
- bone - sound vibration is conducted through the bone behind the ears.
- By sound processing method:
- analog - mainly devices of previous generations, which can only amplify sound and filter out strong noises;
- digital - almost all modern, their adjustment is carried out through computer programs and has high accuracy, and the sound is of excellent quality.
- By type of setting:
- programmable - they can ensure that all the individual characteristics of the user are taken into account and remember the entered program, are configured via a computer;
- non-programmable - their adjustment is done manually using the built-in regulators.
 Manufacturing technology:
Manufacturing technology:
- standard - those that can be bought in medical equipment stores or ordered via the Internet and then customized for yourself;
- individual - are made by specialists after a series of studies and take into account absolutely all the features of a given user.
- By installation method:
- intracanal - made on the basis of an impression of the auditory canal, into which the structural elements of the device are inserted, have a weak power and a very fragile body;
- in-the-ear - are installed inside the auricle, of medium power and do not require individual manufacturing;
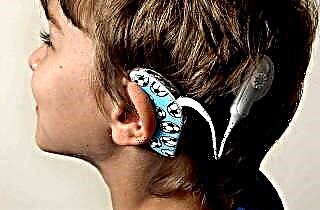
- behind-the-ear - the most popular among all types of ear aids, are fixed on the auricle with the insertion of an earmold into the ear canal, have sufficient power and good sound quality;
- pocket-sized - the most powerful devices, as they are large enough to provide the strength and quality of sound, recommended for the elderly; are placed in a pocket, and the insert is placed in the ear canal (connected by a cord);
- implants - implanted into the patient's body through a surgical operation, provide excellent quality and purity of sound.

A separate category includes children's hearing aids, which are smaller, have a different design and take into account the structure and growth of the child's auricle. Usually, only the BTE is suitable for the smallest children, but other models can be tried with age.
Application features
With a wide variety of hearing aids, their choice is made difficult for the consumer, first of all, by the fact that each type has its own characteristics, which make them optimal only for a small category of people. Simply put - each type of device has its own pros and cons, which must be taken into account.
Here are some of the pros and cons of the different types:
 Digital - with high accuracy, settings require more or less regular visits to a specialist, since all operations are performed only through a connection to a computer and a special program. For people with disabilities who find it difficult to independently move long enough distances, such models are not suitable. They would be better off purchasing analog hearing aids, or they may have to look for an opportunity to invite a specialist to their home. The same applies to programmable models.
Digital - with high accuracy, settings require more or less regular visits to a specialist, since all operations are performed only through a connection to a computer and a special program. For people with disabilities who find it difficult to independently move long enough distances, such models are not suitable. They would be better off purchasing analog hearing aids, or they may have to look for an opportunity to invite a specialist to their home. The same applies to programmable models.- Bone conduction - they do not block the auditory canal, but use an installed vibrator that acts on the mastoid process of the temporal bone, located behind the ear. They allow you to return hearing to those who cannot be helped with the help of air devices. But due to constant pressure on tissue and bone, inflammation and even necrosis can develop. Long-term continuous wearing of such a device is not recommended.
- Individual ITEs are maximally ergonomic, as they take into account all the bends and features of the auditory canal. It is a virtually invisible earmold that is inserted deep into the ear canal and secured with adjacent tissues. With such a device, you can lead a normal life, engage in active sports and feel very comfortable. Its main disadvantage is its higher cost in comparison with the standard behind-the-ear, and also that, due to its small size, it is impossible to provide good sound amplification. Only suitable for people with mild hearing loss.
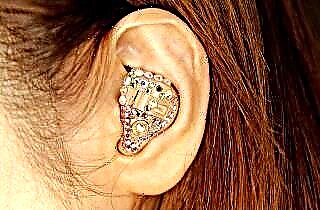
 A pocket-sized hearing aid is best suited for people with very hearing impairments and impaired motor coordination. It doesn't need to be handled too carefully, has a fairly large, sturdy body and delivers loud, high-quality sound. A variety of such devices can be considered barrettes, which have a variety of modern designs and are fixed on the hair. Perfect for women of all ages, comfortable and almost invisible.
A pocket-sized hearing aid is best suited for people with very hearing impairments and impaired motor coordination. It doesn't need to be handled too carefully, has a fairly large, sturdy body and delivers loud, high-quality sound. A variety of such devices can be considered barrettes, which have a variety of modern designs and are fixed on the hair. Perfect for women of all ages, comfortable and almost invisible.- Implants - depending on the model, they are installed behind the auricle or in the middle ear. It is constantly in the patient's body, providing high-quality sound for 24 hours per knocking. Ideal solution for people with severe hearing loss that does not respond to treatment. However, the cost of the implant itself and the operation for its installation starts from several thousand euros, which is far from affordable for all patients.
That is why behind-the-ear hearing aids remain the bestseller today and are produced by all well-known manufacturers. These models have only one drawback - they are visible. In addition, when playing sports, they can fly off.
There are many more advantages: they have a beautiful design, a variety of sizes, they are securely fixed, easily removed, provide good strength and sound quality, and most importantly, they have a minimum of contraindications. This type of device is suitable for people of all ages - from the smallest to the elderly. A specialist will help you choose the best option.

 Manufacturing technology:
Manufacturing technology: Digital - with high accuracy, settings require more or less regular visits to a specialist, since all operations are performed only through a connection to a computer and a special program. For people with disabilities who find it difficult to independently move long enough distances, such models are not suitable. They would be better off purchasing analog hearing aids, or they may have to look for an opportunity to invite a specialist to their home. The same applies to programmable models.
Digital - with high accuracy, settings require more or less regular visits to a specialist, since all operations are performed only through a connection to a computer and a special program. For people with disabilities who find it difficult to independently move long enough distances, such models are not suitable. They would be better off purchasing analog hearing aids, or they may have to look for an opportunity to invite a specialist to their home. The same applies to programmable models. A pocket-sized hearing aid is best suited for people with very hearing impairments and impaired motor coordination. It doesn't need to be handled too carefully, has a fairly large, sturdy body and delivers loud, high-quality sound. A variety of such devices can be considered barrettes, which have a variety of modern designs and are fixed on the hair. Perfect for women of all ages, comfortable and almost invisible.
A pocket-sized hearing aid is best suited for people with very hearing impairments and impaired motor coordination. It doesn't need to be handled too carefully, has a fairly large, sturdy body and delivers loud, high-quality sound. A variety of such devices can be considered barrettes, which have a variety of modern designs and are fixed on the hair. Perfect for women of all ages, comfortable and almost invisible.

