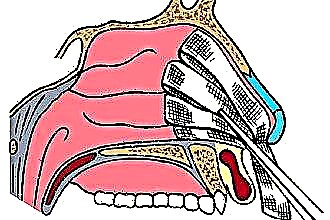
Acute sinusitis is a disease that manifests itself as an inflammatory process in the maxillary sinuses (sinuses). It is accompanied by fever, partial or complete loss of olfactory function, headaches and other clinical signs. Acute maxillary sinusitis lasts no more than 12 weeks, after which it is either completely cured or transformed into a chronic form. But such a disease is dangerous not only for this. In the absence of adequate and timely treatment, orbital and intracranial complications may occur.
Key causes of the disease
 Acute catarrhal sinusitis is a multifactorial disease, that is, it can be caused by numerous adverse conditions. Most often, it develops against the background of infectious diseases of the upper respiratory tract (tonsillitis, colds, runny nose, and so on). But in some cases, bad teeth can act as a reason. As a rule, these are the four teeth in the upper jaw. In this case, we are talking about the odontogenic form of sinusitis.
Acute catarrhal sinusitis is a multifactorial disease, that is, it can be caused by numerous adverse conditions. Most often, it develops against the background of infectious diseases of the upper respiratory tract (tonsillitis, colds, runny nose, and so on). But in some cases, bad teeth can act as a reason. As a rule, these are the four teeth in the upper jaw. In this case, we are talking about the odontogenic form of sinusitis.
And yet, most doctors are inclined to believe that the cause should be sought precisely in viruses and bacteria. They penetrate into the maxillary sinuses through the nasal cavity (sometimes by a hematogenous route, that is, through the blood) and begin to actively multiply. For this reason, a strong inflammatory process occurs, the sinus mucosa swells. The anastomosis connecting the sinus with the nasal cavity is blocked. As a result, mucus cannot be evacuated from the sinus, which creates favorable conditions for the further development of pathogenic microflora.
In addition, acute sinusitis is often associated with the following risk factors:
- curvature of the nasal septum;
- vasomotor rhinitis (runny nose);
- rhinitis of the hypertrophic type with subsequent enlargement of the turbinates;
- allergic conditions;
- significant decrease in immunity;
- untreated rhinitis, seasonal colds, acute respiratory infections and other ailments;
- the presence of staphylococci and other pathogenic bacteria in the body;
- congenital defects of anatomical nasal structures;
- mechanical trauma to the head and, in particular, the nose;
- adenoids (more often in children) and so on.
Symptoms
What clinical manifestations indicate acute sinusitis? First of all, it should be noted the severe nasal congestion and runny nose. These are the first symptoms of acute sinusitis, which do not go away even after using strong drugs to narrow the blood vessels. If relief does come, it won't be long. After a while, nasal congestion and discharge from the nose recur.
It is impossible not to say about headache - another symptom of the disease. Intense pain sensations increase with head tilt and have a pulsating character. In some cases, pain can spread to the frontal or occipital region.
As a rule, the pain is worse in the morning, immediately after a night's sleep. This is due to the fact that a certain amount of mucus accumulates in the maxillary sinus during the night, and the rise provokes pressure.
It should be noted that acute sinusitis, the symptoms of which are quite diverse, is almost always accompanied by an increase in body temperature. This is one of the signs of intoxication of the body - poisoning with the waste products of pathogenic bacteria.
If we are talking about an acute form of the disease, then the temperature rises to high febrile values - up to 40 degrees. In the chronic form, it rarely exceeds subfebrile values (up to 38 degrees).
 Acute sinusitis can be accompanied by bad breath. Moreover, even after a morning exercise using a toothbrush and paste, it still does not disappear anywhere.
Acute sinusitis can be accompanied by bad breath. Moreover, even after a morning exercise using a toothbrush and paste, it still does not disappear anywhere.
Very rarely, acute sinusitis provokes severe toothache. This is especially true when patients have the roots of the upper teeth located too close to the maxillary sinuses. A clear sign of an inflammatory process in the sinuses is a complete or partial violation of the olfactory function.
The sinuses are very close to the optic nerves. If a patient is diagnosed with acute purulent sinusitis, characteristic symptoms may appear in the form of increased sensitivity to light, profuse and frequent lacrimation, swelling of the lower eyelids, and so on.
What about complications
Acute bilateral sinusitis or acute left-sided sinusitis is dangerous not only in itself. In the absence of adequate treatment, it not only quickly becomes chronic, but also provokes severe and dangerous complications. This is due to the fact that the maxillary sinuses are in close proximity to vital organs (eyes, ears, brain).
What consequences can be expected when ignoring paranasal sinus problems:
 Ocular (orbital) complications. As a rule, they are presented in the form of retinal edema, suppuration of orbital tissues and venous thrombosis. Often, acute bilateral sinusitis causes a significant decrease in visual acuity.
Ocular (orbital) complications. As a rule, they are presented in the form of retinal edema, suppuration of orbital tissues and venous thrombosis. Often, acute bilateral sinusitis causes a significant decrease in visual acuity.- Complications of the hearing organs. This includes various ear pathologies. First of all, it is otitis media (inflammation of the middle ear). Most of it appears in children. Purulent foci provoke severe pain in the head and ears. Often, sinusitis causes partial hearing loss.
- If the inflammatory process and infection penetrate from the mucous membrane into the bone tissue, complications appear in the form of osteoperiostitis - pathological processes in the bones.
- But the most dangerous are intracranial complications. First of all, this is meningitis - an inflammation in the cerebral cortex. It appears when pus and, accordingly, pathogenic microflora penetrate into the intracranial space. Meningitis is often fatal.
