When the inflammation of the lining of the sinuses lasts more than eight weeks, doctors diagnose chronic maxillary sinusitis. It usually occurs as a consequence of acute sinusitis caused by a bacterial or viral infection. According to statistics, half of the diagnosed sinusitis is of this form. The disease proceeds in waves: after the exacerbation stage, remission occurs, and then exacerbation again. If left untreated, inflammation engulfs nearby organs and causes complications.
Species and pathogens
 The disease can develop only on one side, and it can simultaneously cover two sinuses. Each of these cases is characterized by congestion from inflammation, shortness of breath, pain.
The disease can develop only on one side, and it can simultaneously cover two sinuses. Each of these cases is characterized by congestion from inflammation, shortness of breath, pain.
By the nature of the course of sinusitis, its occurrence, there are:
- fibrous;
- allergic;
- cystic;
- purulent;
- polypous;
- catarrhal.
Most often, the causative agent of the disease is Haemophilus influenzae or streptococci, but mold, yeast-like fungi, anaerobic bacteria, and viruses can also cause it. In addition, these microorganisms can form complex compounds, which makes it difficult to find the right treatment.
Causes of the disease
Chronic sinusitis develops as a result of prolonged exposure to the sinus mucosa of pathogenic organisms: one or their conglomerate. Inflammation is aggravated by anatomical defects of the respiratory organ, which can be congenital or acquired. The most common occurrence is a deviated nasal septum or polyps.
Also, the infection can penetrate the lower sinus wall because it is too thin. The situation occurs due to inflammation of the gums, dental caries and other diseases of the oral cavity. In such cases, they speak of chronic odontogenic sinusitis.
The following factors contribute to the development of the disease:
- tendency to allergic reactions;
- cold weather;
- various diseases that weaken the immune system;
- hypovitaminosis;
- bad habits;
- barotrauma;
- regular inflammation of the upper respiratory tract.
Features of the course of the disease
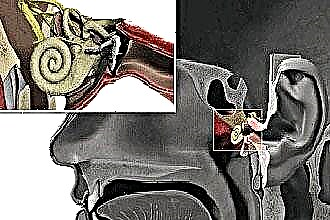
 To understand what chronic sinusitis is, and how it proceeds, you need to navigate a little in the structure of the human skull. So, it has four types of paranasal sinuses: maxillary (located behind the cheekbones), wedge-shaped (which are behind the eyes), ethmoid (on the bridge of the nose) and frontal. They perform the function of cleansing, moisturizing and heating the air that comes from the nose. In a healthy person, they are filled only with air. The patient is filled with mucus, which is separated from the inflamed walls. This mucus flows through small channels into the nose, but if the sinuses are infected and swollen, the channels become blocked and the mucus stagnates in them.
To understand what chronic sinusitis is, and how it proceeds, you need to navigate a little in the structure of the human skull. So, it has four types of paranasal sinuses: maxillary (located behind the cheekbones), wedge-shaped (which are behind the eyes), ethmoid (on the bridge of the nose) and frontal. They perform the function of cleansing, moisturizing and heating the air that comes from the nose. In a healthy person, they are filled only with air. The patient is filled with mucus, which is separated from the inflamed walls. This mucus flows through small channels into the nose, but if the sinuses are infected and swollen, the channels become blocked and the mucus stagnates in them.
There are several forms of chronic sinusitis. If there is a discharge of mucus, which has a viscous consistency, we are talking about a productive form of sinusitis.
Purulent discharge of medium intensity speaks, respectively, of a purulent form. If the discharge is watery, sinusitis is exudative. Regardless of the form in which the disease proceeds, it is always accompanied by nasal congestion.
Symptoms of the disease
If we are talking about a disease at the stage of remission, then the characteristic signs are not pronounced. Patients complain about:
 slight swelling of the face in the sinus area;
slight swelling of the face in the sinus area;- sore throat, especially when swallowing, often with pain;
- loss of smell against the background of nasal congestion;
- severe headache, and its source is difficult to determine;
- fatigue, weakness.
