If you notice that the child has a stuffy nose, but there is no snot, then the most important thing in the treatment of this condition is to choose the most effective medications with a minimum number of adverse reactions. Before starting therapy, it is necessary to establish the cause of rhinitis.
Why does the child speak through the nose?
 To understand the reasons why the child does not breathe through the nose, but there is no snot, it is necessary to analyze the period that preceded the deterioration of the condition. We are interested in:
To understand the reasons why the child does not breathe through the nose, but there is no snot, it is necessary to analyze the period that preceded the deterioration of the condition. We are interested in:
- contact with a sick person, an allergen;
- hypothermia; prolonged inhalation of dry air;
- nutritious diet.
To assess the general condition, it is necessary to measure the temperature in children, pay attention to their activity and appetite.
Congestion in infants
In the chest period, some physiological features are distinguished, due to which the mucous membrane of the nasal passages can swell, and nasal sounds appear. There are several reasons why it is difficult for an infant to breathe through the nose:
- unfavorable living conditions. This applies to dry air when the nasal mucosa is irritated for a long time and dries up. Dry crusts can also form, which aggravate nasal congestion in infants and make breathing difficult. The air becomes dry during the heating season, in hot weather, as well as when the air conditioner is running;
- a newborn may have a clogged nose due to the adaptation of the mucous membrane to new conditions. The fact is that in the prenatal period the nasal mucosa was in contact only with the amniotic fluid. After giving birth, she is subjected to a massive attack of dust, microbes, allergens and other provoking factors. As a result of this, the mucous membrane may temporarily swell, and the baby has gundositis. The habituation process can be delayed for the first 2-3 months of the postpartum period;
- eruption by a tooth. As soon as you notice that the baby has a stuffy nose, check if a tooth is coming through. The gums become somewhat edematous, the baby is capricious and does not sleep well. The swelling can spread to the nasopharynx, which is why children have a stuffy nose.
Causes of a stuffy nose without a runny nose
Now let's look at the reasons that can provoke nasal congestion without snot in children of any age:
- viral infection of the body. In the first stage of the common cold, frequent sneezing is observed, the child nasal, and there is little mucus in the nasal passages. When the disease enters the second stage, children are worried about rhinorrhea, and the nose does not breathe completely;
- mechanical impact. Injury to the tissues of the nasal cavities is fraught with bleeding and swelling of the mucous membrane. If a foreign body has entered the nasopharynx, immediate assistance is required.
Moving an object into the larynx increases the risk of laryngospasm and suffocation.
- cold. After prolonged exposure to the cold factor (draft, strong wind, rain), a child's nasal congestion may appear. If you start treatment on time (drinking plenty of fluids, warming procedures, strengthening the immune system), it is likely that the disease will not progress;
- allergy (unlikely). Usually, an allergic reaction is manifested by pronounced rhinorrhea (abundant transparent mucus flows from the nose). Depending on the aggressiveness of the provoking factor and the characteristics of the immune system, allergies can also be accompanied by cough, skin rashes, swelling of the lips, eyelids, itchy eyes, and lacrimation. If signs of illness worsen at night, dust mites may be the allergen;
- side effects of medications. If the child's nose does not breathe, nasal is observed, but snot does not appear, it is necessary to remember what medications the baby was taking on the eve of the deterioration of the condition. The reaction can be expressed as local or systemic symptoms;
- vasomotor rhinitis. It develops against the background of hormonal fluctuations, with diseases of the nervous system or exposure to unfavorable environmental factors. At night, when children lie on their side, the nose breathes badly through the lower nostril;
- deformation of the septum and other structural abnormalities of the nose increase the risk of mucosal edema after the influence of negative factors;
- constantly stuffy nose due to large polyps or cancers. They disrupt air permeability by reducing the diameter of the nasal passages;
- sinusitis and other inflammatory diseases of the paranasal sinuses lead to swelling of the mucous membrane. The child speaks through the nose, but there is no snot. With an exacerbation of chronic diseases of the nasopharynx, there is the appearance of snot in a child, a headache, as well as an increase in nasalness;
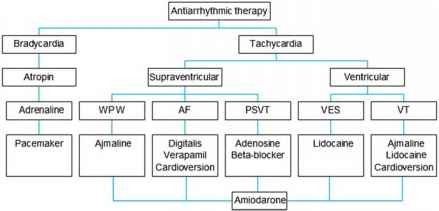
- adenoids are one of the most common pathologies in pediatric otolaryngology. When parents begin to tell the doctor about the child, the symptoms of the disease, the specialist first of all excludes the adenoids. Often, pathology is diagnosed at the age of 3-7 years. In older children, the likelihood of detecting adenoid growths is extremely low, since after 8 years the hyperplastic tissue of the nasopharyngeal tonsil atrophies and decreases in size. With an increase in the volume of lymphoid growths, nocturnal snoring appears, the child speaks in the nose, but the snot does not flow.
