The term "otitis media" refers to inflammatory diseases of the ear with various localization and symptoms. Such a pathological condition can develop at any age, but more often a violation is diagnosed in children, due to the structural features of the Eustachian tube, with the help of which the tympanic cavity of the middle ear is connected to the nasopharynx.

Types of otitis media in children are classified according to the following criteria:
- the place of development of the disease - external, middle, internal;
- the course of the pathological process - acute, subacute, chronic;
- cause of occurrence - traumatic, viral, allergic;
- the nature of the inflammation is catarrhal, exudative, purulent.
Each of the types of this disorder is accompanied by characteristic clinical manifestations. Let us consider in more detail the types of otitis media in children.
Otitis externa
The pathological process is localized on the visible part of the auricle. The first manifestations of the disease in this case are suppuration or boils.
The disease occurs due to scratching, exposure to infectious agents, insect bites. The development of this disorder due to diabetes mellitus is possible.
Varieties of otitis externa:
- acute infectious limited purulent otitis media. With this disorder, a purulent element forms in the outer region of the ear. The disease is accompanied by characteristic symptoms, which allows an accurate diagnosis to be made without additional diagnostic measures. Signs of pathology: painful sensations when opening the mouth; an increase in the size of closely located lymph nodes; swelling of the skin around the ear.
- acute infectious diffuse purulent otitis media. A severe form of disorder in which there is a flow of pus from the middle ear. The pathogenic elements in this situation enter the outer ear and characteristic symptoms of the pathological process appear: swelling and redness of the skin in the outer ear, the course of pus with a characteristic odor, pronounced painful sensations.
Otitis media
In this situation, the eardrum and the middle ear area are included in the pathological process. Often, as a result of a cold or a viral disease (ARVI, etc.), average viral otitis media occurs in children.

Types of pathology:
- acute infectious purulent otitis media. In this case, ear congestion is noted; suppuration; ear pain; increase in temperature values.
- acute infectious exudative otitis media. Such a disorder, due to edema, is accompanied by a narrowing of the lumen of the Eustachian tube. As a result, the excretion of fluid (exudate), which is intensively produced during inflammation, is impaired. This contributes to the strengthening of the pathological process, which is manifested by the following signs: pronounced hearing loss; there is a sensation of fluid overflowing inside the ear; exudate accumulates in the middle ear; upon visual examination by a specialist, the tympanic membrane has a grayish tint and a clear vascular pattern.
- acute hemorrhagic otitis media of the middle ear. In such a situation, the fluid becomes bloody. The violation is accompanied by the following symptoms: bluish tinge of the eardrum; increasing hearing impairment; accumulation of red-brown fluid in the tympanic cavity.
- acute traumatic otitis media. This type of disorder appears very often in children. With outdoor games, the risk of ear injury is very high. If the child is worried about painful sensations in the ear cavity, it is necessary to check for the following signs - hearing impairment, a wound on the auricle, spotting. If these symptoms occur, you should immediately seek medical attention.
- chronic infectious purulent otitis media. In this case, due to a violation of the exit of exudate, an opening is formed in the eardrum, from which pus continuously flows out, hearing loss is noted. Over time, a scar forms on the hole, which is often the cause of severe hearing impairment.
- chronic allergic exudative otitis media. The development of the disease occurs due to a violation of the exit of exudate from the middle ear. Allergic otitis media in a child often appears against the background of chronic inflammation in the sinuses of the nose, uncontrolled use of antibiotics, and allergic reactions of the body. Signs of the disease: ear congestion, retracted eardrum, hearing loss.
- chronic adhesive otitis media. This is a severe complication of otitis externa or otitis media, which were not cured in the early stages of development. Adhesions form on the auditory tube. The consistency of the exudate becomes excessively thick, it is difficult to remove from the ear cavity, as a result, the disease is even more severe. In this case, there is intense tinnitus, rapid hearing impairment.
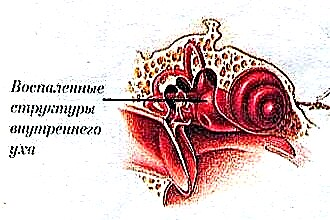
Internal otitis media
In the absence of proper therapy for chronic otitis media, the pathology spreads to the inner ear and affects the labyrinth of the cochlea. This violation is called "labyrinthitis" and is accompanied by the following symptoms:
- dizziness;
- deterioration in coordination;
- pronounced tinnitus;
- vomiting;
- rapid hearing loss.
Labyrinthitis is the most severe form of otitis media. It is impossible to make a correct diagnosis based on a visual examination; a number of medical studies are required.
Salpingootitis
The auditory tube connecting the middle ear and the nasopharynx, in the absence of any pathologies, is closed, and it opens only when swallowing, yawning. In the case of penetration of infectious agents into the Eustachian tube (mainly from the nasopharynx), an inflammatory process develops, which is called "salpingootitis". In children, this disease often occurs with inflamed adenoids, enlarged tonsils. Also, a violation can be provoked by streptococcal, staphylococcal, pneumococcal infections. The course of the disease may not be accompanied by any symptoms (temperature readings are normal, painful sensations are absent).
A prolonged asymptomatic course of inflammation without treatment can provoke bilateral salpingotitis.
It is almost impossible to cure such a disease without partial hearing loss. In this regard, if a child complains of a minor hearing impairment, tinnitus, ear congestion, you should contact a medical institution and conduct the necessary examination.
Therapy for otitis externa and otitis media is carried out on an outpatient basis, with otitis media of the inner ear, hospitalization and the use of antibacterial drugs for a long time are required. Therefore, one should promptly respond to the first symptoms of a developing disease and carry out adequate therapeutic measures.