The palatine tonsils (tonsillae) are damaged by an infectious disease such as tonsillitis. The pathological process can be acute and chronic, unilateral (the gland is damaged on one side) and bilateral. Acute tonsillitis can be completely cured by conservative methods. But with a belated appeal to a specialist or as a result of the use of illiterate therapy, angina is complicated by many pathological conditions. One of the serious complications is the overflow of an acute process into a chronic one. Unfortunately, conservative therapy does not always help with chronic tonsillitis. Laser treatment of tonsils is by far the most effective way to get rid of the disease.
What is chronic tonsillitis
 A chronic process means a sluggish course of the disease with periods of exacerbation and remission. The pathogenic microflora that is constantly in the oropharynx has an extremely negative effect on the entire body. Rheumatism, inflammatory processes in the cardiovascular, genitourinary, respiratory, and nervous systems may develop. Therefore, adequate and timely treatment of chronic tonsillitis is no less important than the treatment of angina.
A chronic process means a sluggish course of the disease with periods of exacerbation and remission. The pathogenic microflora that is constantly in the oropharynx has an extremely negative effect on the entire body. Rheumatism, inflammatory processes in the cardiovascular, genitourinary, respiratory, and nervous systems may develop. Therefore, adequate and timely treatment of chronic tonsillitis is no less important than the treatment of angina.
Causes
- frequent sore throats 4-6 times a year;
- violation of nasal breathing due to curvature of the nasal septum;
- adenoids and adenoiditis;
- inflammatory processes in the ENT organs;
- polyps in the nose.
Stages
- compensation stage - the body independently copes with pathology;
- stage of decompensation - the glands lose their functions and themselves become a source of spread of microbes.
Symptoms
- persistent sore throat, moderate to intense;
- enlargement of the tonsils, pain in them;
- swelling of the nasopharyngeal mucosa;
- plugs in the lacunae of the tonsils;
- moist cough;
- subfebrile body temperature, which lasts for a long period;
- halitosis;
- instant exacerbation of the disease when exposed to adverse factors: cold food or drink, wet feet, hypothermia, drafts, frequent and abrupt changes in weather, contact with an infected person;
- decreased performance, increased fatigue;
- decreased appetite;
- recurrent joint pain, which can occur each time in a different joint. The knee and wrist joints are most commonly affected.
Children are susceptible to chronic tonsillitis due to anatomical features: narrow deep lacunae with branching slit passages
Treatment
Chronic inflammation of the palatine glands is very often accompanied by concomitant processes: rhinitis, adenoiditis, sinusitis, pharyngitis, carious teeth, periodontitis. Therapy should be comprehensive and aimed at eliminating the causes. Chronic tonsillitis is treated with conservative and surgical methods.
Conservative treatment includes elimination of secondary infection, regular debridement of the tonsils and oral cavity, ultraviolet treatment, radiation therapy, antibiotic injections into the tonsils, fortifying, desensitizing therapy, irrigation of the tonsils with antiseptics, warming compresses, lubrication, rinsing. Conservative methods are effective in the case of a local nature of the process, which is limited only to the tonsils. With therapeutic methods, you can achieve a short-term remission.
Surgical methods:
- galvanic acoustics, diathermocoagulation - methods are not often used at present, they consist in opening lacunae (lacunotomy) and evacuating detritus, purulent foci, eliminating a closed space in the tonsils;
- dissection of lacunae is rarely used due to the high risk of bleeding from the tonsils;
- tonsillectomy - a radical operation for the complete
 removal of tonsils;
removal of tonsils;
Tonsillectomy is more often performed in childhood.
- cryosurgery - exposure of an organ to low temperatures, at which the death of pathological cells occurs. The method is used if there are contraindications to tonsillectomy;
- electrocoagulation - removal of the affected area using high frequency currents;
- laser ablation of tonsils - rejection of a part of an organ using cauterization with laser radiation.
