Alcoholic cardiomyopathy is a change in the structure of the heart under the influence of alcohol or its radicals, which is characterized by disruption of work and further loss of function.
Causes
According to statistics, alcoholic cardiomyopathy is observed in half of alcohol addicts. At the same time, the following factors increase the likelihood of its development:
- cardiovascular diseases in close relatives;
- violation of immunity and metabolism;
- improper nutrition;
- smoking;
- psycho-emotional and physical stress.
The mechanism of myocardial damage by alcohol
When alcohol is ingested in large quantities, most of it is metabolized by liver cells to acetaldehyde. This substance is extremely toxic and, when absorbed into the blood, poisons many organs, and the heart is no exception.
The breakdown product of ethanol affects cardiomyocytes as follows:
- nutrition, electrolyte balance and metabolic processes are disturbed;
- there are problems with the synthesis of contractile protein;
- discoordination develops between contraction and relaxation;
- the contractile activity of the myocardium changes due to a violation of the structure of the conducting system and a large number of arrhythmogenic substances;
- the production of cytokines and other substances that provoke an autoimmune reaction is stimulated;
- mitochondria, which are the main energy supplier in the cell, are destroyed;
- hypoxia and gradual tissue atrophy occurs with their replacement with fibrous fibers.
In addition to ethanol, other harmful products often enter the patient's body, which are added to low-quality alcohol (preservatives, dyes, stabilizers, heavy metals and other chemicals). They further aggravate the process of organ damage, including the heart.
All of the above mechanisms lead to an increase in all parts of the heart, and fatty deposits accumulate under the epicardium at this time. The muscle becomes thin, weak and cannot provide a normal flow of blood to the organs. The disease ends with hemodynamic disturbances and congestive heart failure.
The most common signs
Symptoms of alcoholic cardiomyopathy depend on the form of the disease:
- Classic type. After quitting alcohol, there is often a significant improvement, which directly depends on the time of abstinence. After resuming use, the condition deteriorates sharply.
- Pseudoischemic. It manifests itself as cardialgia, which resembles angina pectoris, but it is not stopped by nitroglycerin and is not associated with physical activity. An increase in pain syndrome is observed after the ingestion of another portion of ethanol.
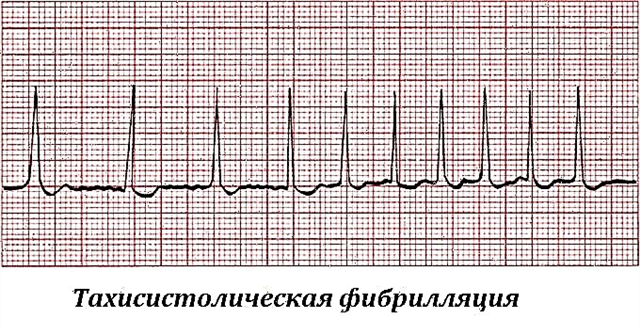
- Arrhythmic. The disturbance of the rhythm in the form of extrasystole, atrial fibrillation, ventricular tachycardia comes to the fore. In some cases, this is the only sign of alcoholic cardiomyopathy. Often, severe attacks lead to cardiac arrest.
Table: modification of symptoms depending on alcoholic experience
| Stage of the disease | Signs |
| Initial (4 - 5 years of continuous alcohol use) | Weakness, fatigue, drowsiness, increased sweating, rhythm disturbances, chest pain. Vegetative abnormalities (feeling hot, cold hands and feet) |
| Developed (up to 10 years of alcoholic experience) | Increase in all parts of the heart, shortness of breath, choking at night, swelling of the legs. Dry cough or little phlegm, acrocyanosis, pallor of the skin |
Terminal (damage to all organs and systems) | Encephalopathy, sleep disturbance, personality change, anasarca, enlarged liver and spleen, cardiac asthma, pulmonary edema |
Under the influence of several factors at once (atherosclerosis, old age, smoking, poor nutrition), the development of insufficiency occurs much faster - a person may die after 2 - 3 years of alcohol consumption.
