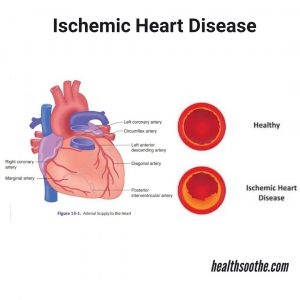
Symptoms of upper limb atherosclerosis are extremely rare. Lipid abnormalities and plaque deposition are diffuse and usually affect all arteries. Obvious manifestations of this pathology are primarily reflected in the state of the heart and brain. In exceptional cases, signs of impaired blood flow in the hands come to the fore.
What vessels are affected
Atherosclerotic plaques are most often localized in the subclavian artery. This paired vessel leaves the aorta and feeds the head, heart, and arms. According to statistics, in 2% of cases, there is a violation of blood flow on both sides. Most often, this phenomenon is observed on the left. Narrowing of the lumen leads to the appearance of a retrograde outflow with the development of "steal syndrome" and is accompanied by numbness of the hands and vertebrobasilar abnormalities. Much less common is a separate blockage of small vessels in the forearm, wrist and hand.
Important! Partially oxygen and nutrients to the upper extremities come from the brachiocephalic trunk, but if the blood flow in it is disturbed, neurological symptoms come to the fore.
Symptoms and Signs
Atherosclerosis of the upper extremities manifests itself as a nonspecific symptomatology, which depends on the stage of the pathology:
- At first, a partial slowdown in blood flow is weak or not noticed by the patient. Sometimes a person feels chilliness in the fingers of the hand on the side of the lesion, worse tolerates the cold.
- Gradually, the condition worsens, soreness appears in the distal parts, a transient violation of sensitivity in the form of itching, crawling creeps or burning. It intensifies with stress on a sore limb or during sleep.
- When the lumen of the artery is closed by more than 50%, obliterating atherosclerosis occurs, and the hand freezes even at normal temperature. Unpleasant sensations grow and pass from the fingers and hands to the forearm area and become permanent, disturbing both during exercise and at rest. Fine motor skills are difficult to perform (buttoning, writing, tying shoelaces). Nails become dull and break, hair loss begins, convulsive twitching of individual muscle fibers.
- The last stage is manifested by ulcers on the arm, pronounced edema and the appearance of areas of necrosis, the skin becomes cyanotic. There is a complete loss of ability to work. A neglected form of atherosclerosis leads to the need for amputation of a limb or death of the patient as a result of the development of gangrene.
Doctor's advice: how to suspect a disease
In order to avoid surgery, treatment and prevention of the progression of upper limb atherosclerosis in the early stages should be started. I want to recommend seeing a doctor right away if there is at least one sign of a problem with blood supply in the arm:
- pain and discomfort in the fingers and hands, as well as in the area of the vessel;
- pallor of the skin, loss of natural color;
- when the pressure changes, the difference on the right and left hand is more than 20 mm Hg. Art .;
- the appearance of seizures, which intensify with physical exertion;
- hypersensitivity to cold or temperature extremes;
- deterioration of the condition of the nails and hair on the arm;
- violation of sensitivity, itching, burning or creeping on the skin;
- muscle weakness in one of the limbs;
- rapid fatigue when performing normal activities that previously did not cause difficulties.
Diagnostics and examinations
To diagnose atherosclerosis, a patient is interviewed. Usually I find out when the first sensations and changes appeared. Neurological pathologies are often accompanied by similar symptoms, but they most often develop in a shorter period of time.
From the moment the deposition of cholesterol begins on the wall of the vessel and until signs of the disease appear, several years can pass, so you need to understand the duration of the development of pathology.
The skin on the affected limb is paler or bluish compared to the healthy hand, colder to the touch. On it, the pulse is felt weaker, blood pressure is lower. Asking to stand for 3 minutes with your arm raised parallel to the ground is almost impossible for the patient. Neurological tests show a decrease in sensation.
A laboratory study of blood in atherosclerosis will show an increase in cholesterol, triglycerides and low density lipoprotein levels. Additional assistance in diagnostics is provided by instrumental techniques:
- Duplex scanning. It is not highly informative in this case, but it can confirm the presence of "steal syndrome", that is, the presence of a reverse direction of blood flow.
- MRI or CT. Provides a complete picture of the lesion with high accuracy and is used to determine the need and method of surgical treatment.
Treatment methods
Treatment of atherosclerosis of the vessels of the upper extremities is best started at an early stage. In this case, drug therapy and adherence to a diet with restriction of calories and cholesterol foods can help. Physical activity will be useful, especially breathing, dynamic and static exercises, which are carried out with a sore and healthy hand, walks in the fresh air. In the last stages, only surgery can provide real help.
Medicines
I usually recommend the following groups of medicines for use:
- statins - they lower cholesterol levels by inhibiting its production in the liver (Atorvastatin, Rosuvostatin, Simvastatin);
- antiplatelet agents and thrombolytics to prevent the formation of blood clots and complete occlusion of the site of narrowing of the artery;
- vascular agents to improve blood flow and relieve spasm;
- analgesics or local novocaine blockade with severe pain syndrome.
When is surgery needed?
Angioplasty with stenting helps to restore the lumen of the artery. To do this, a catheter with a balloon is sent to the affected vessel, in which there is a special durable tubular device installed in the narrowing area, it strengthens the wall and does not allow it to fall off. The price in Moscow for this operation ranges from 55 to 150 thousand rubles, while the cost of the stent is negotiated separately.
A pathogenetically grounded operation is endarterectomy, when plaque is removed from that part of the inner lining of the vessel where it is located. The cost of the intervention in different clinics in the capital is from 49 to 140 thousand rubles.
The principle of this procedure is clearly visible in the photo:
Bypass surgery involves the installation of a bypass route to normalize blood flow. It is most often performed on the coronary arteries, but is often used to eliminate ischemia in the periphery. The price of such an operation can vary from 14 to 21 thousand rubles.
Any operation for atherosclerosis does not eliminate the cause of the disease. If you do not take drugs to lower cholesterol, continue to abuse smoking and fatty foods, new areas with impaired blood flow may appear.
A case from practice: why you need to operate on time
I want to tell you an interesting case from my practice. A 56-year-old man came with complaints of a cold snap in his left hand, pain and burning sensation in the forearm, dizziness, fainting.On examination, there were signs of atrophy, blue skin, a violation of the structure of the nails and the absence of hair. The pulse is weak on both limbs, on the left - threadlike, the pressure on the affected arm is 30 units lower.
After examination and questioning, it turned out that a year ago the patient was diagnosed with atherosclerosis of the subclavian artery, and prescribed drugs that he took for a short time. At the same time, an operation was recommended to restore blood flow (stenting), which he refused. The result was muscle atrophy in the arm. The patient is currently undergoing preparation for surgical treatment to avoid necrosis and amputation.