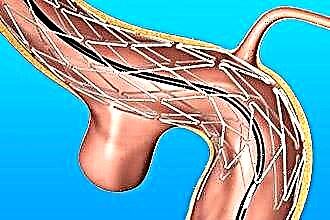
Stapedoplasty (calibrated stapedometry) is an operation to replace a structural element of the middle ear (stapes) to improve hearing. The direct indication for surgical treatment is otosclerosis. ENT disease is characterized by abnormal growth of bone tissue, as a result of which the mobility of the auditory ossicles is impaired.
When carrying out stapedoplasty in case of otosclerosis, the surgeon performs prosthetics of the stapes or its elements, due to which sound conduction in the chain of the auditory ossicles is normalized. Cardinal treatment of ENT disease leads to full or partial restoration of the functions of the auditory analyzer. In 90% of cases, calibrated stapedometry allows achieving permanent regression of conductive hearing loss.
Indications and contraindications

Hearing-improving surgery (stapedoplasty) is indicated when the sound signals passing through the auditory ossicles are blocked. Pathological changes occur as a result of the immobilization of the stapes, caused by the growth of bone tissue. Ignoring the problem leads to the development of permanent hearing loss or a complete loss of the ability to perceive sounds.
Surgical intervention is carried out in the following cases:
- bilateral otosclerosis;
- persistent conductive hearing loss;
- adhesive otitis media;
- negative Rinne test.
Calibrated stapedometry will only be effective in treating conductive hearing loss. Prosthetics in the development of cochlear and mixed otosclerosis will not bring the desired therapeutic results.
Surgical intervention is possible with normal patency of the ear canals and the absence of somatic diseases leading to the development of hearing loss. Hearing-improving operations are contraindicated for:
- abnormal ear structure;
- infectious lesion of the ENT organs;
- chronic ear inflammation;
- contraindications to the use of anesthesia;
- external otitis media;
- acute course of otosclerosis.
Before stapedoplasty, patients undergo a thorough examination, during which pathologies that can affect the course of the operational process are identified. In the absence of serious contraindications, preliminary preparation of the patient takes place, followed by prosthetics of the stapes.
contraindications, preliminary preparation of the patient takes place, followed by prosthetics of the stapes.
Survey
Calibrated stapedometry is one of the complex ENT operations performed with the development of ear pathologies that affect the functioning of the auditory analyzer. Before carrying out surgical procedures, the patient undergoes an examination, which includes the delivery of standard tests (biochemical analysis of blood and urine) and specific examinations by an ENT doctor:
- audiometry;
- tomography;
- tympanometry;
- samples of Zhelle and Rinne;
- vestibulometry;
- radiography;
- reflexometry.
Based on the results obtained during the examination, the specialist is convinced of the need to implement hearing aids. The otosurgeon determines the optimal method of stapedometry, as well as the type of the prosthesis itself, which can be:
- teflon;
- titanium;
- fluoroplastic;
- steel;
- wire-fat;
- platinum-titanium.
Important! Teflon prostheses are cheaper, but they are not recommended due to the high risk of deformation of the anvil end.
Operating methods
Hearing-improving surgery for otosclerosis is performed under local anesthesia. Approximately 90% of patients do not feel discomfort during the process of replacing the stapes with a prosthesis, which takes no more than 2 hours. In the process of prosthetics, the following techniques can be used:
- stapedotomy - excision of a part of the stapes with a laser knife, followed by replacement of the missing element with a prosthesis. Surgical intervention is carried out using a defocused laser beam. In this case, a perforated hole is created at the base of the damaged bone, into which an autovein and a prosthesis are inserted. During surgical treatment, minor damage to the vestibule of the ear labyrinth occurs. However, experts note the possibility of developing necrosis;
- stapedectomy - complete removal of the mineralized stapes, accompanied by the replacement of the structural element with autocartilage. The operation eliminates the likelihood of tissue necrosis, which ensures an almost 100% positive outcome of surgical treatment. With total stapedectomy, a very rapid decrease in the bone-air gap is noted, which halves the rehabilitation period.
In case of bilateral otosclerosis, prosthetics of the second ear is carried out no earlier than six months after the operation of the first one.
Rehabilitation
The effectiveness of surgical treatment is largely determined by the thoroughness of adherence to the rules, which must be adhered to for 6-12 months. Failure to follow the recommendations leads to the development of complications leading to hearing impairment. Stapedoplasty for otosclerosis will be effective if the following rules are taken into account:
 refusal from heavy physical exertion;
refusal from heavy physical exertion;- refusal from diving and air travel;
- the use of conservative treatment agents;
- elimination of loud noises.
During the first 3-4 months after hearing aids, it is undesirable to listen to music with headphones.
Failure to comply with basic rules entails hearing impairment and the following complications:
- sepsis;
- meningitis;
- labyrinthitis;
- acute otitis media;
- ear liquorrhea;
- displacement of prostheses;
- paresis of the facial nerve;
- necrosis of the tissues of the middle ear;
- obliterating otosclerosis.
In order to track the occurrence of pathological changes in time, it is advisable to be examined by an otolaryngologist within 1 year after hearing aids. Audiometric tests will determine if there are any abnormalities in the conduction of sound signals by the ossicles and prosthesis.
Patient Testimonials
According to the reviews of patients who underwent stapedoplasty, the success of the operation is largely determined by the clarity of adherence to the rules in the postoperative period, as well as the accuracy of the diagnosis. In 90% of cases, patients notice a subjective improvement in hearing, which is confirmed by the results of an audiogram. In the first few months after hearing aids, the sounds are indistinct, but within six months they "crystallize".
In 50% of cases after childbirth, patients who have undergone calibrated stapedometry experience hearing impairment, which is associated with swelling of the mucous membranes in the middle ear and, accordingly, displacement of the prosthesis.
However, it should be borne in mind that approximately 10% of patients complain of malfunctions in the vestibular apparatus and a slight exacerbation of hearing. In case of serious head injuries, cases of complete hearing loss are possible, which are associated with a displacement of the prosthesis. Sometimes this may indicate the progression of otosclerosis and the need for repeated surgery.

 refusal from heavy physical exertion;
refusal from heavy physical exertion;