Laser treatment of tonsils
Today, experts are trying to preserve the tonsils in affordable ways. This is due to the fact that the palatine glands are involved in the formation of immunity and are an obstacle to the pathogenic microflora. If the tonsils are completely absent, then a direct path opens for the penetration of microbes into the human body.
Laser destruction of tonsils is the most successful organ-preserving alternative to radical tonsillectomy.
Types of laser treatments
- Fiber-optic laser - used in case of damage to most of the glands.
- Holmium laser - is used to remove lesions inside the organ, while the surrounding tissues are preserved intact.
- Infrared Laser - Used to sever and bond tissue.
- Carbon laser - used to remove lesions, resulting in a decrease in the volume of the organ.
Indications and contraindications
Laser treatment is indicated in the following cases:
- too frequent exacerbations up to four times a year or more;
- lack of a lasting effect of conservative therapy;
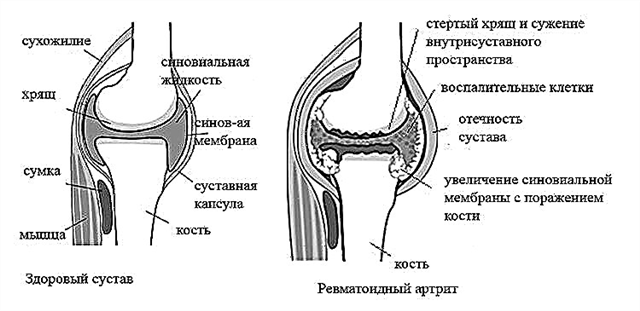
- the presence of complications of tonsillitis: pericarditis, myocarditis, endocarditis, rheumatism, heart defects, glomerulonephritis, reactive arthritis, paratonsillar abscess, blood poisoning;
- rheumatism, rheumatic fever.
Contraindications:
- acute inflammatory processes;
- malignant tumors;
- diabetes mellitus in the stage of decompensation;
- decompensated heart disease (heart failure, defects, cor pulmonale);
- decompensated diseases of the respiratory system (respiratory failure, pulmonary emphysema, cystic fibrosis, fibrosing alveolitis, lung defects, others);
- bleeding tendency;
- period of pregnancy;
- children under ten years of age.
Advantages and disadvantages
Benefits of laser treatment:
- practically bloodless minimally invasive method;
- deep penetration into tissues;
- no harmful radiation;
- local anesthesia minimizes the risk of developing allergic reactions, excludes intolerance to general anesthesia drugs;
- short duration of the procedure: 15 to 30 minutes;
- no hospitalization is required, the procedure is performed on an outpatient basis;
- working capacity does not decrease;
- there is no long recovery period;
- there is no need for antibiotic therapy after surgery,
 since there is no open wound;
since there is no open wound; - fast recovery;
- treatment is carried out in one visit.
Flaws:
- slight pain or discomfort after the cessation of anesthesia;
- tissue burn is not excluded;
- since the glands are not completely removed, there may be relapses of the disease;
- the procedure requires the highest medical qualifications;
- relatively high cost of the operation.
Technique of the procedure
The laser acts on the tonsils with waves of the same length with destructive and sintering effects. With the help of the destructive effect, the affected areas are removed, with the help of the sintering effect, bleeding and the occurrence of open wounds are not allowed.
Cauterization of tonsils with a laser is performed on an outpatient basis.
The patient is injected with local anesthetic 2% lidocaine or ultracaine. The specialist chooses the required wavelength. The laser performs destruction (destruction) and ablation (cauterization) of the affected tissues.After the procedure, the patient remains under the supervision of a doctor for about an hour. The rehabilitation period lasts from three days to two weeks. For this period, topical antiseptics and diet are prescribed.
In modern laser devices, the power of the outgoing radiation flux is regulated. This allows the procedure to be carried out as efficiently as possible in each specific case.

 removal of tonsils;
removal of tonsils;
 since there is no open wound;
since there is no open wound;