A feeling of stuffy ears is an altered perception of your own voice and background sounds. Discomfort is caused by disturbances in the operation of the sound-receiving or sound-conducting system of the auditory analyzer. Untimely diagnosis and treatment of pathology can cause the development of serious complications, such as purulent otitis media, meningitis, labyrinthitis, etc.
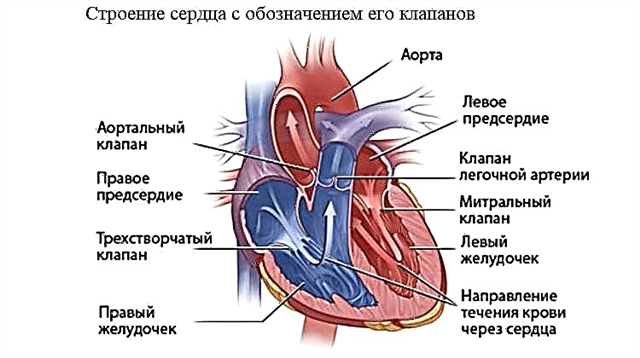
 As a rule, ear congestion is a consequence of inflammatory reactions in the mucous membranes of the nasopharynx, middle ear and Eustachian tube.
As a rule, ear congestion is a consequence of inflammatory reactions in the mucous membranes of the nasopharynx, middle ear and Eustachian tube.
Due to the strong intoxication of the body, the soft tissues swell, which leads to blockage of the auditory canal, which connects the middle ear to the nasopharynx.
A decrease in pressure in the tympanic cavity provokes the appearance of a feeling of congestion in the ears.
Mechanism of occurrence
Why does ears clog? An unpleasant phenomenon occurs due to impaired conduction or perception of sound signals by the auditory analyzer. Failures in the work of the components of the sound-conducting circuit inevitably lead to distortion or weakening of sounds, as a result of which the patient states the fact of hearing loss.
The eardrum not only conducts sound signals, but also amplifies them many times over. Through the ossicles, sound enters the auditory-receptor center, where it is modulated and converted into an electrical impulse. The presence of obstacles in the path of the passage of the sound wave contributes to its attenuation, which leads to a decrease in the threshold of auditory sensitivity.
Much less often, a feeling of stuffiness in the ear occurs due to dysfunction of the main sections of the sound-receiving system. Damage to the ear labyrinth, auditory nerve and hair receptors contributes to hearing impairment and the development of sensorineural hearing loss. In case of untimely access to a doctor, the problem can be eliminated only by surgery.
Causes
Why does my ears keep clogging up? There are many exogenous and endogenous factors that contribute to hearing loss and feelings of congestion. They can be conditionally divided into two categories:
- natural - the formation of sulfur plug, a sharp change in atmospheric pressure;
- pathological - infectious diseases, craniocerebral trauma, abnormal development of the organ of hearing
 and nasal septum.
and nasal septum.
Ignoring the problem can lead to the development of autophony or deafness.
It should be understood that ear congestion without pain does not guarantee the absence of inflammatory processes. If the discomfort persists within a few days, you should seek help from an otolaryngologist. In some cases, the symptom signals the development of benign tumors, serous otitis media or sensorineural hearing loss.
Natural causes
What should you do if your ears are blocked? First you need to find out what factors contributed to the problem. Experts refer to the natural reasons for the appearance of uncomfortable sensations:
- sulfur plugs - an excess amount of sulfur in the external auditory canal contributes to the formation of dense plugs that prevent the penetration of the sound signal into the ear;
- pressure drops - a sharp change in pressure on the ear membrane leads to its stretching and a decrease in elasticity. Often congestion occurs during air travel, diving, traveling in a fast train, etc.;
- moisture in the auditory canal - the ingress of water into the external auditory canal contributes to the formation of a barrier to the passage of sound, as a result of which the audibility of ambient sounds is reduced.
