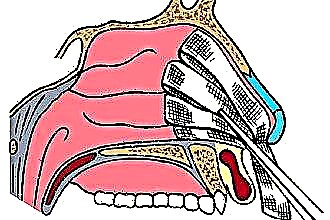
Fungi are literally everywhere, as they are a natural part of the environment. In the nasal cavity of a healthy person, some types of fungi are found. As a rule, they are inactive and do not pose a threat to health. However, under unfavorable circumstances, fungi are activated and begin to multiply rapidly, populating the paranasal sinuses. Thus, fungal sinusitis occurs - one- or two-sided inflammation of the maxillary sinuses, located above the upper jaw.
How to recognize
 Fungal sinusitis is characterized by atypical symptoms. And it arises for completely different reasons than it differs from other varieties of this disease. Accordingly, the treatment of fungal sinusitis requires the use of special therapeutic methods.
Fungal sinusitis is characterized by atypical symptoms. And it arises for completely different reasons than it differs from other varieties of this disease. Accordingly, the treatment of fungal sinusitis requires the use of special therapeutic methods.
The course of fungal sinusitis can be described as rather sluggish. The disease almost always becomes chronic. The rapidly developing invasive type of such ailment is extremely rare. It can appear only with a sharp decrease in immunity. Its main symptoms are severe headache (the whole face can also hurt), acute fever, vision problems, discharge from the nasal passages mixed with blood. If you do not start adequate treatment immediately, the risk of developing superinfection increases significantly. As a result, the person falls into a coma. The lethal outcome from numerous complications occurs in this case rather quickly.
Fortunately, medicine today is at such a level that such a scenario is a huge rarity. In the overwhelming majority of cases, the course of the disease is more or less benign.
With fungal sinusitis, the symptoms are often very blurred. Pronounced signs of the disease do not appear soon.
So, the fungal origin of sinusitis can be recognized by:
- discharge from the nasal cavities of white, white-yellow, brown or even black, jelly-like or curdled consistency;
 streaks of blood in the discharge;
streaks of blood in the discharge;- stench emanating from the nasal passages;
- a bluish tint of the mucous membrane lining the inner nasal cavity;
- swelling of the nose;
- severe complication of breathing through the nose;
- persistent nasal congestion;
- pain in the area of the paranasal sinuses;
- recurring headache;
- toothache concentrated in the upper jaw;
- a feeling of fullness in the maxillary sinuses;
- loss of the ability to smell;
- the occurrence of polyps (a sign indicating an allergic form of the disease);
- swelling of the face only on one or both sides at once, displacement of the eyeball.
If the disease is of an allergic origin, there are almost always other symptoms that indicate this. A person may suffer, for example, from allergic rhinitis, eczema, hives, and so on.
Operative treatment
Treatment of sinusitis, which is of fungal origin, is quite long. After all, first of all, you need to eliminate the main cause of the disease - a fungal infection. And this is extremely difficult to do. Antifungal medications often do not help.
It is also impossible to start the disease - there is a very real risk to life. Therefore, doctors recommend surgical intervention as the only correct and most effective method of treatment.
 Non-invasive forms of the disease are treated only with surgery. The specialist assesses how much the fungus has spread and makes a choice in favor of endoscopic intervention or radical open-type surgery - sinusitis.
Non-invasive forms of the disease are treated only with surgery. The specialist assesses how much the fungus has spread and makes a choice in favor of endoscopic intervention or radical open-type surgery - sinusitis.
Surgical intervention for such sinusitis is performed under general anesthesia. The operation consists in opening one or two maxillary sinuses. Its purpose is to eliminate polyps and any other internal formations in which fungi usually live. Today, such operations are mainly carried out using a sparing "endoscopic" technology. It makes it possible to speed up the onset of recovery and improve the quality of rehabilitation after the intervention.
Invasive forms of this disease are also treated with surgery. Its purpose is to cleanse the paranasal sinuses from the accumulated fungal and necrotic masses.
During the rehabilitation period after surgery, antifungal drug therapy is necessarily prescribed. For this, ketoconazole, amphotericin B and similar drugs are most often used.
Drug therapy
If fungal sinusitis has a non-invasive form, it can be treated without using systemic drugs. To restore general immunity and improve the paranasal sinuses, the patient needs:
- Take immunomodulators. They are needed to increase functionality and improve immune function. It is permissible to take not only synthetic, but also herbal remedies ("Taktivin", "Immunal", "Immunoriks", preparations based on echinacea, and so on). This also includes drugs that stimulate the body's production of interferons - "Arbidol" and "Anaferon".
 Take restorative medicines and so-called adaptogens - tinctures of medicinal plants such as leuzea, aralia, rose hips, ginseng, eleutherococcus and so on.
Take restorative medicines and so-called adaptogens - tinctures of medicinal plants such as leuzea, aralia, rose hips, ginseng, eleutherococcus and so on.- Irrigate the nasal passages with nasal glucocorticosteroids (Avamis, Fliksonase, Nasonex). Thus, the inflammatory process that develops in the maxillary sinuses is suppressed, and the allergic type of fungal sinusitis is treated.
- Introduce antifungal drugs (aerosols, gels, drops, ointments) based on nystatin, fluconazole, ketoconazole, terbinafine and similar active substances into the nasal passages.
- Take antihistamines to suppress the allergic reaction (Zyrtec, Desloratadin, Loratadin).
- Treat the nasal cavities with quinosol solution and other antiseptic agents.
It is quite difficult to treat such sinusitis. As a rule, one therapeutic course is not enough for the onset of complete recovery.
A prerequisite is that all possible factors that can provoke the disease should be eliminated. Failure to do this increases the risk of recurrence.
Recovery is evidenced by the disappearance of symptoms, as well as a negative result of the analysis of nasal discharge.
Let's summarize
 It is much easier to prevent sinusitis of fungal origin, because it takes a very long time to treat it. Note that the most effective method of treating this disease today is surgical. After it, compulsory drug therapy is prescribed. Without an integrated approach, it is unlikely that it will be possible to eliminate a fungal infection.
It is much easier to prevent sinusitis of fungal origin, because it takes a very long time to treat it. Note that the most effective method of treating this disease today is surgical. After it, compulsory drug therapy is prescribed. Without an integrated approach, it is unlikely that it will be possible to eliminate a fungal infection.
For prevention, you should undergo a scheduled examination by an otolaryngologist annually. This is especially true for those who have already managed to undergo this disease.
In addition, you need to monitor your diet. The diet should be fortified with vitamins, not contain baked goods and other sweet delicacies. After all, sugar is a breeding ground for the fungus.
Fungal sinusitis is a very unpleasant disease that can be prevented. To do this, it is necessary to control the state of the immune system, as well as to adequately and timely treat diseases of the nose of an inflammatory nature.

 streaks of blood in the discharge;
streaks of blood in the discharge; Take restorative medicines and so-called adaptogens - tinctures of medicinal plants such as leuzea, aralia, rose hips, ginseng, eleutherococcus and so on.
Take restorative medicines and so-called adaptogens - tinctures of medicinal plants such as leuzea, aralia, rose hips, ginseng, eleutherococcus and so on.