Perspiration in the throat at night, dry mouth, and a desire to cough up - all these symptoms indicate the development of a disease of the respiratory tract, digestive system, or systemic pathology of autoimmune genesis. Depending on the cause of the appearance of symptoms, in addition to perspiration, hyperthermia, malaise, rhinitis and other symptoms of the disease may also disturb.
 Perspiration can be caused by dryness of the oral mucosa due to:
Perspiration can be caused by dryness of the oral mucosa due to:
- dehydrationwhen there is increased fluid loss with diarrhea, vomiting with intestinal infection, with insufficient drinking regime (the daily volume of fluid drunk is less than 500 ml per day);
- atrophic processes in the oropharynxcaused by prolonged inflammation with pharyngitis or laryngitis;
- long-term use of certain medications, for example, psychotropic, antihistamines, diuretic drugs, the use of nasal sprays with a vasoconstrictor effect, atropine and antihypertensive drugs, which include a diuretic component;
- lesions of the salivary glands (sialostasis, sialolithiasis, inflammatory and infectious process), in which the production of saliva decreases or stops;
- oncological processes in the oropharynx of benign or malignant genesis, which is manifested by damage not only to the salivary glands, but also to the surrounding tissues.
- When malignant metastasis dysfunction of internal organs is observed;
- acute or chronic bleeding, large area burns, hectic fever with severe sweating;
- surgical removal of the salivary glands due to their traumatic injury, cancer or chronic inflammation in the absence of the effect of conservative techniques;
- nerve damagethat control the salivary function of the glands;
- anemias of various genesis, manifested by shortness of breath, dizziness, pallor, dry skin, mucous membranes, changes in taste, tinnitus, malaise and psycho-emotional instability;
- severe emotional stressespecially in people prone to anxiety.
Discomfort in the oropharynx is noted with frequent smoking, abuse of alcoholic beverages, breathing through the mouth (due to heavy physical exertion, nasal congestion, shortness of breath due to cardiac or respiratory failure).
Perspiration in the oropharyngeal area can be disturbing when:
- diabetes, when a person notes severe thirst, an increase in daily urine output, and dry mucous membranes;
- thyrotoxicosis, in which the level of thyroid hormones in the circulatory system increases. In addition to perspiration, the patient complains of tremors of the fingers, increased irritability, fever, tachycardia and insomnia;
- systemic diseases (scleroderma, lupus, cystic fibrosis, Sjogren).
Treatment of autoimmune systemic diseases is carried out exclusively by a doctor after a complete examination.
Common causes
Among all the causes of discomfort in the oropharynx, it is worth highlighting pharyngitis, laryngitis, and tracheitis as the most common.
With the development of diseases of the respiratory tract, the patient often complains that at night a sore throat and a cough worse in the morning.
| Disease | The reason for the development | Acute stage | Chronic stage | Complications | Diagnostics |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
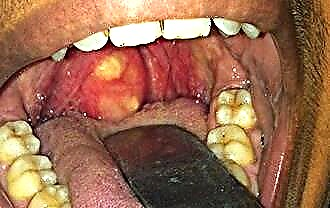
| Pharyngitis - lesion of the posterior pharyngeal wall by an inflammatory process | Viruses (70%) - adenovirus, parainfluenza, rhinovirus; bacteria (25%) - streptococci, 5% - allergies, trauma, irritation with polluted, cold air. | Sore throat, sore throat, soreness when swallowing, subfebrile hyperthermia, lymphadenitis. | Dry, scratched throat or thick phlegm, dry cough, painful swallowing. | Peritonsillar abscess, laryngitis, tracheitis, rheumatism. | With pharyngoscopy, hyperemia of the mucous membrane, tonsils, tissue edema, and mucopurulent plaque are visualized. In a chronic course, the picture with pharyngoscopy depends on the type of disease (catal, hypertrophic, atrophic). The examination of smears allows you to establish the type of pathogenic microorganisms. |
| Laryngitis is a lesion of the laryngeal mucosa by an inflammatory process. | Viruses (80%) - ARVI, measles, influenza, scarlet fever; 20% - hypothermia, dusty, cold air, overstrain of the vocal cords. | Subfebrile hyperthermia, dryness, tickling, sore throat, feeling of a lump, voice hoarseness, soreness when swallowing, dry cough, aphonia. | Symptoms are less intense than acute symptoms. | Laryngeal stenosis, tracheitis. | With laryngoscopy, edema, hyperemia of the laryngeal mucosa are visualized. A small volume of sputum is located on the surface of the ligaments. The picture with laryngoscopy in chronic course depends on the form of the disease (hyperplastic, atrophic). |
| Tracheitis - damage to the trachea by the inflammatory process. Laryngotracheitis or tracheobronchitis is often diagnosed. | Viral, bacterial pathogens, environmental factors, allergies, infectious and inflammatory diseases of the nasopharynx, paranasal sinuses, as well as concomitant somatic pathology. | Seizure cough, sore throat, chest pain, febrile hyperthermia, lymphadenitis. | Persistent cough, especially at night, subfebrile hyperthermia. | Bronchitis, pneumonia, bronchial asthma (with allergic tracheitis). | Laryngotracheoscopy, sputum culture, throat swab. |
Do not forget about the appearance of perspiration and dry cough in case of an allergic reaction. Due to contact of the mucous membrane with allergens, for example, down, pollen, wool, an allergic reaction of a local or systemic nature develops:
- local manifestations are represented by tissue edema, itching, tickling in the oropharynx, which provokes a cough;
- systemic symptoms are represented by Quincke's edema, as well as anaphylactic shock. Symptomatically, pathological conditions are manifested by skin itching, rashes, shortness of breath, bronchospasm, decreased blood pressure and increased heart rate.