If the ear does not hurt, but it is blocked and hears poorly, it is advisable to be examined by a specialist. In about 15% of cases, the symptom signals the development of cardiovascular diseases, such as arterial hypertension, vascular dystonia, hypotension, etc.
Pathological causes
Congestion in the ears, accompanied by dizziness or pain, most often signals the development of inflammation in the organs of the hearing. Ear pathologies occur due to a decrease in the reactivity of the body or infection of the upper respiratory tract.
The appearance of discomfort may be associated with the development of pathologies such as:
- otitis media is an ENT disease characterized by the occurrence of foci of inflammation in the middle, outer or inner ear. As a rule, it develops against the background of general diseases (tonsillitis, pharyngitis, pneumonia, scarlet fever). Swelling of the affected tissues interferes with the conduction and normal perception of sound signals,
 which leads to congestion, tinnitus and heaviness in the head;
which leads to congestion, tinnitus and heaviness in the head; - perceptual hearing loss - an ear pathology that occurs as a result of damage to the main sections of the sound-receiving apparatus (hair receptors, vestibular cochlear nerve, ear labyrinth);
- tubotympanitis - inflammatory processes in the mucous membranes of the Eustachian tube and tympanic cavity. Swelling of the tissues leads to blockage of the ear canal, as a result of which a vacuum is created in the middle ear. Thus, there is excessive pressure on the ear membrane from the side of the external auditory canal.
Perceptual hearing loss is practically not amenable to drug treatment due to the inability of hair cells (auditory receptors) to regenerate.
If ear congestion does not go away within a few days, you need to be examined by a specialist. As a rule, ear pathologies develop against the background of common infectious diseases (flu, measles, colds, tonsillitis), the progression of which is fraught with serious complications.
During pregnancy
In most women, during gestation, around the 2nd trimester of pregnancy, the ear periodically clogs. The occurrence of the problem is often caused by hormonal changes and a decrease in the body's resistance. The production of excess amounts of progesterone and estrogen leads to malfunctioning of the detoxification organs. For this reason, excess moisture accumulates in the tissues, as a result of which the mucous membranes of the ENT organs begin to swell.
Edema of the tissues helps to reduce the inner diameter of the auditory canal, which prevents the normal ventilation of the tympanic cavity. Due to the low pressure in the middle ear, the ear membrane is pulled inward, which leads to uncomfortable sensations.
Important! Ear congestion without pain can signal the development of catarrhal otitis media. Untimely treatment of the disease can cause the development of purulent inflammation.
Other reasons
Why is the left ear blocked? Hearing loss associated with a feeling of congestion in the ears is not always associated with dysfunction of the auditory analyzer.
Malfunctions of the organ of hearing can be associated with diseases of other organs and systems, which include:
- cholesteatomas are benign neoplasms consisting of keratinized epithelial cells, cholesterol and keratin crystals. They arise mainly with the development of chronic purulent otitis media, accompanied by otorrhea;
- Meniere's syndrome is an otolaryngological disease characterized by the accumulation of endolymph in the inner ear cavity. An excess amount of fluid creates pressure on the hair cells, as a result of which hearing decreases and a feeling of congestion arises;
- dysfunction of the temporomandibular joint - inflammation of the joint capsule, accompanied by damage to the neurovascular bundle, which provides innervation to the middle ear;
- otosclerosis - a pathology characterized by the proliferation of bone tissue in the mastoid process; leads to damage to the structures of the sound-conducting system, which is fraught with hearing loss and ear blocking;
- cranial trauma - contact damage to soft tissues and a chain of nerves in the auditory analyzer, which leads to the development of auditory dysfunction.
If the ear is blocked and does not go away, you need to seek help from an ENT doctor for differential diagnosis. An audiological examination will allow you to accurately determine in which link of the sound-conducting circuit there are violations, which will contribute to the correct choice of a suitable course of therapy.
