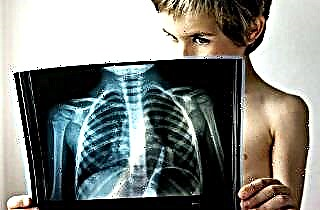
The heart's main function is to pump blood throughout the body. This organ is four-dimensional, each chamber is enclosed by a valve. The work of the left atrium is closely related to the pulmonary circulation. If there are any violations in this process, then this can lead to the development of a disease such as dilatation of the left atrium.

Definition
The human heart, like a hollow muscular organ, has its own margin of safety. It consists of two atria and ventricles, through which blood is pumped throughout the body. Sometimes it happens that its amount entering the cavity exceeds the allowable volume. Thus, the walls are subjected to increased loads, which eventually causes them to stretch (dilatation).
The most common dilatation of the left atrium. A change in its size occurs against the background of a disturbed outflow of blood. An increase in volumes on the left can lead to diseases of the right heart, if you do not resort to timely treatment. This state is dangerous because it does not manifest itself in any way at the first stages of development.
For a complete diagnosis of this pathology, the patient is assigned a number of studies. In the course of their conduct, concomitant diseases are often found, which are the cause of impaired heart function. It can be tachycardia, stenosis, or measuring arrhythmia.
It should be understood that early diagnosis will avoid irreversible consequences, which is why it is important to consult a doctor at the slightest ailment.
Classification and features
Atrial dilation is of two types:
- Tonogenic. It occurs as a result of high pressure and the presence of a large volume of liquid in the chamber. Most often, this form is accompanied by myocardial hypertrophy.
- Myogenic. This type of change occurs due to a variety of heart diseases and leads to a weakening of the contractile function of the myocardium. Such deviations in the cavities are irreversible.
Most often, only one heart chamber is enlarged. The danger of this condition is the risk of developing arrhythmias or chronic heart failure.
 The main function of the left atrium is to deliver oxygenated blood to the left ventricle. After that, it is pumped into the aorta and transported throughout the body. There is a valve between these sections. If its work is disrupted, then dilatation of the left atrial cavity develops. As a result, the blood passes heavily through the narrowed opening, which causes an overload of the heart wall and its stretching.
The main function of the left atrium is to deliver oxygenated blood to the left ventricle. After that, it is pumped into the aorta and transported throughout the body. There is a valve between these sections. If its work is disrupted, then dilatation of the left atrial cavity develops. As a result, the blood passes heavily through the narrowed opening, which causes an overload of the heart wall and its stretching.
There is no definite symptomatology for such changes. It is important that this disease is usually accompanied by other abnormalities in the work of the heart. Most often, patients complain of the onset of symptoms of arrhythmia and stenosis. They are manifested by shortness of breath, cyanosis, or pallor of the skin.
Changes in the right atrium can occur with an increase in pressure in the blood vessels of the small (pulmonary) circulation. Also, similar problems can occur against the background of myocardial infection and pulmonary hypertension. Some heart defects can also lead to an increase in the volume of the right atrium.
For effective treatment of such a phenomenon, first of all, it is necessary to establish the cause and stop it. If this is not done on time, then further hypertrophy and heart failure occur.
The most common treatment is surgery. To achieve a positive result, medical correction of the underlying disease is required.
Symptoms
 Moderate dilatation of the left heart is not accompanied by any symptoms. But with a strong expansion, the following signs already appear:
Moderate dilatation of the left heart is not accompanied by any symptoms. But with a strong expansion, the following signs already appear:
- dyspnea;
- change in heart rate;
- fatigue;
- decreased ability to mental stress;
- constant feeling of weakness;
- swelling of the limbs.
People who play sports at a professional level or hard physical labor have an enlarged left atrium. This is considered normal and does not require treatment. Sometimes patients find out that the chambers are expanded only during a routine examination and do not attach any importance to this, because they feel good.
If this pathology continues to progress, then the person feels not only shortness of breath in a calm state, but also coughing, pain in the chest area, increased sweating and surges in blood pressure.
Causes
The main cause of enlargement of the left atrium is considered to be a narrowing or insufficiency of the valve. In this case, excessive blood filling leads to stress on the muscles and their further stretching. With stenosis, blood always remains in the cavity, and when a new portion arrives, overfilling occurs, as a result of which the department gradually expands.
The reasons for the increase in the volume of the left atrium can be:
- vices;
- excessive physical activity;
- infectious diseases;
- alcohol abuse;
- tumor neoplasms;
- rhythm disturbances;
- autoimmune diseases;
- rheumatism.
 Atrial dilatation actively affects people with high blood pressure. The heart has to contract harder, which leads to abnormal muscle stretching.
Atrial dilatation actively affects people with high blood pressure. The heart has to contract harder, which leads to abnormal muscle stretching.
Expansion of the right atrium occurs against the background of the following factors:
- lung disease;
- pulmonary spasms;
- pulmonary hypertension;
- some types of vices;
- narrowing of the valve.
The growth of one or another part of the heart can occur due to inflammation of the heart muscle, which is a consequence of angina or scarlet fever. A variety of pathologies of an infectious or fungal origin, as well as taking certain drugs, can provoke the development of dilatation.
Forecast
Dilation of both atria requires treatment, as it is a pathological change. It is selected based on the cause of the disease. The generally accepted treatment regimen includes taking ACE inhibitors, antiplatelet agents, agents to improve tissue metabolism and relieve symptoms that accompany coronary heart disease.
With heart failure, the use of glycosides is required. Particular attention is paid to the normalization of the heart rate. For this purpose, beta blockers may be prescribed to the patient.
 Since dilatation is difficult to detect due to the absence of symptoms, drug therapy is not always able to eliminate the changes that have occurred, which may be irreversible. In this case, surgery may be required. If it is not possible to perform an operation, the main goal of treatment is to prevent a blood clot from breaking off. For this, a combination of "Digoxin", beta-blockers and "Warfarin" is used.
Since dilatation is difficult to detect due to the absence of symptoms, drug therapy is not always able to eliminate the changes that have occurred, which may be irreversible. In this case, surgery may be required. If it is not possible to perform an operation, the main goal of treatment is to prevent a blood clot from breaking off. For this, a combination of "Digoxin", beta-blockers and "Warfarin" is used.
If the transformations taking place are ignored, they can cause heart failure or life-threatening arrhythmias. At the same time, the timely detected pathology and its adequate treatment is not a guarantee of success, but will allow to stabilize the condition and improve the patient's quality of life.
By eliminating the cause that triggered the problem, you can stop the progression of dilatation.
An integral part of therapy is prevention and regular examination by a cardiologist. Without these measures, a positive outcome is almost impossible.
To avoid serious heart health problems, you need to:
- Follow your diet and eat healthy foods. The diet should be saturated with plant foods.It is recommended to consume lean meat, fish, seafood, cereals and various types of nuts. It is advisable to exclude fried, fatty foods, as well as foods with a high salt content from the diet.
- Get regular light exercise. It is best to increase the duration of walks in the fresh air, do morning exercises.
- Eliminate all bad habits. It is very important to completely avoid alcohol and cigarettes.
Compliance with a diet, monitoring body weight, regularly visiting a doctor and following his recommendations - all this will allow to suspend the pathological process and improve the quality of life during dilatation.