To avoid all of the above pathologies, you should consult a doctor in a timely manner. Only he will be able to accurately establish the diagnosis, choose the optimal treatment strategy, depending on the type of sinusitis and the individual characteristics of the patient.
Treatment
In most clinical cases, an acute form of sinusitis appears as a result of a viral infection. The primary task is to eliminate severe swelling of the mucous membrane in the nasal cavity. Then, measures are taken to evacuate the pathological contents of the affected sinus (mucus, pus). And only after that, you can start fighting directly with pathogenic microflora, that is, with bacterial agents.
For the treatment of acute sinusitis, local and general (systemic) antibiotics are used:
- "Azithromycin";
- "Bioparox";
- Augmentin;
- "Amoxicillin";
- "Izofra" and some others.
The use of antibacterial drugs is a prerequisite for the successful treatment of acute sinusitis, if it has a bacterial genesis (origin). Nothing else can eliminate pathogenic bacteria.
 But antibiotic therapy should be prescribed only by the attending physician. He also selects the optimal group of such drugs and a specific drug. Self-medication is unacceptable, it can further worsen the clinical picture and lead to numerous complications.
But antibiotic therapy should be prescribed only by the attending physician. He also selects the optimal group of such drugs and a specific drug. Self-medication is unacceptable, it can further worsen the clinical picture and lead to numerous complications.
In addition, the intake of drugs for vasoconstriction is an integral part of drug therapy. For these purposes, aerosols, sprays and drops are used, which quickly relieve puffiness and help remove accumulated mucus outside the sinus.
The most effective are the following:
- Xymelin;
- "Nazivin";
- Pharmazolin;
- Sanorin;
- Galazolin;
- "Naphtizin" and some others.
If the patient's body does not react in any way to nasal corticosteroids, they are prescribed to him in the form of tablets (for example, "Prednisolone"). The same medicines are shown to patients in case of polyposis, allergic and fungal sinusitis.
 To improve your well-being, pain relievers are prescribed - "Ibuprofen" or "Paracetamol". They help lower the temperature. In especially severe cases, your doctor may prescribe a powerful pain reliever such as Codeine.
To improve your well-being, pain relievers are prescribed - "Ibuprofen" or "Paracetamol". They help lower the temperature. In especially severe cases, your doctor may prescribe a powerful pain reliever such as Codeine.
At the final stage of treatment, when the foci of bacteria are practically destroyed, physiotherapy procedures are prescribed. We are talking about needle reflexology, UHF, ultraviolet radiation, sinus catheter and so on. Regular rinsing of the nose and sinuses with antiseptic solutions helps to clear the nasal cavity of mucus well. To thin the mucus, it is recommended to drink plenty of fluids (the rule of a plentiful warm drink).
If drug therapy turned out to be unproductive, a more radical method is used - puncture of the maxillary sinus. The walls of the sinus are calcined, then a tube is inserted to pump out the pathological contents.
Prevention measures
Acute right-sided sinusitis or left-sided sinusitis is always easier to prevent than to treat for a long time and persistently. Pay attention to the following helpful tips to help you avoid this disease and always stay in good shape:
- Maintain your personal hygiene. In autumn and winter, when flu and cold epidemics are raging, avoid crowded places. Always wash your hands after outside. Dress for the season and the weather, and avoid hypothermia (this is one of the key causes of sinusitis).
- Minimize or completely abandon bad habits. First of all, this applies to smoking and drinking alcohol. Tobacco smoke strongly irritates the nasal mucosa, suppresses local and general immunity. If you want to avoid colds and possible sinusitis, this risk factor must be completely eliminated.
- Make it a rule to walk in the fresh air for at least 30 minutes every day, or even better - 45 minutes (but only if you are healthy and well). It is imperative to ventilate living areas daily. This way, you can get rid of disease-causing microbes.
 Monitor the humidity level. It is necessary that it does not fall below 60 percent. Otherwise, the nasal mucosa will regularly dry out, which will negatively affect local immunity. Therefore, we advise from time to time to carry out wet cleaning in all rooms of the house.
Monitor the humidity level. It is necessary that it does not fall below 60 percent. Otherwise, the nasal mucosa will regularly dry out, which will negatively affect local immunity. Therefore, we advise from time to time to carry out wet cleaning in all rooms of the house.- Introduce natural foods and foods rich in vitamins and minerals into your diet. Alternatively, you can buy multivitamin complexes at the pharmacy.
- Simultaneously with taking vitamins, it is recommended to work on hardening the body. Daily contrast showers and cold rubdowns will help to significantly increase the body's immune forces. But what can I say, with the right approach, hardening will get rid of many chronic ailments.
- Always complete the treatment of colds and upper respiratory ailments. Don't let them go by themselves. After all, now we know that sinusitis most often develops against the background of influenza, tonsillitis and other infectious diseases.
At the first manifestations of sinusitis, always contact a specialist and do not self-medicate. This way, you can avoid many dangerous complications.

 Ocular (orbital) complications. As a rule, they are presented in the form of retinal edema, suppuration of orbital tissues and venous thrombosis. Often, acute bilateral sinusitis causes a significant decrease in visual acuity.
Ocular (orbital) complications. As a rule, they are presented in the form of retinal edema, suppuration of orbital tissues and venous thrombosis. Often, acute bilateral sinusitis causes a significant decrease in visual acuity. Monitor the humidity level. It is necessary that it does not fall below 60 percent. Otherwise, the nasal mucosa will regularly dry out, which will negatively affect local immunity. Therefore, we advise from time to time to carry out wet cleaning in all rooms of the house.
Monitor the humidity level. It is necessary that it does not fall below 60 percent. Otherwise, the nasal mucosa will regularly dry out, which will negatively affect local immunity. Therefore, we advise from time to time to carry out wet cleaning in all rooms of the house.