Treatment activities
General recommendations will help get rid of symptoms, speed up recovery, and strengthen the immune defense:
- rest of the vocal cords;
- elimination of the allergic factor;
- drinking plenty of fluids, which accelerates the elimination of toxins, reduces fever and replenishes fluid losses, eliminating hypovolemia;
- vitamin food;
- good rest, sleep;
- reduction of stress factors, physical activity;
- air humidification;
- frequent airing, wet cleaning;
- prevention of contact with people with infectious diseases.
Fight against infectious pathogens
When confirming the viral origin of an infectious pathology, antiviral medicines should be used. They have not only antiviral, but also an immunomodulatory effect.
Symptomatically, a viral infection can be suspected on the basis of rhinorrhea, subfebrile hyperthermia, lacrimation, sore throat, malaise and joint aches. From antiviral medicines, Arbidol, Amizon, Amiksin, Groprinosin, Remantadin, Aflubin, Otsilokoktsinum, Influcid, Ingavirin or Influcid are prescribed.
 If bacterial inflammation is detected in throat swabs, the use of antibacterial drugs is indicated. Of the clinical symptoms, attention should be paid to febrile hyperthermia, severe malaise, severe cough and sore throat.
If bacterial inflammation is detected in throat swabs, the use of antibacterial drugs is indicated. Of the clinical symptoms, attention should be paid to febrile hyperthermia, severe malaise, severe cough and sore throat.
Among the medicines, it is worth highlighting Amoxiclav, Flemoxin, Cefotaxime, Ceforaxim, Azithromycin or Erythromycin, Sumamed. Depending on the results of the antibioticogram, the most effective antibacterial drug is selected.
It is extremely rare that perspiration and coughing can be caused by a fungal infection of the pharyngeal mucosa. Usually, the fungal process is observed after prolonged antibiotic therapy. In this case, antifungal agents are prescribed, for example, Fluconazole.
Local treatment
For medicinal purposes, rinsing solutions, inhalation solutions, spray or tablet formulations are used. Medicines have antimicrobial, anti-inflammatory, decongestant, regenerative and analgesic effects.
- rinsing solutions - Chlorhexidine, Chlorophyllipt, Furacilin, Miramistin, Givalex, Tantum-Verde, Rotokan;
- sprays - Oasept, Givalex, Stopangin, Bioparox, Miramistin, Tantum-Verde, Chlorophyllipt, Strepsils Plus, Septolete;
- solutions for lubricating the mucous membrane of the pharynx - Lugol, Collargol, Carotolin;
- tablets, lollipops - Strepsils, Septolete, Decatilen, Faringosept, Trakhisan, Lisobakt, Lizak.
To obtain the maximum therapeutic effect, it is necessary to abstain for half an hour from eating, liquid after irrigating the mucous membrane, rinsing or lubricating the tonsils with drugs.
During the day, it is recommended to alternate the drugs used for local treatment. The procedures are repeated every 90 minutes.
In addition, a good effect is observed when using inhalation. At home, it is most simple to use a nebulizer, but it is allowed to carry out the procedure "the old fashioned way" over steam:
- inhalations can be carried out with oil (olive, menthol, peach, chamomile, eucalyptus). For one inhalation, it is enough to boil 400 ml of water and add 8 drops of oil. The procedure should be started after the steam has cooled down, which will avoid burning the mucous membrane of the upper respiratory tract. The healing effect consists in moisturizing, softening the mucous membrane, as well as reducing the severity of the inflammatory reaction.
 20 g of pine cones should be brewed with 220 ml boiling water and infused throughout the day in a dark place;
20 g of pine cones should be brewed with 220 ml boiling water and infused throughout the day in a dark place;- for inhalation, you can use a mixture of yarrow infusion (10 ml) and chamomile broth (20 ml).
In the presence of a nebulizer, the inhalation process is greatly facilitated. The advantages of the device include:
- steam temperature control;
- strict adherence to the dose;
- convenience;
- synchronization with breathing is not required;
- constant supply of medication.
The device requires 1 ml of saline to operate. Before use, the drug should be dissolved in saline in a certain proportion. For one procedure, 4 ml of the prepared medicine is enough. With a curative purpose, Furacilin, Dekasan, Dioxidin are prescribed, as well as non-carbonated mineral water (Borzhomi, Essentuki).
Traditional treatment
Herbal medicines should not be taken by people prone to allergic reactions and bronchial asthma.
For gargling, you can use herbal solutions:
- plants (calendula, sage, eucalyptus) with a volume of 15 g must be crushed and poured with boiling water (450 ml). It is recommended to insist for a quarter of an hour, after which it is required to filter, add honey (10 g) and citric acid (1 g).
Herbs such as chamomile, oak bark, viburnum, willow, birch leaves, yarrow, sage and eucalyptus can be used in the treatment. Also, rinses are carried out with a solution of onion juice with a volume of 5 ml per 180 ml of warm water. The most common medicine is soda salt solution. For 220 ml of water, 5 g of components are enough.
In case of inflammation of the tonsils, it is recommended to lubricate their surface with peach oil (30 ml) with propolis tincture (15 ml). For the procedure, you should moisten a gauze pad in the prepared medicine and gently lubricate the throat surface.
To strengthen the immune defense, decoctions of herbs, bee products, ginger and other immune-strengthening agents, such as echinacea, are used.
If a sore throat appears, you should immediately begin treatment at home, preventing the spread of the infectious and inflammatory process to the surrounding tissues. If home therapy is ineffective and symptoms progress, you should consult your doctor.

 20 g of pine cones should be brewed with 220 ml boiling water and infused throughout the day in a dark place;
20 g of pine cones should be brewed with 220 ml boiling water and infused throughout the day in a dark place;