A runny nose (rhinitis) is a common symptom that signals the development of inflammation in the nasal cavity. It can be provoked by both infectious and allergic agents. Despite the similarity of clinical manifestations, rhinitis of various etiologies should be treated in different ways: infectious - with antiviral and antibacterial agents, allergic - with antihistamines. How to distinguish an allergic rhinitis from a cold?
 There are several criteria by which you can establish the true cause of inflammation of the nasopharynx. The manifestations of allergic rhinitis and colds are very similar, but still not identical. Moreover, they are provoked by various reasons, the identification of which helps to diagnose the type of disease. Unfortunately, it is not always possible to establish the cause of rhinitis by symptoms. In this case, the patient is recommended to undergo differential diagnostics at the clinic. After passing certain tests, the ENT doctor will say with 100% probability what exactly caused the appearance of rhinorrhea - an infection or an allergy.
There are several criteria by which you can establish the true cause of inflammation of the nasopharynx. The manifestations of allergic rhinitis and colds are very similar, but still not identical. Moreover, they are provoked by various reasons, the identification of which helps to diagnose the type of disease. Unfortunately, it is not always possible to establish the cause of rhinitis by symptoms. In this case, the patient is recommended to undergo differential diagnostics at the clinic. After passing certain tests, the ENT doctor will say with 100% probability what exactly caused the appearance of rhinorrhea - an infection or an allergy.
Types of rhinitis
How to recognize a disease by its symptoms? First you need to familiarize yourself with the main types of rhinitis. Their manifestations are almost identical, but the mechanisms of development and, accordingly, the methods of therapy are different. According to the modern classification, the following types of rhinitis are distinguished:
- infectious - develops as a result of damage to the upper respiratory system - the nasal cavity and paranasal sinuses, pathogenic microbes and viruses;
- vasomotor - occurs as a result of the expansion of blood capillaries in the nasopharynx, which is caused by a violation of the autonomic innervation of the vessels;
- allergic - manifests itself in the case of penetration of allergens into the nasal mucosa.
It should be understood that there is a lot in common between vasomotor and allergic rhinitis. But the reasons for their development have fundamental differences, and therefore the methods of their elimination will differ significantly. In addition, in some encyclopedias, allergic rhinitis is considered as one of the forms of vasomotor rhinorrhea. The clinical manifestations of pathologies are so similar that not every ENT doctor can distinguish them.
Many people believe that rhinorrhea (hypersecretion of nasal mucus) is a "harmless disease" that can be cured without any problems on their own. But without finding out the reasons for the appearance of a pathological symptom, stuffing yourself with antibiotics and antiviral agents is completely useless. Moreover, irrational treatment of rhinitis is even fraught with complications.
Different reasons - the same consequences
Colds are one of the main causes of rhinorrhea. It is provoked by viruses that penetrate deep into the mucous membrane of the nasopharynx and begin to actively multiply in it. It is from this moment that inflammatory processes in the respiratory tract begin.
Cells infected with infection release toxins into the bloodstream, to which the body often responds with an allergic reaction. Mast cells in the nasopharynx secrete histamine. The penetration of the inflammatory mediator into soft tissues causes inflammation and edema, therefore, in patients with colds and allergies, the nose immediately clogs up and rhinorrhea appears.
The reasons for the development of allergies and acute respiratory viral infections are different, but pathological processes in the nasopharynx in both cases are provoked by inflammatory mediators - histamine and serotonin.
 And with colds and allergies, the concentration of histamine in the blood increases significantly. As practice shows, in allergy sufferers, colds are much more severe, since the number of inflammatory mediators in the body doubles.
And with colds and allergies, the concentration of histamine in the blood increases significantly. As practice shows, in allergy sufferers, colds are much more severe, since the number of inflammatory mediators in the body doubles.
Cold and / or infectious rhinitis?
Are there any differences between a cold and an infectious rhinitis? Some believe that these concepts are identical, while others see fundamental differences in them. What is the situation in reality? To understand the issue, you first need to define the terminology.
A cold is considered a runny nose, which is associated with hypothermia. If rhinorrhea appeared immediately after you got your feet wet or chilled while standing at a bus stop in the fall, there is nothing to distinguish here. Rhinitis is a result of a decrease in local immunity and the subsequent development of a viral infection. In this case, you need to be treated with antiviral pills and nasal agents.
It should be borne in mind that not every infectious rhinitis can be called a cold. Why? Infection is provoked by the development of not only viruses, but also pathogenic fungi or microbes. In this case, bacterial rhinitis should be treated not with antiviral drugs, but with antibiotics. What conclusion can be drawn from this?
Infectious rhinitis includes the common cold, i.e. viral, but not every infectious rhinitis can be called a cold.
