In the modern world, there is more and more talk about the problem of atherosclerosis and its connection with the occurrence of ischemic stroke and myocardial infarction. But cholesterol plaques can affect blood vessels not only in the heart and brain, but also in other organs, disrupting the work of the whole body. Generalized atherosclerosis is a very dangerous disease, since it involves a large number of vessels in different body systems in the process and can have unpredictable consequences for human health.
Description of the disease and possible causes of its occurrence
 Generalized atherosclerosis is a pathology in which cholesterol is layered on the inner walls of the arteries, as a result of which the vascular wall is compacted and its elasticity is lost. In this case, blood circulation is disturbed, as a result of which the organs suffer from ischemia.
Generalized atherosclerosis is a pathology in which cholesterol is layered on the inner walls of the arteries, as a result of which the vascular wall is compacted and its elasticity is lost. In this case, blood circulation is disturbed, as a result of which the organs suffer from ischemia.
There are two main reasons for the appearance of atherosclerotic plaques: damage to the intima (inner lining of the artery) and impaired lipid metabolism. Cholesterol and other fats are immersed in the endothelium of the vessel, forming the base of the future plaque. At the same time, the tone of its wall changes, which leads to a narrowing of the lumen of the artery. As a result, turbulent blood flows appear and the innervation of the vessel is disturbed. Thus, additional layers arise, and therefore the lipid plaque grows, exacerbating the problem.
There are many factors that contribute to the development of atherosclerosis and worsen the patient's prognosis:
- Age and gender. Men over 40 and women over 50 are at risk (women have a decrease in estrogen production during menopause).
- Heredity. Familial hypercholesterolemia is a genetic disorder in which a person suffers from lipid metabolism disorders. In addition, those whose relatives have diabetes, obesity and atherosclerosis are at risk.
- Bad habits, especially tobacco smoking. Harmful substances cause sudden vasospasm and impaired elasticity of the walls.
- Arterial hypertension. Due to the high strength of the blood flow, the walls of the vessels are injured. At the same time, atherosclerosis provokes an increase in pressure (a "vicious circle" is formed).
- Emotional stress. Catecholamines (stress hormones) increase heart rate, blood pressure and blood clotting, increasing blood clotting and causing blood clots.
- Hypodynamia leads to an increase in body weight and lipid accumulation.
In addition, the concept of generalized unspecified atherosclerosis is distinguished, in which it is impossible to establish the cause of the appearance of pathology.
What symptoms bother a person and how to make a diagnosis
The symptomatology of any disease is determined by the localization of fatty plaques and the degree of vasoconstriction. With generalized atherosclerosis, complaints can be combined. Depending on the location of the blockage, the following types of pathology are distinguished.
- Symptoms of atherosclerosis of the vessels of the head:
- dizziness and flickering of flies in front of the eyes with sudden movements;
- blood pressure surges;
- tingling or numbness in the limbs;
- drop in visual acuity;
- feeling tired, unwell;
- speech disorder;
- ischemic stroke.
- Coronary artery sclerosis:
- paroxysmal pain in the region of the heart of an angina pectoris;
- dyspnea;
- an electrocardiogram (ECG) has signs of ischemia;
- the presence of heart failure;
- disturbances in the rhythm and conduction of the heart;
- myocardial infarction.
- The defeat of the vessels of the lower extremities is characterized by intermittent claudication. When a patient walks, pain occurs sharply, which passes after a while.
- Atherosclerosis of the arteries of the abdominal cavity is manifested by cramping pain in the abdomen, the appearance of cold sweat, and hypotension.
- The pathology of the renal arteries is asymptomatic for a long time, but with the progression of occlusion, persistent, difficult to treat hypertension appears.
Diagnosis of atherosclerosis is based on collecting the patient's history (including family history), the presence of clinical symptoms, physical examination, which includes palpation, auscultation, and blood pressure measurement. It is obligatory to study the lipid profile, which shows the level of total cholesterol, triglycerides, the ratio of fats of various fractions.
