Sinusitis is an inflammation of the maxillary paranasal sinuses. At the same time, at first glance, the throat and lower respiratory tract are not directly affected, cough does not occur in all patients and does not belong to the main symptoms of sinusitis. However, coughing with sinusitis is a common occurrence in both adults and children. Next, we will consider in more detail the possible causes of this phenomenon, complications from it and methods of treatment.
Causes of cough
 The main symptoms of sinus inflammation are:
The main symptoms of sinus inflammation are:
- discomfort in the area of the nose and the projection of the maxillary cavities,
- increased body temperature, from 37 to 39 degrees, depending on the pathogen and the stage of the disease;
- a feeling of congestion and difficulty in nasal breathing;
- discharge from the air pockets of mucus and pus;
- pain syndrome radiating to different parts of the head;
- decreased sense of smell;
- general weakness and fatigue.
At the same time, with sinusitis and coughing is not uncommon. It is a secondary symptom and can torment a person, both in the acute form of the disease, and in the chronic one.
A cough can develop with an acute viral or bacterial form of sinus inflammation. In this case, pathogenic microorganisms act not selectively, covering both the upper respiratory tract and all the cavities of the internal nose, causing tissue edema and narrowing of the connecting canals, and the lower respiratory tract - the lungs and bronchi. It is the coverage of the bronchi and lungs with pathogens that causes a painful dry, unproductive thump, which responds with pain and does not alleviate the patient's condition.
In fact, this type of cough does not directly depend on sinusitis, it goes along parallel paths with it. A person who has been attacked by the virus takes measures to relieve the most unpleasant symptoms, including the throat reflex. Mucolytic agents do their job within several days of treatment - sputum begins to cough up, coughing becomes productive and not so painful. Often, in such cases, a person learns that he has sinusitis only after the main signs of a viral infection have passed.
In other cases, it is the maxillary sinusitis that causes the cough. This happens if pathogens become pathogenic bacteria or allergens, as well as polyps or cysts. The negative effect of the bacterial flora on the mucous membranes of the paranasal sinuses leads to increased secretion of the goblet glands and the appearance of pus in the exudate. In an effort to evacuate the accumulating mucus as quickly as possible, ciliated epithelial cells work in an enhanced mode.
Detachable accessory pockets appear in the nasal cavity and can be excreted in two ways:
- Through the anterior nasal passages and nostrils, which looks like the usual snot and dried crusts.
- Through the back of the nasopharynx into the throat, then spit out or swallowed. In this case, mucus flows down the back of the pharynx, causing severe perspiration. Further, part of the secretion enters the larynx and trachea, where it is perceived by the receptors as an atypical liquid. This activates the reflex aimed at removing it from the respiratory tract.
 In the acute form of sinusitis, a lot of exudate enters the trachea, so the cough is wet, and a large amount of sputum is coughing up. This is a signal that the disease has passed the initial stage and in the future the condition will worsen. It is necessary not to waste time and begin to comprehensively treat sinusitis with medication, eliminating its negative impact on other body systems.
In the acute form of sinusitis, a lot of exudate enters the trachea, so the cough is wet, and a large amount of sputum is coughing up. This is a signal that the disease has passed the initial stage and in the future the condition will worsen. It is necessary not to waste time and begin to comprehensively treat sinusitis with medication, eliminating its negative impact on other body systems.
If acute sinusitis lasts a long time or becomes chronic, then purulent sinus discharge flows down the throat almost continuously, but in small quantities.
This situation provokes an almost incessant small cough (especially at night), which is dry in nature, since the amount of fluid relative to the size of the trachea is small, and its traces are not noticeable.
The coughing urge only irritates the walls of the pharynx, but does not bring relief. If sinusitis is not adequately treated, then the regular flow of exudate into the lower respiratory tract threatens with complications such as pneumonia (pneumonia), tracheitis or bronchitis. At the same time, ordinary expectorant drugs do not help, and this phenomenon will not go away by itself.
Cough after sinusitis and features of this symptom in children
Despite the end of the therapeutic procedures, some patients experience coughing as a residual phenomenon. This should not be taken lightly, since it is quite possible that the bronchial tree was affected due to the aggressive effects of the infection (especially in the purulent form of the disease). In this case, the development of bronchitis and the transition of the inflammatory process to the lungs is possible.
If sinusitis is cured, and the reflex does not go away for several days, pains in the sternum begin, you should consult a doctor and undergo fluoroscopy. This can be one of the very unpleasant complications of sinusitis, the treatment of which cannot be postponed in any case, since the pathogen was defeated in one place, but activated in another.
The difficulty in determining the causes of cough in children is that the child is often unable to describe the sensations he is experiencing. Therefore, parents treat children for a runny nose, colds, SARS, and the real cause of the disease is recognized only when the disease turns into a purulent form. It is necessary to pay attention, in addition to the pronounced symptoms, to the general condition of the baby: if he becomes lethargic, inactive, eats poorly, then it will be useful to see the otolaryngologist.