Features of infectious and allergic rhinitis
An infectious rhinitis is an inflammation of the upper respiratory tract caused by infectious agents (virus, bacteria, fungus). Most often, inflammatory processes in the respiratory tract are caused by the multiplication of viruses.
It should be understood that a runny nose is not a disease, but only its manifestation. It occurs against the background of the development of ARVI, tonsillitis, pharyngitis, sinusitis, etc.
Infectious rhinitis from allergic rhinitis will always differ in the presence of symptoms of intoxication:
- muscle and joint pain;
- increased body temperature;
- decreased appetite;
- nausea and / or vomiting;
- moderate headaches;
- fast fatiguability.
But here, too, there are some nuances that you should be aware of. Firstly, intoxication can also occur with allergies, but at later stages of development. Secondly, with ARVI, poisoning of the body with toxins can be prevented within a day, and with allergies, within a few days.
With colds, rhinorrhea goes away on its own within a week, but with allergies, the forecasts are not so rosy. Until the patient independently or with the help of a doctor identifies and eliminates the causative allergen, the inflammatory reactions in the nasal cavity will continue. What is the reason?
It should be understood that the activation of defense mechanisms in the body, provoked by an infection, is indeed justified. Thanks to her, pathogenic viruses and microbes in the respiratory organs are destroyed, after which the immune system "calms down". But allergies are a consequence of an inadequate reaction of the same immune system. She perceives the molecules of dust, perfumes, animal hair as "strangers" that need to be destroyed immediately. But these substances do not really pose a threat to humans.
In addition, it is simply impossible to destroy all irritating agents, unless, of course, the allergic person decides to wipe all allergens from the face of the earth. As you know, these include wind-pollinated plants, woolly animals, washing powders, dust, honey, milk, some medicines, etc. So it turns out that the body can actually cope with a cold - on its own or with the help of drugs, but not with allergies. Allergens need to "run" or protect themselves with barrier drugs.
Summary table of differences
What is the difference between an allergic rhinitis and a cold? We have already found out that allergies are caused by irritants, i.e. allergens, and infection with viruses or bacteria. It is almost impossible to independently identify the type of agents provoking inflammation.This can only be done by a doctor after donating blood to patients for clinical analysis.
It is possible to identify the disease and determine the type of rhinitis according to the criteria that are presented in the table:
| Criteria | Allergic rhinitis | Infectious rhinitis |
|---|---|---|
| main symptoms | nasal congestion watery nasal discharge frequent sneezing eye redness lacrimation eyelid swelling puffiness of the face dark circles under the eyes ear congestion | nasal congestion thick nasal discharge intermittent sneezing |
| pathogens | household, medicinal, food, plant and industrial allergens | viral and bacterial infection |
| how long does rhinitis last | until the allergen is eliminated | about 7 days |
| side diseases | allergic laryngitis and pharyngitis | tonsillitis, bronchitis, pneumonia |
| skin allergy test results | positive | negative |
To independently determine the type of rhinorrhea, you need to remember if any of your close relatives had an allergy. According to statistics, allergic rhinitis, especially seasonal, is very common in people whose parents suffered from allergic diseases. According to immunologists, it is not the allergy itself that is genetically transmitted, but only the predisposition to it.
If at least one of the parents suffers from hypersensitivity to some allergen, the probability of the disease manifesting in the child will be 30%.
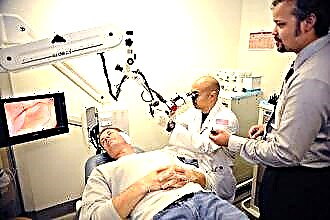
Differential diagnosis in the clinic
Unfortunately, it is not always possible to independently figure out the causes of rhinorrhea. Sometimes colds and allergies occur in an atypical form, and therefore the symptomatic picture undergoes some changes. Surely an ENT doctor will help to diagnose diseases and determine the most appropriate method of treating a cold.
Differential diagnosis of ENT diseases in polyclinics is carried out using rhinoscopy. If during the examination it turns out that the nasal mucosa has acquired a pale pink tint, most likely the reason for this is an allergic reaction. Usually, with an infectious lesion of the nasopharynx, the mucous membrane turns red and becomes covered with viscous mucus. But even this is not enough to determine the type of the disease with 100%.
It is possible to establish the allergic nature of inflammation of the ENT organs through additional research:
- immunological analysis;
- cytological examination of nasal mucus;
- peripheral blood test.
If IgE immunoglobulins are found in the blood, the doctor will diagnose allergic rhinitis. For its treatment, the patient will be prescribed antiallergic, vasoconstrictor and anti-inflammatory drugs.