Diagnosis of alcoholic cardiomyopathy
In terms of clinical manifestations and morphology, alcoholic cardiomyopathy is similar to dilated idiopathic. Making an accurate diagnosis requires additional examination methods.
ECG changes
It is usually noted:
- high T waves in the right chest leads, ST depression;
- smoothed T or biphasic;
- dilated, split or enlarged and pointed P (pulmonary);
- signs of rhythm and conduction disturbances (extrasystole, paroxysms of flutter and flickering);
- left ventricular hypertrophy in the form of an increase in the QRS complex, which is gradually leveled due to the development of right ventricular dilatation.
Symptoms on the electrocardiogram with this cardiopathology are not specific. The same deviations are observed in other cardiomyopathies, angina pectoris, hypertension and chronic cor pulmonale.

Ultrasound of the heart
Echocardiography provides important information. With the help of ultrasound, you can see:
- an increase in the volume of cavities;
- decrease in myocardial contractility;
- regurgitation in the mitral and tricuspid foramen due to relative valve insufficiency;
- damage to the brachiocephalic arteries;
- the presence of blood clots inside the ventricles or atria.
Scintigraphy and other methods
Radionuclide methods are also used to diagnose ischemic cardiopathy. The two-dimensional image helps to assess the anatomical and topographic features of the heart muscle and detect pathological zones at the early stages of the process. In alcoholic cardiomyopathy, scintigraphy usually reveals multiple defects in isotope accumulation as a result of diffuse fibrous replacement of normal tissue.
On the x-ray, hypertrophy of the heart is visible, and in case of serious insufficiency, the phenomenon of congestion in the lungs. ESR may be increased, leukocytosis, iron deficiency or megaloblastic anemia are observed (found in alcoholism in 40% of cases). Biochemical analysis reveals elevated enzymes (creatine phosphokinase, aspartic aminotransferase).
Treatment
Treatment of alcoholic cardiomyopathy consists in a complete rejection of spirits, since taking medications against the background of a continuing intake of ethanol will not bring any results. If it is impossible to stop alcohol abuse on your own, you may need the help of a narcologist.
Lifestyle redefinition
This includes not only quitting drinking, but also smoking. Proper nutrition involves a diet with a reduction in salt, animal fat, and spicy foods. It is important that the menu is complete and contains protein, vitamins and minerals. Reducing fluid intake is recommended for edema. Dosed physical activity, sleep, minimization of stressful situations are required.
Drug therapy
Taking medications is the main method for improving the condition in alcoholic cardiomyopathy. For this, the following groups of drugs are used:
- To relieve high blood pressure, antihypertensive drugs are used: Ramipril, Lisinopril, Valsartan.
- Extrasystole, flutter and flickering are treated with antiarrhythmic drugs (Sotalol, Amiodarone).
- For edema, diuretics are used (Furosemide, Torasemide, Spironolactone).
- Lowering cholesterol levels is achieved through the use of statins (Atorvastatin, Rosuvastatin).
- Antiplatelet agents and anticoagulants (Aspirin, Warfarin) help prevent the formation of blood clots and blockage of blood vessels.
- Severe deficiencies and associated fibrillation are treated with cardiac glycosides (Digoxin). Although a number of specialists prefer to completely abandon them due to negative side effects.
In the absence of the effectiveness of conservative methods, surgical techniques are used. These include cardiomyoplasty, pacemaker, or heart transplant.
Forecast: can sudden death occur?
Death from alcoholic cardiomyopathy, according to statistics, occurs within 5 - 7 years from the onset of its onset in the absence of treatment and continued drinking. The reason for this is numerous complications in the form of thrombosis and embolism, severe forms of arrhythmia. The entry of blood clots into the coronary or cerebral vessels results in a stroke or heart attack. In this case, the prognosis is extremely unfavorable. This disease in drinking people most often leads to sudden death.