In the first 48 hours after the birth of the baby, the neonatologist examines the baby, performs auscultation of the lungs and valves. In some children, murmurs are found, in most cases functional, that is, not provoked by a serious organic lesion of the valve apparatus or congenital defects. However, sometimes a heart murmur in a newborn is pathological and indicates a congenital disease.
In older children, swirls may appear after an illness. Modern diagnostic methods make it possible to identify the cause of cardiac murmurs from the first day of a child's life. For this, a cardiologist or pediatrician conducts a full diagnostic examination and, if pathological noise is detected, prescribes the necessary treatment.
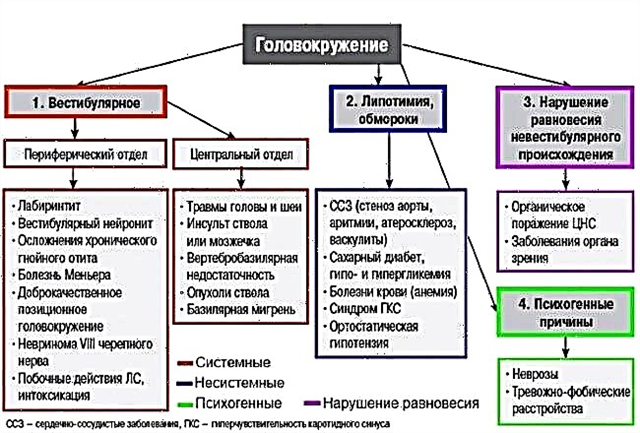
What is a heart murmur and what is it like
Thanks to the work of the cardiovascular system, tissues and organs receive the necessary nutrients and oxygen. After birth, a significant restructuring of blood circulation in the pulmonary vessels occurs in the child's body, the dominant of the right ventricle changes to the left, physiological closure of the ductus arteriosus is observed, the pressure in the pulmonary trunk increases to facilitate the work of the left ventricle. Such changes cause cardiac murmurs.
During the examination, the doctor conducts auscultation using a phonendoscope, alternately listening to the heart valves:
- mitral;
- aortic;
- pulmonary valve;
- tricuspid valve.
The auscultation method helps to assess the frequency and rhythm of tones, their melody and timbre.
Causes of occurrence
The most common sources of heart murmurs in a child are associated with impaired blood flow and turbulence in the supravalvular aorta, pulmonary trunk, or organ cavities. The causes of this hemodynamic disorder are a defect in the valve apparatus or septum, vascular aneurysm, a decrease in blood viscosity against the background of anemia, and such cases:
- if the baby is premature, the source of the noise is an insufficiently formed heart, incomplete closure of the aortic duct after birth;
- when a soft systolic murmur is heard in the first three days after birth, this indicates anatomical obstruction of the ventricular outlets, which requires daily monitoring in dynamics;
- mixed systolic-diastolic murmur more often occurs when the aortic duct is incompletely infected, which closes at the end of the restructuring from the fetal blood flow after birth;
- the most common cause of heart murmur in a newborn is an open aortic duct (vortexes are quiet, blowing, more audible between II and I heart sounds);
- listening to noises in a child during systole is convenient on the third or fourth day with cardiomyopathy and impaired transitional circulation, the formation of a pathological shunt from the right heart to the left and vice versa;
- the main symptom of the pathology of the organs of the cardiovascular system and congenital valve defects is hemodynamic disturbance, cyanosis (blue skin), arterial hypoxemia and a decrease in saturation (blood oxygen saturation) of less than 75%;
- in older children, the source of noise is a past illness, colds, tonsillitis or ARVI. As a result, the inflammatory process and bacterial culture provoke damage to the heart valves, endocarditis (inflammation of the endocardium);
- if a child is over five years old and a noise is heard during auscultation, it is often the cause of an anomaly of the left ventricle, an accessory chord, which can only be detected by ultrasound of the heart. When there is no hemodynamic disorder, treatment is not required.
Unlike pathological murmur, functional murmur is always heard during systole, it is with less intensity. In newborns, auscultation determines a greater spread of vortexes beyond the boundaries of the heart. If the child does not have a rapid heartbeat, there is no cyanosis and signs of heart failure, then such a noise is not dangerous, but requires observation. It is enough to have an assessment of functional noises in the dynamics of time, registration of cardiogram data, ultrasound of the heart.
Correct actions
The basis for the prevention of heart disease in children is compliance with regular medical examinations by a neonatologist and pediatrician according to the algorithm:
- The primary examination is carried out by a neonatologist at the maternity hospital, when cardiac activity is assessed with the help of auscultation.
- Screening for the diagnosis of congenital heart defects is done if noises are observed in the organ.
- Based on the data of saturation and ultrasound of the heart, the doctor confirms or removes the diagnosis.
- After discharge from the hospital, the child is supervised at home for up to a month by a general practitioner. Normally, after the third or fourth week, the venous duct closes and the circulatory system begins to function fully. A physical examination helps to identify the slightest deviation from the norm, diagnosing noise in newborns.
- Especially important is the infant's age (infant up to a year), when the complete restructuring of blood circulation is completed and the doctor draws a conclusion about the nature of the noise.
- Cyanosis of the skin is the main symptom of hemodynamic disturbances. In combination with severe weakness, dizziness and low hemoglobin, these are indications for examination.
- In addition to auscultation, all children with signs of heart murmurs should be referred for phonocardiography, echocardiography, ultrasound of the heart and great vessels.
- Refusal to examine and treat a child with heart murmurs leads to serious hemodynamic disturbances, heart failure. Regular examinations with a pediatrician help prevent the development of organ pathology.
Conclusions
Most of the heart murmurs are functional, but without proper detailing of complaints and observation, it is impossible to determine the nature of the blood flow disturbance. Neonatologists and cardiologists examine and treat newborn babies for up to 28 days, and later - pediatricians.