Exacerbation of sinusitis is characterized by a deterioration in the patient's well-being. The body temperature sometimes rises to 37.7 ° C, the headache worsens, especially when a person leans forward, a feeling of heaviness on the face constantly pursues.
The pain can be bursting, as at this time the sinuses overflow with mucus and press on its walls. Sore throat and coughing remains. In addition to swelling under the nose, swelling of the eyelids appears, and sometimes conjunctivitis develops.
Diagnostics
To establish sinusitis most accurately helps an X-ray and computed tomography. It clearly shows whether the sinus is covered by an inflammatory process, whether there are polyps or cysts in the maxillary sinus.
However, these methods are not used to diagnose the disease in children and pregnant women. For them, the diaphanoscopy method is used, which is carried out using a Hering lamp. Diagnostics is carried out in a dark room, when a closed mouth is illuminated from the inside with a special small lamp. If there is sinusitis, light will not come through.
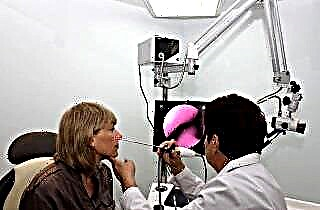
Endoscopy is also performed. Then an optical probe is inserted into the sinus and the sinus is examined on the image displayed on the monitor.
To carry out an accurate diagnosis, a sinus puncture can be used, which is carried out with a Kulikovsky needle. The puncture is done by inserting a needle through the nose into the sinus wall. After pumping out the pus, the sinus is washed, and the discharge is sent for research.
For example, if the secretion in a special solution darkens, we are talking about the fungal form of the disease. Then the use of antibiotics is not justified, antifungal agents are prescribed.
To complete the picture of the diagnosis, it is advisable to undergo an examination by a neuropathologist, maxillofacial surgeon, and dentist.
Treatment of chronic sinusitis
 The danger of the chronic form is that it is impossible to get rid of the disease completely and forever. However, the treatment is varied, depending on the stage of the course of the disease. So, with an exacerbation, therapeutic measures are aimed at destroying pathological microorganisms that caused inflammation, as well as normalizing breathing through the nose. For this, the sinuses are sanitized, which prevents the development of colonies of microorganisms in the sinus.
The danger of the chronic form is that it is impossible to get rid of the disease completely and forever. However, the treatment is varied, depending on the stage of the course of the disease. So, with an exacerbation, therapeutic measures are aimed at destroying pathological microorganisms that caused inflammation, as well as normalizing breathing through the nose. For this, the sinuses are sanitized, which prevents the development of colonies of microorganisms in the sinus.
Washing is carried out with special disinfectant solutions, for example, furacilin, dioxidin. After the washing procedure, enzyme preparations and antibiotics, such as Lidaza, are injected into the sinuses.
At the same time, antibacterial drugs of the fluoroquinolone or cephalosporin group are taken. Prescribed drugs that act directly on the site of inflammation. For example, antibacterial "Bioparox".
 Sprays or drops are also needed to narrow blood vessels, which relieve swelling on the mucous membrane. But you should always take into account that these drugs are taken in short courses so as not to become addictive.
Sprays or drops are also needed to narrow blood vessels, which relieve swelling on the mucous membrane. But you should always take into account that these drugs are taken in short courses so as not to become addictive.
Sometimes combined drugs are used to relieve several symptoms of the disease at the same time. For example, "Rinofluimucil" has mucolytic and decongestant effects.
To support the body weakened by the disease, especially during the period of activation of viral infections, it is recommended to take immunocorrectors. The choice of a specific medicine and course of treatment should be left to the doctor.
If the allergic nature of sinusitis is established, antihistamines are prescribed. Sometimes the administration of topical hormonal drugs is indicated. But, again, the specific choice remains with the doctor.
Sometimes an exacerbation of a chronic disease requires urgent intervention by a surgeon. Then the doctor prescribes a sinus puncture in order to remove pus, restore the patency of the sinus, and inject antibacterial drugs into it.This greatly improves the patient's condition, but one should not think that one puncture will be enough for the sinusitis to go away forever. In fact, if you do not engage in treatment, this procedure will have to be resorted to more than once.
