Otitis media is an infectious disease characterized by damage to the main parts of the auditory analyzer. Depending on the localization of the pathogenic flora, distinguish between internal, external and otitis media. In most cases, the development of ENT pathology is preceded by septic inflammation of the nasopharynx and lower respiratory tract.

Bilateral otitis media in a child is dangerous with severe local complications, which include meningitis, brain abscess, mastoiditis, facial paresis, etc.
Due to the lack of reactivity of the child's body, the infection spreads rapidly, provoking inflammation of adjacent tissues. When the first signs of the disease are found, you should seek the help of a specialist. In the case of the timely passage of drug therapy, local and general symptoms of inflammation disappear within 7-10 days.
Etiology
Bilateral otitis media is a dangerous ENT disease, untimely treatment of which can lead to dysphonia and conductive hearing loss. According to statistics, more than 80% of children under the age of 3 years have suffered from an infectious inflammation of the middle ear. The high morbidity in children is largely due to the anatomical features of the structure of the auditory analyzer and the practical absence of the specific, i.e. acquired immunity.
In children, the Eustachian tube is much shorter and wider than in adults. It is located almost horizontally, which facilitates the penetration of pathogens from the nasopharynx into the tympanic cavity. The looseness of the ciliated epithelium and insufficient blood supply to the mucous membranes of the ENT organs greatly increases the risk of bacteria and viruses entering the tissues of the middle ear.
Factors that can contribute to the development of otitis media include:
- bacterial rhinitis;
- hypovitaminosis;
- adenoiditis;
- infectious diseases;
- ear canal injury;
- hypothermia;
- water entering the ear.
Due to the high density of the tympanic membrane, a pathological secret localized in the tympanic cavity can be evacuated not into the external auditory canal, but into the inner ear, which is fraught with the development of labyrinthitis.
Symptoms
Children under 2 years of age cannot directly inform adults about the presence of ear discomfort. For this reason, parents seek help from specialists already at the stage of perforation of the ear membrane and evacuation of purulent masses into the external auditory canal. However, it should be borne in mind that delayed treatment of the infection can lead to serious complications and even deafness.
The development of pathological processes in the auditory analyzer can be evidenced by:
- hyperthermia;
- enlargement of the cervical lymph nodes;
- restlessness;
- poor sleep;
- lack of appetite;
- tearfulness;
- involuntary palpation of the auricles.
Older children complain of dizziness, ear pain, a feeling of stuffiness and general weakness. Treatment of otitis media can only be prescribed by an ENT doctor after the patient undergoes the necessary examination.
Stages of development of otitis media
As a rule, otitis media occurs in five stages, which alternate one after another. The principles of treatment directly depend on the severity of the course and the stage of development of bilateral otitis media. The earlier treatment is started, the lower the likelihood of post-infectious complications:
- Stage 1: noise and congestion in the ears, slight malaise and a slight increase in temperature;
- Stage 2: shooting and throbbing pains in the ear, headaches, dizziness;
- Stage 3 (pre-perforative): increasing pain in the ear, radiating to the neck, back of the head, eyes and pharynx, febrile fever, hearing loss, vomiting;
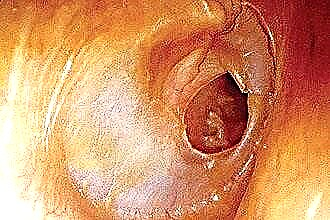 Stage 4 (perforated): perforation of the ear membrane, evacuation of purulent exudate into the external auditory canal, reduction of pain;
Stage 4 (perforated): perforation of the ear membrane, evacuation of purulent exudate into the external auditory canal, reduction of pain;- Stage 5 (reparative): regeneration of the mucous membrane in the middle ear, restoration of the integrity of the tympanic membrane, recovery.
Bilateral otitis media in children often proceeds in an atypical form, characterized by the manifestation of all the symptoms of pathology at once.
In the absence of drug treatment at stage 4 of the development of pathology, there is a risk of pus penetrating deep into the ear, which is fraught with meningitis and abscess. Due to the low resistance of the body to pathogenic agents, purulent inflammation can lead to the destruction of the ossicles and hair receptors, as a result of which the child may develop hearing loss.
Drug treatment
What should be the treatment for acute ear inflammation? For relief of local manifestations of pathology and the destruction of pathogenic flora, medicines of symptomatic and pathogenetic action are used. Complex therapy of ENT diseases accelerates the regression of catarrhal and purulent processes in the ear, which prevents the development of complications.