How to get rid of a sinus cough with medication
It is necessary to immediately stipulate that a sore throat and cough are secondary signs of inflammation of the maxillary cavities, therefore, attempts to get rid of only this symptom, without general treatment of sinusitis, have no chance of success.
Drug treatment of inflammation of the maxillary pockets consists in a complex effect on the pathogen in order to suppress its activity, as well as to eliminate symptoms that threaten the life of the body as a whole or any of its systems. As a rule, these signs are of the greatest concern to the patient and give him maximum inconvenience. In addition, preventive measures are required to enhance the effect of drugs and accelerate the healing process.
Conservative treatment includes the following areas:
- Suppression of the action of pathogenic bacteria that multiply in the airways using antibiotics. In this case, drugs of various types are used, depending on the specific causative agent of the disease, identified during bacteriological examination of a smear from the nasal mucosa. The most common tablets are penicillins (Amoxiclav, Flemoxin solutab, Augmentin) or macrolides (Macropen). Injections of cephalosporins (Cefazolin, Ceftriaxone) are often prescribed, the same powders are also used for washing the sinuses. Local antibiotics, which are sprayed into the nasopharynx (Bioparox), have worked well. They have few side effects due to their low level of absorption into the bloodstream. Moreover, such drugs allow you to quickly create a high concentration of the active substance in a specific affected area.
 Elimination of fever and pain.Doctors recommend knocking down body temperature after reaching 38.5 degrees, with the exception of patients with hyperthermia intolerance. The most common drugs are based on paracetamol (Panadol), ibuprofen (Nurofen) and acetylsalicylic acid (Aspirin). In addition to the antipyretic, these drugs also have an anti-inflammatory effect, which helps well against the pain in the head that is characteristic of sinusitis. The doctor's prescriptions should be strictly followed, since all these funds have contraindications and side effects.
Elimination of fever and pain.Doctors recommend knocking down body temperature after reaching 38.5 degrees, with the exception of patients with hyperthermia intolerance. The most common drugs are based on paracetamol (Panadol), ibuprofen (Nurofen) and acetylsalicylic acid (Aspirin). In addition to the antipyretic, these drugs also have an anti-inflammatory effect, which helps well against the pain in the head that is characteristic of sinusitis. The doctor's prescriptions should be strictly followed, since all these funds have contraindications and side effects.- Removal of edema of tissues of the nasal cavity and accessory chambers. This can be done in two ways. Drops and sprays injected into the nasal passages have a local vasoconstrictor effect. The choice in pharmacies is very large, the action time varies from 4 hours (Tizin, Naphtizin), to 8 hours (Otrivin, Galazolin) and even up to 12 hours (Rinazolin, Nazivin). In this case, it is imperative to take into account the fact that drops cannot be used for more than 7 days, since nosebleeds may develop, and with longer use, the mucous membrane may atrophy. Combined drugs with antihistamine, anti-inflammatory and antipyretic effects, usually used for acute respiratory viral infections and influenza (TeraFlu, Coldrex), give a general anti-edema effect, including on the lower respiratory tract.
- Cleansing and disinfection of the nasal passages with antiseptic agents. They can be injected into the nose (Protargol, Polydexa, Isofra) or used to flush cavities (Dioxidin).
- In some cases, the most effective use of corticosteroids in the form of sprays (Avamis, Nazonex), which are effective for allergic sinusitis, and also have a positive effect on the immune system.
In our case, a special place should be given to the use of mucolytics - drugs that thin mucus and facilitate its evacuation from the air pockets, and also help to cough up phlegm from the throat with an unproductive cough. Flavamed, Fluditek, Mukodin, Ambroxol, Sinupret, Mukaltin - this is just a small list of products that can be purchased in pharmacies. The doctor will prescribe medication depending on the type of cough (dry or wet), as well as on the presence of contraindications (for example, pregnancy or childhood).
Other ways to stop coughing
In addition to medications, there are a number of methods to eliminate the irritating factor in the throat. They differ radically from each other.
If the patient's condition is severe, then the most effective way is to puncture the maxillary sinus. The puncture is carried out in a hospital setting.
 The inner (medial) wall of the sinus is pierced through the nose with a special needle at its thinnest point. A syringe is attached to the needle, a saline solution is introduced into the chamber, which dilutes the exudate, after which the contents are sucked off.
The inner (medial) wall of the sinus is pierced through the nose with a special needle at its thinnest point. A syringe is attached to the needle, a saline solution is introduced into the chamber, which dilutes the exudate, after which the contents are sucked off.
Then a solution of medicinal substances is poured into the accessory pocket, most often a saline solution with an antibiotic, for example, Tsiprofan.
Puncture helps to dramatically improve the patient's condition, quickly relieve the most severe and unpleasant symptoms, including relieving sore throat.
If necessary, the procedure can be repeated the next day. Despite the general fear of this operation, it is simple and very effective for an experienced doctor.
