Purulent sinusitis is a disease of the maxillary sinuses, in which their mucous membrane becomes inflamed. It proceeds in an acute or chronic form. Pus, the discharge of which is one of the main symptoms of this disease, is a protein-rich fluid. Since there are bacteria in the pus that provoked inflammation, it can be argued that this ailment is of bacterial origin. And chronic purulent sinusitis is usually the result of unsuccessful self-treatment of the acute form of the disease.
The danger of this disease is the risk of developing serious complications affecting the brain, vestibular apparatus and eyes. You can avoid such a terrible prospect if you recognize the symptoms of purulent sinusitis in time, consult a doctor and undergo a course of complex therapy.
Why is it developing
 The acute form of purulent sinusitis most often occurs when staphylococcus, streptococcus or Escherichia coli enters the maxillary sinus. In children, this disease is usually provoked by mycoplasmas or chlamydia. These pathogenic microorganisms begin to multiply actively when:
The acute form of purulent sinusitis most often occurs when staphylococcus, streptococcus or Escherichia coli enters the maxillary sinus. In children, this disease is usually provoked by mycoplasmas or chlamydia. These pathogenic microorganisms begin to multiply actively when:
- congenital abnormal structure of the internal septum in the nose;
- curvature of the septum inside the nose as a result of injury;
- polyposis of the nasal cavity;
- adenoids in children;
- rhinitis of allergic origin;
- illiterate and late treatment of caries (odontogenic sinusitis);
- chronic diseases of the nasal cavity.
It should be noted that there is always a small amount of microbes in the nose, which get there along with the inhaled air. If the state of the body is in perfect order, and the immune system is working properly, harmful organisms do not have the opportunity to develop and multiply.
Activation of pathogenic microflora in the nose occurs under the above-mentioned aggravating circumstances and weakening of the immune system. An infection penetrates into the maxillary sinuses, as a result of which a liquid saturated with dead leukocytes and bacteria begins to accumulate in them. Thus, sinusitis and pus appear, by which one can suspect the development of this ailment. The mucous membrane lining the cavity of the maxillary sinuses begins to swell and increase in size. As a result, the anastomosis located between the cavities is closed. As a result, the function of drainage and ventilation is impaired, extremely unfavorable stagnation occurs.
How does it manifest
Purulent sinusitis does not arise, as they say, out of the blue. As a rule, a person first suffers from a catarrhal type of this disease. And when a bacterial infection joins the catarrhal sinusitis, the symptoms intensify, which usually manifest the acute form of this ailment.
Purulent sinusitis and the symptoms of this disease are easy to find out. Its main feature is the appearance of bursting pain in the area of the inflamed sinus.

