Pregnancy is often associated with many prohibitions and restrictions that affect almost all areas of life. Expectant mothers are afraid of drafts, which carry the threat of a cold. They refuse to use even familiar and favorite products before - although they really want to. They try not to lift weights, worry as little as possible, because it is known that nervous tension affects the development of the child. However, the greatest number of fears are associated with diseases - and, of course, with drug treatment. Inflammatory ear damage in almost all cases requires the appointment of antibacterial drugs, therefore, the treatment of otitis media during pregnancy is inevitably associated with anxiety about the health of the mother and child. It is important to know what to do in case of ear inflammation in a pregnant woman, what drugs can be included in the therapy regimen.
Treatment principles

Otitis media during pregnancy can proceed in the same way as in women who are not carrying a child. Symptoms are determined by the form of the disease and the severity of the course. Common signs of otitis media are ear pain, fever, general weakness, and headache. With inflammation of the middle ear (otitis media), the pain can be very intense - it weakens only with the onset of suppuration, which indicates the transition of otitis media from the pre-perforative stage to the stage of perforation.
It's no secret that pregnancy is a special condition of a woman's body. During this period, all functional systems are rebuilt, so it is sometimes difficult to predict what the course of the infection will be and the effect of treatment. Nevertheless, the studies carried out indicate the existence of the so-called "critical periods":
- End of the first week of pregnancy.
- The time interval is from 3 to 8 weeks of pregnancy.
- The period from 20 to 24 weeks of intrauterine life of the fetus.
The indicated periods of pregnancy represent the time intervals in which the fetus is most sensitive to damaging influences. Various factors can have an adverse effect, among which drugs are also called. It is wrong to say that therapy should be canceled at this time. However, one should be careful about the list of contraindications and side effects. You should not abuse medications, but you cannot leave a pregnant woman without treatment.
The requirements for drugs for the treatment of otitis media in pregnant women are as follows:
- safety;
- convenient way of application;
- possibility of dosage control

When assessing the safety of drugs, first of all, the likelihood of teratogenic effects must be excluded.
It is also necessary to pay attention to the condition that could serve as a background for the onset of otitis media. It can be a bacterial or viral respiratory infection - including the flu. Given the variety of forms of otitis media and the likelihood of their development as secondary pathologies, it is necessary to draw up a treatment regimen based on a set of objective signs.
Otitis externa
External ear inflammation, or otitis externa, occurs in the following forms:
- limited;
- diffuse.
Limited otitis externa is represented by a furuncle of the external auditory canal, and in the diffuse variant, diffuse inflammation of the skin of the auditory canal and auricle is observed. In the first case, it is necessary:
- the appointment of antibiotic therapy;
- the appointment of analgesics, antipyretics.
Antibiotics are used in tablet or injectable form. Local therapy is indicated in the infiltration stage - the doctor needs to understand whether it will be possible to stop the process without suppuration. If the answer is yes, antiseptics are used, otherwise - ointments that help soften the skin. Treatment of the boil of the external auditory canal at home is associated with a high risk of complications, therefore, it is carried out exclusively under the supervision of a doctor.
With a furuncle in the external auditory canal, surgical treatment may be required.
Treatment of otitis media in pregnant women in the case of a diffuse form includes:
- Ear toilet.

- Applying antibacterial ear drops.
- The use of analgesics.
Cleansing the external auditory canal with otitis externa is carried out using a sterile saline solution, after which the ear must be dried. In the absence of severe pain and fever, it is undesirable to use pain relievers. They, as a rule, are antipyretics (antipyretic) at the same time. In case of severe pain, it is allowed to take Paracetamol (with strict dosage control), subject to an immediate visit to the doctor.
Among anti-inflammatory drugs with an analgesic component for use during pregnancy, Otipax drops are allowed, containing the non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drug Phenazone and the local anesthetic Lidocaine.
Otitis media
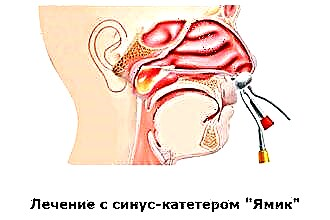
Acute suppurative otitis media is usually accompanied by severe pain. Patients can distinguish pain syndrome against the background of other symptoms, pointing to it in the first place. Treatment of the named form of the disease can be conservative (antibacterial drugs, antiseptics, pain relievers) and operational (tympanopuncture).
How to treat otitis media during pregnancy? Antibiotic therapy for purulent inflammatory lesions of the ear is mandatory. Pregnant women are allowed drugs belonging to the group:
- penicillins (Amoxicillin);
- cephalosporins (Cephalexin, Cefuroxime);
- macrolides (erythromycin).
Penicillin can cause an allergic reaction.
The medicines listed in the list are used for systemic therapy.
Antibacterial drops often contain components that are prohibited for use during pregnancy (for example, an antibiotic from the aminoglycoside group, Gentamicin). Self-medication can harm not only a woman, but also a child. When choosing how to treat otitis media during pregnancy, it is necessary to focus on the ratio of the need for the drug and the risk associated with the use.