To prevent mucus from stagnating and flowing down the throat, you should regularly drain the secret. There are several methods for rinsing the nasal cavity and sinuses:
- Repeated rinsing at home using a mini syringe, a special kettle or a regular syringe without a needle. The solution is prepared using sea or table salt, sea water, saline solutions, hydrogen peroxide, soda, antiseptics, herbal decoctions. The patient tilts his head to one side, the liquid is supplied under a slight pressure into one nostril, and then flows out with pus from the other nostril.
- Use for washing the YAMIK sinus catheter. The manipulation is carried out in a hospital under local anesthesia. This technique can be used for children from 5 years of age. A special design of two balloons is inserted into the nose, connected by a flexible metal tube. The posterior balloon overlaps the nasopharynx, and the anterior balloon overlaps the nasal passage. A syringe is pumped out of this chamber limited by balloons, the resulting vacuum opens the swollen anastomosis and forces the exudate to flow out. The mucus is sucked off with a syringe, after which the accessory chamber is washed with medicinal solutions. With this technique, almost the entire volume of the solution passes through the affected sinus and the swallowing of the infected fluid is excluded.
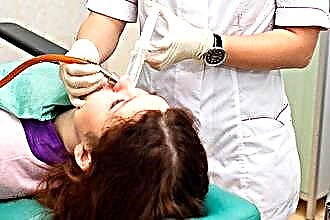 Washing with an aspirator-suction ("cuckoo"). The aspirator creates a reduced pressure in one side of the nose, which promotes the circulation of fluid in the air pocket. Through the other nostril, the doctor pours in a solution, which, after passing through the sinus, together with purulent exudate, is sucked off by an aspirator.
Washing with an aspirator-suction ("cuckoo"). The aspirator creates a reduced pressure in one side of the nose, which promotes the circulation of fluid in the air pocket. Through the other nostril, the doctor pours in a solution, which, after passing through the sinus, together with purulent exudate, is sucked off by an aspirator.
With the help of various physiological procedures, the effectiveness of drugs can be increased. As a rule, physiotherapy is prescribed in the period after the removal of acute symptoms of the disease. They are widely used in practice:
- exposure to ultra-high frequencies;
- electrophoresis with drugs;
- laser therapy.
Elimination of cough with sinusitis at home
Traditional medicine offers a wide range of remedies that can improve the flow of mucus from the nose and soothe an irritated throat:
- Traditional steam inhalation. The most common way is to boil potatoes in their uniforms, drain the water, bend over the pan and, covering your head with a towel, breathe in hot steam for a few minutes. You can be more creative and add aromatic oils of pine, cypress or cedar to hot water before inhalation. It will also help boost immunity.
- Use for inhalation of herbal decoctions. Method of preparation: 5 tablespoons of chopped herbs are poured with one liter of boiling water, then boiled over low heat for half an hour. In a few minutes you can start inhaling. Plants such as sage, St. John's wort, plantain, chamomile, linden blossom are well suited for this. Breathing steam with sinusitis with a cough can be through the nose and mouth.
- Milk-based drinks. Honey is added to warm cow's milk and mixed thoroughly. You can also mix milk and butter (50 g butter per glass of milk). Methods that have been tested are also milk with figs or soda. It is useful to drink these mixtures during the day and, especially, at night to relieve dry cough attacks and improve sleep.

 Elimination of fever and pain.Doctors recommend knocking down body temperature after reaching 38.5 degrees, with the exception of patients with hyperthermia intolerance. The most common drugs are based on paracetamol (Panadol), ibuprofen (Nurofen) and acetylsalicylic acid (Aspirin). In addition to the antipyretic, these drugs also have an anti-inflammatory effect, which helps well against the pain in the head that is characteristic of sinusitis. The doctor's prescriptions should be strictly followed, since all these funds have contraindications and side effects.
Elimination of fever and pain.Doctors recommend knocking down body temperature after reaching 38.5 degrees, with the exception of patients with hyperthermia intolerance. The most common drugs are based on paracetamol (Panadol), ibuprofen (Nurofen) and acetylsalicylic acid (Aspirin). In addition to the antipyretic, these drugs also have an anti-inflammatory effect, which helps well against the pain in the head that is characteristic of sinusitis. The doctor's prescriptions should be strictly followed, since all these funds have contraindications and side effects. Washing with an aspirator-suction ("cuckoo"). The aspirator creates a reduced pressure in one side of the nose, which promotes the circulation of fluid in the air pocket. Through the other nostril, the doctor pours in a solution, which, after passing through the sinus, together with purulent exudate, is sucked off by an aspirator.
Washing with an aspirator-suction ("cuckoo"). The aspirator creates a reduced pressure in one side of the nose, which promotes the circulation of fluid in the air pocket. Through the other nostril, the doctor pours in a solution, which, after passing through the sinus, together with purulent exudate, is sucked off by an aspirator.