If the development of the inflammatory process continues, the intensity of pain increases. In this case, the pain is no longer concentrated in one zone, but spreads over a wider space. In some cases, there is a headache that gets worse if you tilt your head. Sometimes it gives off to the upper jaw - then it becomes very problematic to chew.
Part of the face above the inflamed maxillary sinus may swell and slightly redden. If, on the right and on the left side of the nose above the cheeks, significant swelling appears, as well as swollen eyelids, the likelihood of developing purulent sinusitis of the bilateral type is high.
The swollen mucous membrane lining the nasal cavities leads to a complication or even complete absence of full breathing through the nose. Moreover, the nose can be blocked not only from one side, but also from both sides at once (they distinguish between unilateral or bilateral sinusitis). The result is a significant deterioration in the ability to distinguish between odors.
The discharge, periodically appearing from the nose with purulent sinusitis, takes on a yellowish or greenish color and is accompanied by an unpleasant odor. This thick and offensive substance gradually fills the maxillary sinuses. Often it is changes in the nature of nasal discharge that indicate the development of this particular type of sinusitis.
Along with the already mentioned symptoms, signs of intoxication of the body are growing. The temperature rises significantly - it can reach 39-40 ° C. General weakness, chills and sweating join it.
Diagnostic methods
To correctly diagnose purulent sinusitis, not only clinical, but also paraclinical methods are traditionally used. Only after completing the collection of the necessary information, the doctor can establish an accurate diagnosis.
 First of all, the doctor asks the patient in detail about his complaints. Points such as headache, nasal congestion, maxillary sinus pain, voice changes, and chronic cough are important. Then the specialist carefully examines the patient for the presence of reflex dilatation of the blood vessels of the skin under the eyes.
First of all, the doctor asks the patient in detail about his complaints. Points such as headache, nasal congestion, maxillary sinus pain, voice changes, and chronic cough are important. Then the specialist carefully examines the patient for the presence of reflex dilatation of the blood vessels of the skin under the eyes.
Particular attention is paid to the examination of the inner surface of the nasal cavity. It can be swollen, inflamed, and contain traces of recurrent pus.
Today, purulent sinusitis is most effectively diagnosed with an X-ray. This method allows a good view of the paranasal sinuses. On the resulting X-ray, sinusitis looks like a small white spot on the maxillary sinus. If you look at a picture of a healthy person for comparison, you can see that the color of the sinuses will be comparable in intensity to the eye sockets. Despite the fact that this diagnostic method is the most convenient and accurate, there are some limitations in its appointment. For example, pictures of a child with rhinitis and sinusitis will be identical.
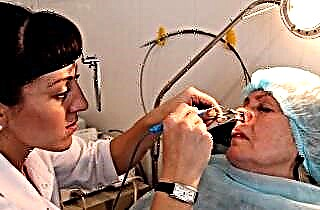
The most informative diagnostic method is puncture. This procedure is carried out using a small needle. The doctor should pierce the wall of the maxillary sinus with it and suck out pus from there, if it is there.
Puncture is an extremely simple measure. If it is done by an experienced specialist, one can hope for almost complete painlessness. However, it should be borne in mind that this procedure is done quite rarely and only when other methods are powerless.
The fact is that after it, emphysema of the cheeks (when air enters the soft tissue) and an abscess may appear, blood vessels become clogged. True, if the doctor conducts the event competently and thoroughly flushes the inflamed area, the risk of such complications is minimal.
How the acute form differs from the chronic
Purulent sinusitis, like many inflammatory diseases, can occur in 2 forms - acute or chronic. The acute form is characterized by a sharp and very active beginning.
Chronic is characterized by a sluggish course and blurred symptoms. As for the clinical picture, we emphasize that it also has differences in both forms.
| Symptoms | Acute form | Chronic form |
|---|---|---|
| General well-being | Chills, weakness, increased sweating. | Lethargy and general malaise. |
| Body temperature | High. | Subfebrile. |
| Head | Very intense pain in the frontal area with an increase and a feeling of pressure in the area of the bridge of the nose when clenching the teeth and tilting the head in different directions. | Incessant pain of moderate intensity. |
| Nose | Swelling of the mucous membrane and significant nasal congestion, accompanied by pain, if you press on the maxillary sinus area. | The nose is obstructed constantly, breathing through the nose is difficult. |
| Nasal discharge | With an admixture of pus, as well as mucus and pus. The volume of discharge is average. | Mucous membranes, as well as with an admixture of pus during an exacerbation. The volume of discharge is significant. |
Nasal discharge in both forms of the disease can be greenish-yellow or brown. Their passage is complicated. In addition, unpleasant pressure is often felt in the area of the bridge of the nose, and the headache, annoying with sinusitis, is pressing. In some cases, sinus inflammation is accompanied by a toothache.
With regard to external signs, both forms are characterized by swelling of the eyelids and slight swelling in the area of the bridge of the nose. Often, the swelling and congestion are so severe that a person has to breathe exclusively through the mouth.
Odontogenic purulent sinusitis
The so-called odontogenic sinusitis stands apart among the different types of purulent sinusitis. Why apart? Because the reason for its development lies not in inflammation of the mucous membrane, which is lined with the maxillary sinuses or the nasal cavity, but in a dental disease. If the upper jaw is affected by any purulent-inflammatory process, it is quite capable of spreading to the paranasal sinus located in the immediate vicinity. This leads to odontogenic inflammation.

The main symptom of an odontogenic variety of purulent sinusitis is considered to be a toothache that occurs only on one side. In this case, all other symptoms indicating inflammation of the paranasal sinuses are also present.
Two doctors should treat this disease at once - a dentist and an otolaryngologist. If you do not first solve the problem of a dental nature, then the inflammatory process will not disappear anywhere. It is for this reason that a visit to the dentist is required first.
The prognosis for the odontogenic variety of purulent sinusitis is considered very favorable. As soon as the problem teeth are healed or removed, the inflammation will stop. As a rule, a standard therapeutic course is enough to finally defeat the disease.
Bilateral sinusitis
If, in parallel with the inflammation of the mucous membrane, which is lined with the maxillary sinuses, there are still any complications, there is a high risk of developing bilateral sinusitis. This ailment is usually acute. If the treatment is ineffective, the form of the disease becomes chronic.
In many patients with diagnosed purulent bilateral sinusitis, doctors observed:
 significant swelling in the place where the sinuses are;
significant swelling in the place where the sinuses are;- copious discharge of mucus from the nasal cavity;
- nasal congestion and loss of smell;
- lacrimation;
- high body temperature;
- signs of body intoxication;
- lethargy, apathy, insomnia.
Bilateral sinusitis is extremely rare. This disease is characterized by a rather pronounced symptomatology. It almost always proceeds in a severe form.
It can be provoked by almost any ailment of an infectious or inflammatory nature. For differential diagnosis, the doctor palpates the area of the paranasal sinuses. The diagnosis is confirmed if the patient experiences pain.
Bilateral sinusitis is treated with a complex method - drug therapy in combination with physiotherapy procedures.
And finally
The best and easiest way to treat the acute form of purulent sinusitis. However, if you ignore its symptoms or self-medicate at random, it becomes chronic. The latter is dangerous in that it is capable of provoking the development of rather serious complications.
For the above reason, it is highly undesirable to self-medicate with sinusitis, take any medications without the supervision of a doctor, or expect that inflammation and pus will disappear on their own. Such actions can thoroughly harm yourself.
To successfully cure purulent sinusitis, it is necessary to allow mucus and pus to flow freely and unhindered from the maxillary sinuses. For this, patients, as a rule, are prescribed medications that eliminate swelling of the nasal mucosa. By the way, if drug treatment is started on time, you can quickly get rid of this disease and at the same time avoid the prospect of having a puncture.

 significant swelling in the place where the sinuses are;
significant swelling in the place where the sinuses are;