The puncture itself is not always safe. Due to the anatomical features, severe bleeding may appear, there is a high risk of leakage of fluid that surrounds the spinal cord or brain. Such intervention can lead to partial loss of vision, the development of meningitis, and sometimes even death.
The period of remission is characterized by a sluggish and mild course of the disease, therefore, they are limited by methods of physiotherapy. Most often, UHF, phonophoresis with cortisone, electrophoresis with lidase, ultrasound are used on the sinus area.
Additionally, magnetotherapy is prescribed to the pharyngeal region. Treatment with the microclimate in salt caves - speleotherapy - is useful.
What is the danger
 Sinusitis in itself does not pose a danger to life, except for those cases when the maxillary pause is very close to the brain. This anatomical feature, in the absence of adequate treatment, can lead to meningitis or frontal sinusitis, which are already really life-threatening.
Sinusitis in itself does not pose a danger to life, except for those cases when the maxillary pause is very close to the brain. This anatomical feature, in the absence of adequate treatment, can lead to meningitis or frontal sinusitis, which are already really life-threatening.
Also, an advanced form of the disease, which has not been properly treated, spreads the infection to neighboring organs. First of all, on the eye socket, causing visual impairment. Often in such cases, the patient's eyes bulge, he is pursued by severe headaches in the eye socket.
Complications can go to the ears, provoking otitis media. If the bottom wall of the sinus is too thin, the inflammation spreads into the mouth, and the patient is at risk of losing teeth.
Disease prevention
Sinusitis, even with a chronic form, can cause various complications:
 osteomyelitis of the upper jaw and frontal bone;
osteomyelitis of the upper jaw and frontal bone;- cysts;
- brain diseases;
- diseases of the organs of vision, hearing and others.
Knowing how dangerous sinusitis is, it is worth thinking about the prevention of the disease. It consists, first of all, in adequate treatment in the acute stage. Since it is almost impossible to completely cure chronic sinusitis, the stage of remission also requires proper treatment.
At this time, it is recommended to strenuously guard against possible infectious diseases: not to be in crowded places, to observe personal hygiene. Timely cleanse and treat foci of chronic infection, especially in the throat and nose.
In the case of acute respiratory viral infections or colds, it is necessary to carry out a comprehensive full treatment until the disease completely goes away. The ideal means of prevention during such periods is vaccination against influenza and various infections.
If possible, you should correct the defects of the nasal septum, remove polyps, if any. And, of course, you need to give up bad habits, balance your diet, include regular physical activity in your life, monitor your sleep schedule, and proper nutrition. Walk in the fresh air often and wash your nose and throat with a light saline solution.
If sinusitis is allergic in nature, it is important to avoid contact with allergens, during the flowering period, start a course of antihistamines on time. The room in which a person with chronic sinusitis is located should have a normal level of humidity.
The body also needs the proper level of hydration. Drink at least six glasses of pure water a day. This normalizes the functioning of the immune system, helps the body to remove harmful substances, and improves metabolism. Plus, getting enough water helps to avoid thickening of the mucus in your sinuses.
 Chronic sinusitis can worsen with frequent flights. With a pressure drop during takeoff and landing, patients complain of discomfort in the middle ear and sinuses. To avoid this, it is recommended to use special inhalers, decongestant nasal drops before the flight.
Chronic sinusitis can worsen with frequent flights. With a pressure drop during takeoff and landing, patients complain of discomfort in the middle ear and sinuses. To avoid this, it is recommended to use special inhalers, decongestant nasal drops before the flight.
The nasal mucosa can become irritated in the pool when it comes into contact with chlorinated water. By the way, such water can cause other complications on ENT organs. Therefore, people with chronic sinusitis are advised to wear special earplugs when exercising in the pool.
You should not engage in diving, snorkeling and other activities related to swimming and diving at the stage of an exacerbation of the disease. The ingress and stagnation of water in the nose and ears, pressure drops can lead to the active development of infection.

 slight swelling of the face in the sinus area;
slight swelling of the face in the sinus area; osteomyelitis of the upper jaw and frontal bone;
osteomyelitis of the upper jaw and frontal bone;