From instrumental examination methods are carried out:
- chest x-ray to confirm calcification or aortic aneurysm;
- angiography - a study of blood vessels using a contrast agent to determine the degree of its obliteration and the functioning of blood circulation;
- Ultrasound of the arteries with Doppler ultrasound reveals the sites of foci of atherosclerosis, the presence of blood clots and measures the blood flow velocity;
- ECG for the diagnosis of ischemia, arrhythmia, blockades.
What directions in treatment exist
In the treatment of generalized atherosclerosis, various methods are used, both medical and surgical, as well as diet, physiotherapy. The treatment regimen, drugs and dose selection are chosen only by the doctor in each specific case, self-medication is unacceptable.
Drug treatment includes taking the following groups of drugs:
- statins and fibrates reduce the synthesis of their own fats (Rosuvastatin, Atorvastatin, Clofibrate);
- nicotinic acid and its derivatives reduce the level of triglycerides, establish the required ratio of high and low density lipids;
- sequestrants of bile acids remove them from the body, lowering cholesterol;
- also prescribed drugs for the correction of concomitant pathology: antiplatelet agents, hypotensive, sugar-reducing, etc.
Surgical treatment methods:
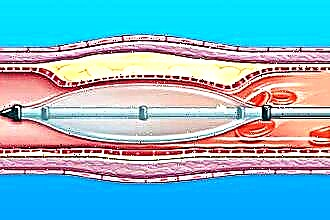 balloon angioplasty and stenting;
balloon angioplasty and stenting;- coronary artery bypass grafting;
- reconstructive surgery on arteries (angioplasty, resection and vascular replacement).
The above surgical interventions are aimed at eliminating complications of the atherosclerotic process.
Physiotherapeutic methods include: Bernard's currents, UHF therapy, electrophoresis, healing baths (hydrogen sulfide, radon), but their effectiveness has not been scientifically proven. Remedial gymnastics, training walking are mandatory.
A comprehensive early approach to solving the problem of atherosclerosis will help prevent the occurrence of severe complications and, if possible, avoid surgical intervention.
Forecast, duration and quality of life ahead
 The patient's prognosis directly depends on the timely diagnosis, the severity of the pathology, the selected treatment and adherence to all the doctor's recommendations. The first thing a patient needs to start doing is to eat right. It is necessary to exclude from your diet fatty meats, semi-finished products, foods with a high level of trans fats (cookies, cakes, margarine, sweets), avoid the use of simple carbohydrates (baked goods, instant cereals, sweets). Instead, it is recommended to increase the amount of fiber-rich foods (vegetables, fruits, whole grain breads, cereals with minimal processing). It is advisable to add sea fat fish, various vegetable oils (olive, sesame, sunflower) to your menu.
The patient's prognosis directly depends on the timely diagnosis, the severity of the pathology, the selected treatment and adherence to all the doctor's recommendations. The first thing a patient needs to start doing is to eat right. It is necessary to exclude from your diet fatty meats, semi-finished products, foods with a high level of trans fats (cookies, cakes, margarine, sweets), avoid the use of simple carbohydrates (baked goods, instant cereals, sweets). Instead, it is recommended to increase the amount of fiber-rich foods (vegetables, fruits, whole grain breads, cereals with minimal processing). It is advisable to add sea fat fish, various vegetable oils (olive, sesame, sunflower) to your menu.
If there is a problem of excess weight, you need to get rid of those extra pounds. This will help a balanced diet and moderate physical activity: walking, cycling, swimming. It is strictly forbidden to smoke and consume alcohol. Bad habits contribute to the growth of atherosclerotic plaques and can be fatal.
If the doctor's recommendations for treatment and lifestyle modifications are not followed, the following complications are possible:
- myocardial infarction;
- stroke or transient ischemic attack (TIA);
- aneurysm and rupture of the aorta;
- persistent uncontrolled hypertension;
- arteriolonecrosis;
- chronic renal failure.
Conclusions
Generalized atherosclerosis is a chronic progressive disease that can lead to serious complications and death. To reduce the risks and prevent the occurrence of a heart attack or stroke, you must adhere to the doctor's recommendations and carefully monitor your health. Even in the absence of severe symptoms of the disease, but the presence of provoking factors or heredity, you need to periodically undergo examinations, control the level of cholesterol and other lipids.

 balloon angioplasty and stenting;
balloon angioplasty and stenting;