Possible complications
 If a child has a stuffy nose, and there is no snot for a long time, there is a risk of serious complications:
If a child has a stuffy nose, and there is no snot for a long time, there is a risk of serious complications:
- hearing impairment, smell, development of the speech apparatus;
- malnutrition, when a newborn loses weight due to inadequate nutrition. In the absence of nasal breathing, the feeding process becomes difficult, which requires special attention from the parents;
- slowing down of physical development, as a result of prolonged hypoxia. Insufficient oxygen supply to the internal organs is fraught with disruption of their formation and increasing dysfunction;
- inflammatory diseases of the lower respiratory tract, which is caused by inhalation of cold, unpurified air through the mouth;
- decrease in mental abilities, which makes it difficult for the child to perceive the material of the school curriculum.
The risk of complications is highest in premature babies, children with congenital immunodeficiency and severe autoimmune diseases.
Therapeutic tactics
Therapeutic methods are aimed at creating optimal conditions in the children's room and the use of medications. An integrated approach allows you to restore breathing through the child's nose and prevent unwanted consequences.
Microclimate change
After a complete diagnosis, the doctor can give recommendations on how to improve the baby's living conditions. They include:
- an increase in humidity up to 65%, for which a special humidifier is used. If it is absent, you can put an aquarium in the children's room or hang wet clothes on a heat source;
- reduce the temperature to 20 degrees;
- regularly ventilate the room to reduce the concentration of allergens, dust, microbes in the air;
- carry out wet cleaning daily without the use of aggressive detergents;
- remove books, carpets that collect dust from the room.
Also, proper nutrition, drinking regimen and walks in the park are important for the child.
Medication assistance
When there is swelling of the nasal mucosa, but without a runny nose in a child, you can use to facilitate breathing:
- saline preparations for washing the nasal passages. In the pharmacy you can buy Dolphin, Aqua Maris. Note that it is not recommended for infants to use solutions in aerosol form, only drugs for drip are permissible;
- inhalation with saline. It is better to use a nebulizer for the procedure. It greatly facilitates the procedure and has a good healing effect;
- oily products such as Pinosol, eucalyptus, peach, pine oil for gentle removal of dry crusts. Before you start cleansing the nose, you need to lubricate its inner surface with an oil solution, wait 5 minutes. Softened crusts will not be able to injure delicate tissues in the nasal passages;
- vasoconstrictor drugs are prescribed only with the threat of otitis media and the inability to breastfeed the baby.
What is prohibited for children?
In order not to harm the baby, parents should know what not to use in the treatment of young children:
- antibacterial drugs. Before using them, a medical consultation is required. Incorrect conduct of antibiotic therapy is fraught with generalization of infection and disturbance of microflora;
- nasal agents with a vasoconstrictor effect. Failure to comply with the recommendations for the use of these drugs increases the risk of drying out of the nasal mucosa and the occurrence of medication rhinitis;
The maximum therapeutic course of vasoconstrictor drugs is 7 days.
- rinse the nasal cavities by injecting saline solution under pressure (syringe, syringe). It is also dangerous to forcefully draw in liquid through one nostril. Infected solution from the nose can penetrate into the auditory tube, ear cavity, provoking the development of otitis media;
- oil inhalations;
- herbal infusions for washing the nasal passages, if the baby has an increased risk of allergies.
Prolonged nasal congestion in a child without snot may indicate both an unfavorable microclimate in the house and immunodeficiency. With insufficient strength of the immune defense, the body cannot cope with inflammatory, infectious diseases. The consequence of this can be the chronization of the pathology and the occurrence of severe complications, which is extremely undesirable in childhood. That is why strong immunity is so important for children.