Ear wax is a physiological process. Due to the presence of antiseptic and antimicrobial substances in its composition, earwax performs a protective function in the ear. In addition, it prevents excessive wetting of the external auditory canal and the development of stagnation in it. Therefore, the presence of sulfur in the ear is the prevention of inflammation of both the outer and middle ear.
In most cases, the ear wax is freed on its own. In addition, the removal of wax from the ears is made possible by regular cleaning of the ear canal. However, in some cases, it accumulates excessively, which can lead to the formation of ear plugs.
Signs of an ear plug
The presence of ear plugs is a pathological process and is accompanied by the development of certain clinical symptoms.
Typical signs of ear plug formation are ear congestion, tinnitus, hearing loss, up to the development of deafness.

In cases where the ear plug is located in the immediate vicinity of the eardrum, dizziness and nausea may occur. When an infectious agent enters the external auditory canal, the ear plug can contribute to the development of ear inflammation. Let's talk more about how to remove wax from your ears.
ENT procedures
The most effective way to get rid of earwax is to immediately contact a specialist, where the necessary medical care will be provided in a specialized office. With the development of this process, consultation with an otolaryngologist is especially important, since similar symptoms can occur with ear inflammation. A timely consultation and the appointment of the correct treatment will contribute to the fastest recovery. At the same time, in the presence of an ear plug, the doctor will be able to analyze the cause of its appearance, give recommendations on further tactics and rules for holding the ear toilet.
The presence of a sulfur plug is an indication for its washing out. After inserting a syringe with saline into the ear, the doctor makes movements with the piston, flushing out the dense ear plug. If necessary, several similar manipulations are performed until the liquid becomes transparent. If there are signs of otitis externa, ear drops with antiseptic, anti-inflammatory effects may be recommended, or containing an antibacterial component.
containing an antibacterial component.
Patient-guided ear toilet
How to clean your ears from wax at home depends on the availability of available tools. The most common way to remove ear wax is to use a syringe or syringe without a needle. Having typed warm boiled water into a pear or syringe, under pressure it is necessary to release a stream of water into the external auditory canal. Repeat these rinses until the water flowing out of the ear is clear. The procedure should be carried out very carefully so as not to injure the skin of the external auditory canal and, especially, the eardrum.
Despite the analogy with the procedure carried out by a specialist, washing out the sulfur plug at home is fraught with the risk of injury to the eardrum. The ENT doctor has the skills to carry out such a procedure. In addition, the specialist controls this manipulation visually, which prevents damage to the ear. In this regard, carrying out the procedure in a specialized office is more preferable.
Use of medications
Currently, the assortment of pharmacological agents is varied, than to wash the ears from wax. The most effective and safest pharmacological drugs used even in children are
- A-Cerumen;
- Remo-wax;
- Audi spray and Audi baby.
These topical drugs are used as prophylactic agents for excessive sulfur production. In addition, they help clear the wax from the ears in the presence of sulfur plugs.
For preventive purposes, drugs can be used twice a month. Removal of sulfur plugs using these pharmacological agents can take 3-4 days. During this time, this drug should be instilled into the ear at the frequency set out in the instructions, and then the dissolved sulfur plug can be washed out with prepared saline or warm water. The dosage form can be in the form of a spray or ear drops, depending on the patient's preference.
A very popular way to clear wax from your ears is with 2% hydrogen peroxide. To do this, a few drops of hydrogen peroxide are instilled into the ear to be cleaned, after which the patient should lie on his side for 10-15 minutes, and the buried ear should be on top.
Hissing is an indication of the effect of hydrogen peroxide and should not be a cause for concern.
After the required time has elapsed, the patient should turn over on the other side. The solution with the remaining sulfur will flow freely from the instilled ear. You can dry the ear canal by using cotton tourniquets or tampons. If necessary, the procedure should be repeated in the next 2-3 days.
Usually, such an ear toilet is well tolerated. The procedure is characterized by ease of implementation and availability. Moreover, it is quite safe. However, the appearance of severe burning and pain during the manipulation indicates the need to stop it immediately.
In this case, you should seek advice from an otolaryngologist. It may be necessary to clarify the diagnosis, and we are not talking about the presence of cerumen, but the development of otitis media with perforation of the tympanic membrane.
The presence of an injured eardrum is a contraindication for any procedure using pharmacological drugs.
When choosing a method of how to remove wax in the ear, an important condition must be observed. It consists in the fact that the cork must come out by itself. Do not use ear sticks or similar devices to aid in the procedure. There are cases of severe complications associated with rough cleaning of the ear canal. After the remnants of the sulfur plug are washed out with the solution, the ear should be rinsed with warm water. Many otolaryngologists advise not to wipe the auricle and ear canal after water procedures with a towel or napkin to prevent excessive serum formation, but to dry it with a hairdryer.
Risk group
How to remove wax in the ears is a problem that is most relevant for those groups of the population who have an increased production of sulfur or a reduced ability to remove it. Most often, the formation of an ear plug is characteristic of
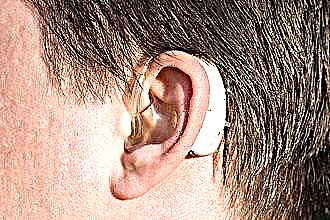 patients who wear hearing aids;
patients who wear hearing aids;- workers in dusty premises (mines, weaving industries, cement plants);
- mill workers;
- divers and swimmers;
- people with a genetic predisposition to ear wax retention, that is, having a narrow and tortuous ear canal.
Such patients should find their own individual approach to solving this problem. In cases where the ear plug is formed due to excessive production of sulfur, you need to work out the optimal frequency of ear cleansing. If there are anatomical features of the structure of the ear, preventive measures with the periodic use of pharmacological agents are more appropriate.

 patients who wear hearing aids;
patients who wear hearing aids;