Due to the increased sensitization of the child's body, the classical treatment regimen for children includes only low-toxic drugs that are not capable of causing a strong allergic reaction. These include:
| A drug | Category | Operating principle | Age restrictions |
| "Paracetamol" | antipyretic | lowers temperature, eliminates inflammation and pain in the ear mucosa | from 3 years |
| "Sofradex" | ear drops | has anti-inflammatory, anti-allergic and anti-edema effect on the mucous membranes of the ENT organs | from 1 year |
| Telfast | antihistamine | inhibits the synthesis of cyclooxygenase, which prevents the production of inflammatory mediators; relieves puffiness, which helps to restore the ventilation function of the Eustachian tube | from 6 years |
| Claritin | antihistamine | inhibits the activity of histamine receptors, thereby eliminating allergic reactions and swelling in the mucous membranes of the middle ear | from 2 years |
| "Amoxicillin" | penicillin antibiotic | destroys gram-positive and gram-negative microbes that synthesize penicillinase | from 1 year |
| Cefuroxime | cephalosporin antibiotic | inhibits the development of bacteria synthesizing beta-lactamase | from 6 months |
| "Biseptol" | sulfonamide | blocks the reproduction of pathogens in the ciliated epithelium, resistant to streptococci, meningococci, staphylococci, proteus, etc. | from 12 years old |
| "Nazivin" | vasoconstrictor nasal drops | eliminates swelling of the nasopharyngeal mucosa by reducing vascular permeability | from birth |
Important! Children should be treated exclusively under the supervision of a specialist in order to avoid the development of complications - labyrinthitis, meningitis, brain abscess, etc.
Physiotherapy procedures
Physiotherapy treatment is usually prescribed at the stage of resolving inflammatory processes in the auditory analyzer. To accelerate the regeneration processes and the final destruction of pathogenic flora, phototherapy, electrotherapy, mechanotherapy, etc. are used. It is necessary to treat bilateral otitis media taking into account the following characteristics:
- the age and gender of the patient;
- the physical state;
- stage of development of pathology;
- medical history and anamnesis.
Physiotherapy procedures are aimed at restoring normal blood circulation in tissues. Intensive nutrition of cells with oxygen and nutrients accelerates the epithelialization of the ear mucous membranes. In pediatric therapy, the following treatment methods are used to treat otitis media:
- electrophoresis - the introduction of anti-inflammatory and antiseptic solutions into the affected tissues by means of an electric current; helps to eliminate pathological foci, restore tissue integrity and increase local immunity;
 ultra-high-frequency therapy (UHF-therapy) - exposure of the hearing organ to high-frequency electromagnetic fields; relieves pain, accelerates the regression of inflammation and the process of epithelialization of the mucous membrane in the tympanic cavity;
ultra-high-frequency therapy (UHF-therapy) - exposure of the hearing organ to high-frequency electromagnetic fields; relieves pain, accelerates the regression of inflammation and the process of epithelialization of the mucous membrane in the tympanic cavity;- magnetotherapy - the effect of a constant magnetic field on tissues affected by inflammation; unlike UHF therapy, it does not lead to tissue heating, which prevents burns;
- darsonvalization - treatment of inflammatory processes with high-frequency impulse currents; helps to increase the tone of peripheral vessels, restore tissue trophism, relieve pain and inflammation.
Can a sore ear be warmed up? Heat therapy can be used exclusively at the stage of resolving pathological processes. Warming up the ear with a reflex lamp increases blood flow to the affected areas, as a result of which stagnant processes are eliminated.
Dry heat allows you to eliminate pain, accelerate the regeneration of epithelial tissues and prevent the reproduction of pathogens. In the process of thermotherapy, several important rules must be taken into account, namely:
- the patient's eyes are closed to prevent drying out of the mucous membrane;
- the blue lamp is set at a distance of 20-30 cm from the diseased ear;
- the duration of the procedure should be approximately 5-7 minutes;
- it is advisable to carry out at least 3 sessions of therapy per day.
Physiotherapy prevents the recurrence of pathology and helps to strengthen local immunity. Apparatus treatment of ENT pathologies in children should be accompanied by the intake of anti-inflammatory and antimicrobial medications.

 Stage 4 (perforated): perforation of the ear membrane, evacuation of purulent exudate into the external auditory canal, reduction of pain;
Stage 4 (perforated): perforation of the ear membrane, evacuation of purulent exudate into the external auditory canal, reduction of pain; ultra-high-frequency therapy (UHF-therapy) - exposure of the hearing organ to high-frequency electromagnetic fields; relieves pain, accelerates the regression of inflammation and the process of epithelialization of the mucous membrane in the tympanic cavity;
ultra-high-frequency therapy (UHF-therapy) - exposure of the hearing organ to high-frequency electromagnetic fields; relieves pain, accelerates the regression of inflammation and the process of epithelialization of the mucous membrane in the tympanic cavity;