Can a newborn snore?
 It is generally believed that snoring is a problem exclusively for adults. But ronchopathy - this is what this phenomenon is called in medicine - can occur in infants.
It is generally believed that snoring is a problem exclusively for adults. But ronchopathy - this is what this phenomenon is called in medicine - can occur in infants.
Snoring occurs when there is a certain obstruction in the airways that prevents air from circulating freely through them... Another factor that provokes ronchopathy is the vibration of the palatine muscles. They, like all other muscles in the body, relax during sleep and begin to tremble. The result is a characteristic sound.
Also, the likely cause of snoring in newborns is compression of the trachea by the thymus gland. The latter is an organ of the immune system, which is located in the chest.
The listed reasons are of a physiological nature and are not associated with pathologies of internal organs. But, besides them, there are other factors that cause ronchopathy and indicate the presence of abnormalities.
The main causes of snoring in babies
If ronchopathy does not have a physiological basis, then its development is usually associated with edema and narrowing of the soft mucous tissues located in the nasal passages and pharynx. The child cannot fully breathe through the mouth, which is why snoring occurs. The reasons for this phenomenon can be very diverse.
Age and hygiene
Age anatomical features. In newborns, the size of the chest and head is large, while the nose is small. Due to this imbalance, snoring may occur when deeply inhaling air during sleep.
Lack of hygiene. In this case, a violation of nasal breathing, which provokes snoring, is caused by the presence of dry crusts in the nose and the accumulation of mucous masses.
Excessive dry air in the room where the baby is located can also cause snoring. If the humidity level is less than 50%, excessively dry air currents dry out the nasal mucosa and lead to fragility of the blood vessels located in this area. Under these conditions, nasal breathing becomes difficult, and snoring occurs during sleep.
Congenital pathologies
The child may snore due to the congenital narrowness of the gap through which air passes. This is the case if the palatine curtain and the nasal septum are too close to each other. Such anomalies are eliminated only by surgery.
Another congenital pathology is choanal atresia. This deviation develops during intrauterine development. Choanas are internal nostrils that connect the nasal cavity to the pharynx. The latter is separated from the nasal cavity by a thin membrane, which subsequently dissolves. Under the condition of the action of pathogenic factors, this membrane remains and subsequently most often degenerates into bone tissue.

Malocclusion. If the baby has such congenital structural features of the facial bones as a shift of the lower jaw towards the inside, then the larynx may be partially overlapped by the palate. Under these conditions, a narrow gap is formed through which it is difficult for the air stream to penetrate.
Possible diseases
A symptom may indicate the following pathologies:
- the presence of a foreign object in the nasal passages of the child. A foreign body provokes swelling of the mucous membrane, which makes normal nasal breathing difficult and the baby snores;
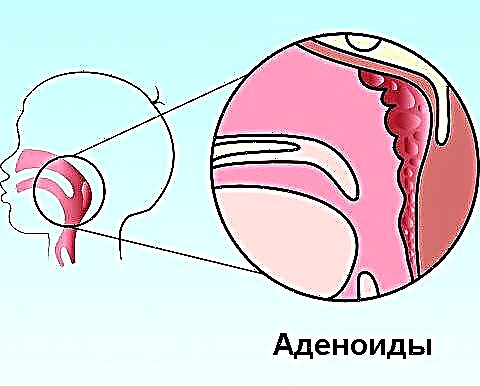
- overgrowth of the adenoids. Ronchopathy is the result of a proliferation of tonsils in the nasopharynx. When this happens, the adenoids block off part of the airway and make it difficult for the infant to breathe. In some cases, pathological enlargement of the palatine and pharyngeal tonsils is congenital;
- allergic edema of the mucous membranes of the nasal passages. This happens when a child comes into contact with probable allergens: household dust, animal hair, pollen;
- obesity. Violation of nasal breathing and associated snoring during sleep is observed in obesity of the third degree and above. The cause of ronchopathy is an excess of fatty masses that line the soft internal tissues, including the pharyngeal mucosa;
 rhinitis of a viral nature. The newborn snores during sleep due to this pathology. The disease has symptoms similar to a common rhinitis, but pathogenic microorganisms also cause fever and severe weakness, pain in the throat. Mucous masses that are secreted through the nasal passages, in this case, acquire a green or yellow tint;
rhinitis of a viral nature. The newborn snores during sleep due to this pathology. The disease has symptoms similar to a common rhinitis, but pathogenic microorganisms also cause fever and severe weakness, pain in the throat. Mucous masses that are secreted through the nasal passages, in this case, acquire a green or yellow tint;- apnea. This is the most dangerous pathology for a child, which is expressed in sudden, short-term breath holdings lasting no more than 10-15 seconds. When the attack ends, the child tries to catch his breath and make up for the lack of air. Because of this, the speed of air flow in the nasopharynx increases, which causes snoring.
Other systemic pathologies
If an infant snores, grunts and sniffs in a dream, one can suspect pathological processes that extend to other internal organs and body systems. In this case, sniffling is caused by such diseases:
- runny nose of a cold or allergic nature;
- epilepsy;
- cysts, polyps, or tumors in the nasal passages;
- hypothyroidism and other functional disorders in the thyroid gland;
- angina;
- pneumonia;
- bronchial asthma;
- laryngitis.
