What to do if a noise appears in the ear that is clearly audible to the patient and at the same time invisible to others? The search for an external acoustic stimulus usually remains unsuccessful. Some patients complain of intermittently increasing sound, which may occur along with a decrease in hearing acuity, others are constantly disturbed by obsessive noise phenomena, interfering with sleep, rest and work tasks. The pulsating sounds that occur at any time of the day, even in silence, are not at all a harmless symptom. The reasoning behind the pulsating tinnitus should not be delayed. The problem of noise phenomena in the ear is dealt with by doctors of various profiles - including therapist, otolaryngologist, neuropathologist, vascular surgeon.
Causes

Sounds, the perception of which is not associated with the presence of an external source, should not normally occur. Why is there a pulsating noise in my ear? The emergence of acoustic phenomena, characterized by patients as "pulsation of sound", is typical for the following pathologies:
- Glomus swelling of the ear.
- Arterial aneurysm of the cerebral vessels.
- Arteriovenous fistulas of cerebral vessels.
- Hypertonic disease.
- Chronic sensorineural hearing loss.
The causes of pulsating tinnitus are dangerous changes - for example, a checklist lists conditions that can lead to cerebral hemorrhages. Therefore, it is categorically impossible to ignore the appearance of "noise background".
A feature of pulsating noise in vascular pathology of the brain is its belonging to objective acoustic phenomena. This means that the sound heard by the patient can also be heard by the doctor - with the help of a special device (phonendoscope) during the examination. Thus, not only the presence, but also the significance of the symptom is confirmed. Vascular disorders detected at the initial stages are much easier to correct.
It should be emphasized that in the presence of an arterial aneurysm of the cerebral vessels, noise is not present in all cases.
Although it is often singled out as a classic symptom, it is sometimes possible to diagnose aneurysm only after its rupture and the appearance of vivid clinical manifestations.
 Pulsating noise in the ear is not always the same, it differs depending on the nature and form of the pathology provoking it. It is worth noting that the appearance of a "sound pulse" in the area of the hearing organ is not always characteristic only of older patients and can also be observed in young people and children.
Pulsating noise in the ear is not always the same, it differs depending on the nature and form of the pathology provoking it. It is worth noting that the appearance of a "sound pulse" in the area of the hearing organ is not always characteristic only of older patients and can also be observed in young people and children.
Low-frequency noise and pulsation in the ear with a glomus tumor, or paraganglioma, usually occurs on one side. Therefore, a pulsating noise in the right ear when a cyanotic or reddish mass located behind the tympanic membrane is detected during otoscopy is a sufficient basis for a diagnosis.
In hypertension, noise and pulsation in the ears can act as an early sign, occurring during the period of an increase in blood pressure. The pulsating sound that appears with sensorineural hearing loss may be associated with the presence of a tumor, toxic effects of drugs, or hereditary diseases.
Therapy tactics
The choice of treatment for patients who complain of a pulsating noise in the left ear, "background sound" in the right ear, or note bilateral localization of acoustic phenomena, should be determined by the primary disease.
It should be remembered that pulsating noise in the ear is only a symptom, and not an independent pathology.
Even if the appearance of an obsessive sound is the only symptom, it is necessary to search for a disease that acts as a provocateur. Sometimes the noise level can be influenced by compression of the carotid artery on the affected side - this is one of the clinical signs characteristic of the presence of a carotid-cavernous anastomosis in vascular pathology of the brain. However, this is just a symptom that cannot be considered as a way to improve the condition; pressure on the vessel can only be applied by a doctor in the order of examination for a limited time.
Thus, the causes and treatment of pulsating tinnitus are inextricably linked concepts. To save the patient from the "sound background", it is necessary to find out what caused its appearance. Before using any methods of therapy, it is necessary to carry out diagnostics, including both laboratory and instrumental methods.
Treatment features
Since the occurrence of "background noise" provokes different causes, the treatment of pulsating noise in the ear and the choice of conservative or surgical methods depends on the specific clinical situation.
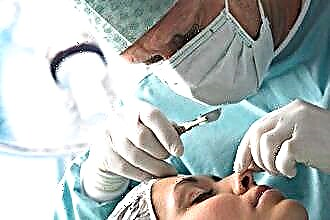
 Patients who have a glomus tumor require surgery. In this case, the tumor tissue is completely removed. The duration of the manipulations and the level of risk depend on many factors - in particular, on the patient's age, the size of the tumor. Radiation therapy and chemotherapy are considered as additional and alternative methods of treatment, however, surgery remains the option of choice, the effectiveness of which is difficult to dispute.
Patients who have a glomus tumor require surgery. In this case, the tumor tissue is completely removed. The duration of the manipulations and the level of risk depend on many factors - in particular, on the patient's age, the size of the tumor. Radiation therapy and chemotherapy are considered as additional and alternative methods of treatment, however, surgery remains the option of choice, the effectiveness of which is difficult to dispute.
With arterial aneurysm of the brain, neurosurgical correction of the defect is indicated. There are several methods of surgical intervention, which are divided into the main types - "open" and endovascular. Determining the type of operation is the task of the attending physician, who makes a decision after examining the patient.
When choosing a method of surgical treatment, preference is given to the least traumatic one.
Neurosurgical intervention is also necessary in the presence of arteriovenous anastomosis of the cerebral vessels. In the case of a carotid-cavernous anastomosis, partial or complete exclusion of the pathological compound from the circulation is carried out by means of intravascular occlusion.
Algorithm of therapy for patients with essential hypertension includes mainly conservative methods of treatment. The only exceptions are some types of pathologies leading to an increase in blood pressure - for example, renovascular hypertension. In most cases, medical correction with the help of drugs of various groups (beta-blockers, angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitors, diuretics, etc.) is sufficient.
Correction of the manifestations of chronic sensorineural hearing loss is carried out with the help of pharmacological preparations from the groups of anxiolytics, nootropics, correctors of cerebral circulation. These funds cannot return the lost function of the auditory organ and are mainly used to influence the unpleasant sensations associated with a decrease in hearing acuity - in particular, on the "background noise". The most commonly used:
- Cavinton.
- Phenibut.
- Picamilon, etc.
To achieve the disappearance of the pulsating noise in the ear, it is necessary to completely eliminate its cause. All doctor's instructions should be followed carefully. If an operation is performed, it is required to follow the recommendations for the preoperative and postoperative period.