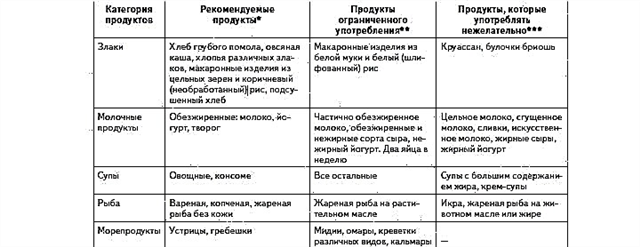
Painful sensations in the ear area are very often a symptom of otitis media. The disorder is an inflammatory process that can be localized in any part of the ear cavity. Otitis media is an urgent problem, since this disease is quite common - the disorder is diagnosed in 9 out of 10 children under 5 years of age. Inflammation of the ear can lead to severe irreversible consequences, therefore, the treatment of the disease must be timely and correct. How is otitis media treated in children? Below we will consider the most effective medicines.
What should you do first?

A small child cannot always tell what exactly bothers him. With the development of otitis media, the child will behave restlessly, be capricious, touch the sore ear, his sleep and appetite are disturbed. To determine the presence of otitis media, you need to apply light pressure to the tragus (a small protrusion in the front of the ear). With inflammation in the ear, this action will cause severe pain. Also, otitis media may be accompanied by discharge from the ear canal.
The development of the inflammatory process in the ear cavity is almost always accompanied by severe painful sensations. To eliminate an unpleasant symptom, anti-inflammatory drugs are used, which also normalize temperature indicators (often with otitis media, the body temperature is increased). The most effective medicines are Nurofen, Ibuprofen, Panadol.
After the relief of acute pain, the child must be shown to the otolaryngologist. Otitis media has several forms that differ in the nature of the course, respectively, and the therapeutic actions for each type of otitis media will be different. Therefore, self-medication is categorically contraindicated. Using medication on your own, especially if the eardrum is damaged, can lead to hearing loss.
Most often, the inflammatory process in the ear cavity develops against the background of ARVI.
In this regard, treatment is carried out using anti-inflammatory, vasoconstrictor and various symptomatic agents. Bacterial and purulent otitis media are also common in children, in which case antibiotics are required.
Next, we will consider drugs for the treatment of otitis media in children.
Ear drops
These funds can have anti-inflammatory, antibacterial, combined effects. The most optimal drug is selected by a specialist, taking into account the course of the pathological process and the general condition of the child.
- Otipax. It is an effective pain reliever for otitis media in a child. The drug belongs to non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs and copes well with the symptoms of the disease at an early stage of its development. The medicine can even be used for infants.
- Otinum. The drug has an effect similar to the previous medication, but with severe painful sensations it is not used.
- Normax. The medicine produces an antibacterial effect and is used for purulent and chronic inflammatory processes.
- Otofa. An antibacterial agent used to treat acute and chronic otitis media. According to the prescription of the treating vulture, this drug can be used even if the integrity of the tympanic membrane is violated.
- Polydexa. The medication has not only antibacterial, but also antihistamine effect, due to which the edema provoked by the inflammatory process is reduced.
- Anauran. A glucocorticosteroid with a combined effect. The drug eliminates edema and has a detrimental effect on pathogenic microflora.
In case of an inflammatory process in the area of the outer ear, camphor oil and boron alcohol can be used as ear drops.
With otitis media in children and adults, these funds help to get rid of severe painful sensations and stop the pathological process at the initial stage of development.
Boric alcohol is used as follows: slightly heat the agent and drip 2 drops into the sore ear, the procedure is performed 3 times a day. Camphor oil for otitis media in children is used several times during the day and 2-3 drops are instilled into the ear cavity.
Antibacterial agents
In case of bacterial and purulent inflammation, in addition to the local use of antibacterial agents, the doctor may prescribe systemic antibiotic therapy. In most cases, specialists take a wait-and-see attitude and are in no hurry to use systemic antibiotics.
However, these medicines for otitis media for children are prescribed without fail if the child under 2 years old, temperature values reach 40 ºС, there is severe pain.
under 2 years old, temperature values reach 40 ºС, there is severe pain.
Antibiotics are classified into several groups:
- penicillins. Antibacterial drugs in this group have minimal side effects and are most often prescribed. Penicillin antibiotics include: Ampicillin, Amoxicillin, Sultamicillin.
- cephalosporins. Today, medicines of this group are used more and more often for the treatment of children. Modern drugs practically do not have a negative effect on the body and are more effective than penicillins. Most often, the drug Zinat is used, but if a stronger drug is required, the antibiotic Zedex can be used strictly according to the specialist's prescription.
- macrolides. These antibacterial agents are prescribed only in the absence of a positive result from the use of other drugs. Since macrolides can have a negative effect on the immune system. These drugs include Azithromycin, Clarithromycin and others.
Antihistamines and nasal drops
To eliminate edema of the mucous membrane and accelerate the removal of purulent masses from the ear cavity, nasal drops with a vasoconstrictor effect are used - Nazivin, Naphtizin, Tizin.
If otitis media has developed against the background of a bacterial rhinitis, Isofra nasal drops are used. Provided that it is used correctly, this product practically does not have a negative effect. The course of treatment with such a medicine should be no more than 10 days.
Isofra nasal drops can be an effective alternative to tableted antibiotics. Antihistamines can also help relieve swelling. In childhood, Suprastin is most often used.
Antiseptic
With the development of otitis externa, in order to prevent the further development of the pathological process, it is recommended to wash the ear cavity with antiseptics. The most popular drug of this action is Miramistin. The drug shows high efficiency in the fight against viruses and fungi, while it has no side effects. The use of Miramistin as part of complex therapy will significantly speed up the healing process.
Provided timely and adequate therapy, the prognosis for otitis media is favorable.
The disease can last from 1 to 3 weeks. The duration of the inflammatory process and the likelihood of complications will depend on the tactics of treatment.