Diagnostics
What types of examinations do you need to undergo if your ear is blocked? First of all, the specialist will examine the external auditory canal for the presence of perforated holes in the eardrum and tissue hyperemia. If you suspect ear diseases, the patient will be offered to undergo the following types of diagnostics:
- audiometry - determination of the threshold of auditory sensitivity in relation to sound signals of varying intensity and frequency;
 video endoscopy - examination of the outer and middle ear cavity using an endoscope, which allows you to determine the presence of foci of inflammation in soft tissues;
video endoscopy - examination of the outer and middle ear cavity using an endoscope, which allows you to determine the presence of foci of inflammation in soft tissues;- tympanometry - a study of the functions of the middle ear, during which a specialist assesses the degree of mobility of the auditory ossicles and tympanic membrane;
- computed tomography is a method of obtaining a layered image of the brain and temporal bones, thanks to which it is possible to determine the presence of mechanical damage and tumors in the organ of hearing.
What to do if the right ear is blocked after a cold? Post-infectious complications, accompanied by hearing loss, most often signal the development of pathogenic flora in the main parts of the auditory analyzer. In the presence of otorrhea, the specialist should make a culture of the discharge from the external auditory canal. Thus, it is possible to determine the degree of sensitivity of pathogens to the components of antifungal and antibacterial agents.
Drug therapy
To eliminate the vacuum in the ear, the specialist may prescribe medication, physiotherapy, or surgery. The principle of therapy directly depends on the factors that provoked the appearance of the problem. As part of pharmacotherapy, the following types of medications are used to relieve an unpleasant symptom:
- vasoconstrictor drops (Nazol, Snoop) - reduce vascular permeability, which leads to an increase in the inner diameter of the auditory canal and restoration of ventilation of the tympanic cavity;
- anti-inflammatory drops ("Otipax", "Sufradex") - contribute to the regression of foci of inflammation in the mucous membrane of the nasopharynx and the Eustachian tube;
- antiviral drugs ("Kagocel", "Remantadin") - kill pathogenic viruses that provoke the development of bullous and diffuse otitis externa;
- antifungal agents ("Candibiotic", "Amphoglucamine") - inhibit the activity of mold and yeast-like fungi that cause the development of otomycosis;
- antibacterial drugs ("Dexon", "Amoxicillin") - destroy aerobic and anaerobic bacteria that lead to the development of purulent otitis media.
Important! During antibiotic therapy, it is advisable to use probiotics to prevent dysbiosis.
Removing plugs
 Why does it periodically stuff up the ears? Failure to comply with basic hygiene rules is one of the most common causes of discomfort. If moisture enters the external auditory canal, an air blockage can form in the ear, preventing the evacuation of fluid. To remove it, experts recommend rinsing the ear with saline, heated to a temperature of 37-38 degrees.
Why does it periodically stuff up the ears? Failure to comply with basic hygiene rules is one of the most common causes of discomfort. If moisture enters the external auditory canal, an air blockage can form in the ear, preventing the evacuation of fluid. To remove it, experts recommend rinsing the ear with saline, heated to a temperature of 37-38 degrees.
If the ear is sharply laid, this may indicate a blockage of the ear canal with a sulfur plug. The onset of the problem is often preceded by a slight hearing impairment associated with a partial blockage of the ear canal. To dissolve earwax and eliminate the plug, experts recommend using cerumenolytics. They include surface active components that soften dense masses and facilitate their evacuation. If the right ear is blocked, it is more advisable to use drugs such as "A-cerumen", "Remo-Wax", "Aqua Maris Oto", etc.
High-density corks, which do not dissolve with cerumenolytics, are removed during the kerutage using a special probe.

 and nasal septum.
and nasal septum. which leads to congestion, tinnitus and heaviness in the head;
which leads to congestion, tinnitus and heaviness in the head; video endoscopy - examination of the outer and middle ear cavity using an endoscope, which allows you to determine the presence of foci of inflammation in soft tissues;
video endoscopy - examination of the outer and middle ear cavity using an endoscope, which allows you to determine the presence of foci of inflammation in soft tissues;