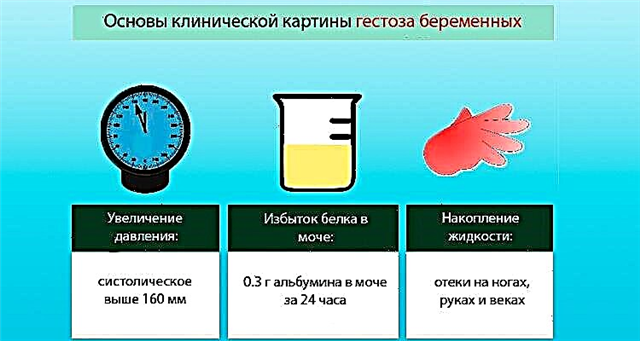
How the scintigraphy method works
The principle of operation of myocardial scintigraphy is based on the ability of the heart muscle to accumulate a radioactive pharmaceutical preparation, the radiation of which is captured by a recording apparatus (gamma camera).
The accumulation of radiopharmaceuticals in the heart muscle is directly proportional to the volume of coronary blood flow. Thus, the functional state of the myocardium in the corresponding area of blood supply is assessed.
The doctor together with the patient makes a decision, weighs the risks and benefits of diagnostics. Radiation of a radioactive pharmaceutical product is negligible. The patient receives the same dose during a conventional X-ray examination. It should be noted that modern drugs (99mTc) used in radiological procedures have a gentle effect, do not interact with other medications and do not cause allergic reactions.
Today there are such types of scintigraphy: the classic version, single-photon emission computed tomography, positron emission tomography and transmission emission technology. The essence of the study is the same in all variants, only the method of image visualization changes. Myocardial scintigraphy prices vary but remain low.
Indications
Myocardial scintigraphy with physical or pharmacological stress is not a screening study method, since it has strict indications and should be performed only as directed by the attending physician in the following cases.
- Diagnosis of ischemic heart disease:
- stable angina and exertional angina;
- assessment of circulatory disorders in the myocardium;
- risk assessment of complications;
- assessment of the restoration of vascular patency (plastics of the coronary arteries, bypass grafting and pharmacological thrombolysis).
- Determination of the pathology of the left ventricular blood supply in diseases not associated with ischemic heart disease (cardiomyopathy, myocarditis, angiopathy in diabetes mellitus).
- Assessment of the spread of myocardial changes after a heart attack.
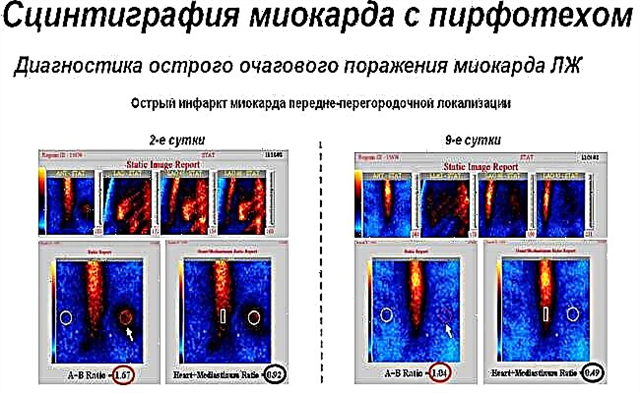
Rice. 1: Photo of the result of scintigraphy after a heart attack
No-load scintigraphy is required for:
- determining the cause of chest pain of unknown origin;
- patients who have contraindications to the procedure, such as left bundle branch block or an implanted pacemaker (pacemaker).
Technique of the procedure
A radiopharmaceutical that is given intravenously produces energy called gamma waves. The recording apparatus (gamma camera) receives the indicator signals, and the system converts the information into an image. This makes it possible to see how certain parts of the myocardium are supplied with blood. A computer can create a 3D model of the heart from multiple images taken in different projections and angles.
The radiologist and cardiologist will give a conclusion based on the resulting image. The basic principle of the assessment is as follows: areas of the myocardium that are well supplied with blood are shown as light, and those where perfusion is low are shown as dark.
The patient is injected intravenously with radiocontrast, after which it is necessary to wait about 40-60 minutes. This is necessary in order for the substance to pass through the liver in the process of metabolism, since the accumulation of the drug in it will give an image similar to the glow of the heart and interfere with an adequate assessment of the results.
Myocardial scintigraphy is available in two versions:
- SM alone is a one-day procedure;
- Exercise SM - requires a visit to the clinic within 2 days to carry out bicycle ergometry.
Scintigraphy is impossible without preliminary preparation, which ensures the quality and reliability of the results obtained. The study is performed on an empty stomach.
If diagnostics with a pharmacological load are planned and the patient is taking drugs acting on the cardiovascular system, one cannot do without consulting the attending physician. Reception of such funds can blur the clinical picture and give false results, which will lead to the wrong prescription of treatment or the need for re-examination. Such medications should be canceled three days before the procedure.
On the eve of testing, it is worth giving up coffee and tea, chocolate and cocoa, as well as Coca-Cola and energy drinks, that is, products with caffeine.
Exercise myocardial scintigraphy gives more accurate data on the state of the cardiac vessels than a study at rest. To do this, the patient is offered to do a certain number of revolutions on a special exercise bike while recording an electrocardiogram. ECG significantly expands the possibilities of diagnosing ischemic disorders in the myocardium.
When physical activity is contraindicated, drugs are used to increase blood flow to the heart, which mimics the heart muscle's response to exercise.
When the scintigraphic images are the same at rest and during exercise, then the blood flow in the coronary arteries is normal. The test may show adequate supply at rest, but after physical stress, a “perfusion defect” (darkening) sometimes appears due to a lack of radiopharmaceutical in the oxygenated area of the myocardium. If the dark area is visualized at rest and after exercise, they speak of a sign of a previous heart attack with the formation of scar tissue.
Contraindications to implementation
Myocardial scintigraphy has contraindications such as pregnancy and breastfeeding (breastfeeding must be stopped for 48 hours to ensure complete elimination of the isotope from the body).
Bicycle ergometry is contraindicated in acute myocardial infarction (48 hours after onset), uncontrolled hypertension and valve pathology, inflammation of the heart muscle (myocarditis) and heart membranes (endocarditis, pericarditis), PE, dissecting aortic aneurysm, heart rhythm disturbances. The procedure is possible only after the condition has stabilized.
The scintigraphic method for examining the myocardium is a simple and safe procedure for the patient, which opens up wide possibilities for the diagnosis of coronary heart disease, its prognosis and control of treatment.
The cost of scintigraphy in the Russian Federation ranges from 4,000 to 15,000 rubles. The option of performing the procedure abroad is possible. In this case, the price may increase 5-10 times, depending on the prestige of the clinic.
The method is indispensable for assessing the volume of damage to the heart muscle, since it allows visualizing healthy areas and pathological foci and has no analogues in terms of information content.