The appearance of pain behind the sternum and in the upper abdomen can be a sign of both cardiac and gastroenterological, surgical pathologies. The need for differential diagnosis, when the stomach hurts and radiates to the heart, determines the further research tactics and the likelihood of emergency medical care. The effectiveness of the treatment of acute conditions such as myocardial infarction or perforation (perforation) of a stomach ulcer depends on the timing of the correct diagnosis and initiation of therapy.
How to identify the source of pain
The peculiarities of the innervation of the internal organs of the chest and abdominal cavity consist in the crossing of the sensory nerves and their individual sections (skin, muscles) of the body - this phenomenon explains the irradiation of pain.
In most cases, the causes and main characteristics of pain in the abdomen and in the heart differ significantly, however, with an atypical course of the disease, variants of similar symptoms are possible.
Pain in the region of the heart is most often associated with impaired blood circulation in the coronary vessels. The lack of transport of oxygen and nutrients causes metabolic problems in the muscle fibers of the ventricles of the organ, as a result of which the accumulation of under-oxidized products irritates the nerve fibers and unpleasant sensations arise.
Main characteristics of cardialgia:
- connection with physical activity, when myocardial oxygen demand increases;
- the nature of the pain - stabbing, cutting, squeezing, high intensity;
- duration - from 15 minutes (angina pectoris) to an hour or more (myocardial infarction, dissecting aortic aneurysm, myocarditis);
- irradiation of pain to the left shoulder blade and arm;
- accompanying symptoms - shortness of breath, increased pressure (characterized by pain in the back of the head);
- the occurrence of arrhythmias against the background of pain syndrome - palpitations, a feeling of interruptions in the work of the heart;
- does not depend on the time of day and food intake;
- pain is relieved by nitroglycerin preparations (with angina pectoris).
The occurrence of unpleasant sensations in the upper abdomen (epigastrium) is caused by irritation of the mucous membrane, stretching of the stomach, due to tissue breakdown in tumor diseases.
Distinctive signs of pain of gastrointestinal origin:
- connection with food intake - hunger pains (gastric ulcer), after eating (hypoacid gastritis or impaired passage (advancement) with pyloric stenosis);
- the nature of the pain - with chronic diseases (aching), with a perforated ulcer ("dagger");
- duration - from 10 minutes to several hours and days;
- irradiation of pain in diseases of the stomach - in the back, duodenum - in the right hypochondrium, biliary tract - in the right shoulder and arm;
- concomitant dyspeptic symptoms - nausea, vomiting, impaired bowel movements (constipation or diarrhea);
- relieve discomfort with drugs that lower acid production, antispasmodics or sorbents.
The emergence of acute pain against the background of chronic pathology does not exclude a situation when the heart and stomach hurt simultaneously with all the characteristic signs of both diseases.
Why does pain in the heart give to the stomach and vice versa?
Conducting a nerve impulse from a site of irritation in internal organs often imitates other diseases. Pain syndrome in the upper abdomen, which is caused by cardiovascular disease, is most often found in the following diseases:
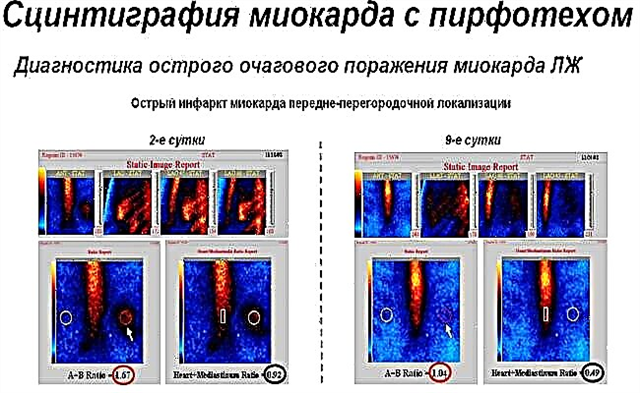
- myocardial infarction - acute circulatory disorders in the coronary vessels, accompanied by necrosis (death) of the muscle fibers of the ventricles. Most often, discomfort occurs when the process is localized in the posterior (diaphragmatic) section. Read more about a heart attack in the article at the link;
- pericarditis - inflammatory pathology, characterized by the accumulation of fibrin or fluid in the cavity of the heart bag;
- congestive right ventricular failure;
- myocarditis - inflammatory damage to the muscle layer of the heart due to autoimmune, viral or bacterial processes;
- aneurysm of the thoracic or abdominal aorta - Thinning and stratification of the vessel wall.
The most common diseases in which stomach pain radiates to the heart:
- peptic ulcers of the stomach and duodenum, peptic ulcer - characterized by a violation of the integrity of the mucous membrane of organs due to the predominance of factors of aggression (bacteria, high acidity, circulatory disorders, malnutrition);
- mesenteric thrombosis - blockage of the lumen of the artery that supplies the intestines. It is accompanied by severe pain syndrome, impaired food passage and exhaustion;
- diseases of the liver and biliary tract - tumors, cholelithiasis, cholecystitis;
- subphrenic and hepatic abscess - localized (limited by the capsule) purulent inflammation. In addition to the pain syndrome, it is characterized by an increase in temperature;
- pancreatitis - bacterial, viral or aseptic inflammation of the pancreatic tissue, which is accompanied by discomfort in the upper abdomen (more on the left), nausea and vomiting.
In addition, pain in the region of the heart and epigastrium is a symptom of lung pathologies: pneumonia (inflammation), pleurisy or spontaneous pneumothorax (air penetration into the pleural cavity through perforation of the chest wall), rupture of lung tissue.
Conclusions
Patients with pain in the sternum or in the upper abdomen must first assess the situation in which the problem arose, recall similar symptoms, if any, and the peculiarities of its progression.
In case of intense pain in the region of the heart and shortness of breath, take a tablet of "Nitroglycerin", after five to ten minutes - repeat. If there is no effect for half an hour, this indicates a possible heart attack, therefore in such situations it is recommended to call an ambulance.
With diseases of the digestive tract, the occurrence of discomfort is a reason for going to the doctor, since taking painkillers "smears" the picture of pathology, which complicates the diagnosis.