To obtain accurate information about why a newborn suffers from ronchopathy, it is necessary to consult a doctor.
Dr. Komarovsky on snoring in babies and its consequences
Dr. Komarovsky believes that most often snoring in babies in the first months of life occurs due to the peculiarities of the anatomical structure, as well as due to the improper microclimate in the room in which the child is located.
The doctor recommends observing the baby for several days in order to identify the presence of additional symptoms that may indicate various abnormalities.
The specialist pays special attention to the risk of complications that arise due to ronchopathy. These include:
 nervous exhaustion, metabolic disorders. This happens if sleep is disturbed as a result of respiratory tract pathology;
nervous exhaustion, metabolic disorders. This happens if sleep is disturbed as a result of respiratory tract pathology;- complete cessation of breathing during sleep. If a child has apnea that was not diagnosed in a timely manner, then this phenomenon can cause death at night;
- decreased immunity and increased risk of transition of acute respiratory diseases to the chronic stage;
- impaired auditory function. Such a deviation is a consequence of a neglected adenoiditis.
The infant may cough, wheeze, and wheeze, which may indicate a problem with nasal breathing. In some cases, this can lead to sudden death. To prevent this, you should consult a doctor to identify the cause of ronchopathy and determine a set of actions.
Treatment approaches
If the child snores due to reasons not related to diseases of the respiratory system or internal organs, then you can do without drugs. In each case, a separate way to fix the problem is selected:
- with dryness of the nasal mucosa caused by too dry and hot air, it is recommended to use humidifiers in the room where the baby is. It is necessary to regularly ventilate the room and carry out wet cleaning.If the humidity is maintained within 50-70%, and the temperature - within 19-200C, it becomes much easier for the child to breathe;
- in case of obesity, it is recommended to visit a nutritionist and consult on dietary correction. It is necessary to increase the physical activity of the child, more often to be with him in the fresh air;
- if snoring occurs when the child sleeps on his back and this is due to physiological characteristics, then you need to turn him over on his side;
- if snoring occurs due to an uncomfortable position that the baby takes during sleep, it is necessary to replace the pillow or change its location. A pillow for a child should be no more than 6 cm thick and not too high. You also need to pay attention to the filling of this product: down and feathers are not suitable for this purpose. A one-year-old child can fully sleep even on a flat surface.
It is important to observe hygiene standards and regularly clean the child's nasal passages with cotton wool twisted with a tourniquet.
Operation
With adenoids in a child, surgical treatment is required. However, for children under 3 years of age, surgery to remove the nasopharyngeal tonsil is not performed. This is due to the fact that it plays an important role in the system of the body's defenses. Thus, early surgery for inflamed tonsils makes the baby's body especially vulnerable to various viral and infectious diseases, and the child will get sick more often. But in emergency cases, with complete obstruction of nasal breathing, the adenoids are eliminated.
Conservative treatment
Conservative methods of treating adenoids consist in the use of the following drugs:
- anti-inflammatory drugs (Ibuprofen, Paracetamol);
- antihistamines (Diazolin, Suprastin);
- vasoconstrictor drops (Tizine);
- immunomodulators (Immunal).
Folk recipes
If the baby does not have allergies, with inflammation of the tonsils, you can lubricate the mucous membranes of the nasal passages with sea buckthorn oil.
For colds, which are accompanied by the release of snot, it is recommended to rinse the nasal passages with a decoction of medicinal chamomile. In this way, the drainage of the nasal cavity can be significantly improved.
Another way to improve nasal breathing in a baby is to rinse the passages with a salt solution. To prepare it, you need to mix 200 ml of water and a teaspoon of salt, mix thoroughly.
Prevention measures
To avoid the phenomenon of ronchopathy in infants, you should adhere to the following recommendations:
- strengthen the child's immunity, temper him, regularly organize walks in the fresh air;
- observe the rules of hygiene, regularly cleanse the child's nasal passages of mucus and crusts;
- make a diet in such a way that the child does not develop obesity;
- prevent hypothermia or overheating of the body;
- correctly position the pillow on which the baby sleeps;
- maintain optimal levels of humidity and air in the room in which the child is.
Snoring in babies is a phenomenon that can be both physiological and indicate the presence of pathologies. In order to prevent dangerous complications provoked by ronchopathy, it is important to determine the cause of its manifestation in a timely manner and eliminate it.

 rhinitis of a viral nature. The newborn snores during sleep due to this pathology. The disease has symptoms similar to a common rhinitis, but pathogenic microorganisms also cause fever and severe weakness, pain in the throat. Mucous masses that are secreted through the nasal passages, in this case, acquire a green or yellow tint;
rhinitis of a viral nature. The newborn snores during sleep due to this pathology. The disease has symptoms similar to a common rhinitis, but pathogenic microorganisms also cause fever and severe weakness, pain in the throat. Mucous masses that are secreted through the nasal passages, in this case, acquire a green or yellow tint; nervous exhaustion, metabolic disorders. This happens if sleep is disturbed as a result of respiratory tract pathology;
nervous exhaustion, metabolic disorders. This happens if sleep is disturbed as a result of respiratory tract pathology;

