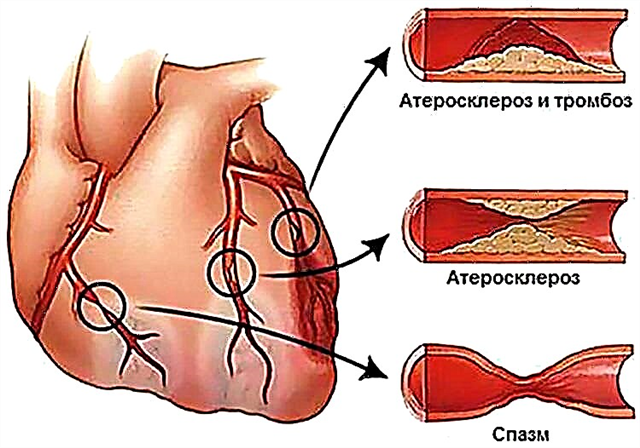
Stress and hypertension are closely related. People who are often worried notice a deterioration in their general well-being. Nervous hypertension is aggravated in the presence of a hereditary predisposition and concomitant diseases.
Development mechanism
The term is understood as a persistent or temporary increase in blood pressure (above 140/90 mm Hg) after a stressful situation.
 The main mechanism of occurrence is the accumulation of oxidants in tissues under the influence of stress. This is manifested by the free oxidation of lipids in cells. Especially this condition concerns the neurons of the nervous system.
The main mechanism of occurrence is the accumulation of oxidants in tissues under the influence of stress. This is manifested by the free oxidation of lipids in cells. Especially this condition concerns the neurons of the nervous system.
The main centers that regulate the level of blood pressure are the medulla oblongata and the cerebral cortex. In these structures, the sensitivity of neurons changes to the action of certain substances (neurotransmitters). This is manifested by the formation of emotional arousal in the brain, which leads to a persistent change in the mechanisms of blood pressure regulation. As a result, temporary nervous hypertension appears, which, without treatment, can acquire a chronic course.
Stress and blood pressure are inextricably linked, thanks to the participation of nitric oxide in this process. Its deficiency is explained by the narrowing of the blood vessels, as a result of which persistent nervous hypertension is formed. This leads to disturbances in the normal functioning of the heart and kidneys.
Increased stress pressure leads to increased release of renin (an enzyme in the kidneys that regulates blood pressure) and angiotensin (a hormone that causes vasoconstriction). At the same time, nervous excitability is increased. This is due to the adverse effects of these hormones. An overestimated level of angiotensin in the blood leads to an increase in the production of adrenaline and norepinephrine. They are stress hormones that protect the body. Adrenaline causes the heart muscle to contract more often, while simultaneously constricting blood vessels. Therefore, in people with pressure at the border of the norm, hypertension is noted on the nervous basis and during complete calmness.
High levels of adrenaline are considered dangerous to the body. Normally, it increases pressure and therefore must be completely consumed. If this does not happen, then there is first a temporary increase in it, and then a permanent one. Long-term stress disrupts the normal functioning of the heart, which over time increases the risk of developing chronic diseases.
Psychoemotional stress provokes the release of catecholamines - adrenaline and norepinephrine. These hormones increase blood pressure. Arterial hypertension from the nerves is caused by the following reasons:
- surgical intervention;
- hypoglycemia (a decrease in the concentration of glucose in the blood below normal);
- trauma;
- alcohol withdrawal;
Approximately 2 hours after surgery, many patients notice an increased level of blood pressure, this is a manifestation of hypertension. The main mechanism that can increase it is the activation of the nervous system. The level of catecholamines in patients under stress is significantly higher than normal values. Postoperative nervous hypertension usually lasts no longer than 24 hours.
The most excitable patient population is those with hypoglycemia. After emotional stress, high levels of adrenaline significantly increase systolic pressure. To a lesser extent, it is affected by norepinephrine.
The emergence of acute stress is possible after the abolition of alcohol, and the increased activity of the nervous system becomes its result. This condition develops 3-4 hours after the last intake of an alcoholic drink. The highest level of catecholamines is observed after injury. This is especially true when the renal artery, kidneys, and adrenal glands are damaged.
Treatment
A large number of factors increase blood pressure. For the treatment of nervous hypertension, medication and non-medication methods are used. Complex therapy is the most effective in comparison with monotherapy (use of a single agent).
 Medication is a way to treat hypertension that improves quality of life while reducing the risk of premature mortality. It is known that until 1950 they did not use medicines to resolve this issue. In the absence of an additional method of treating nervous hypertension among patients, there was a high risk of chronic diseases of the cardiovascular system, complications from other internal organs.
Medication is a way to treat hypertension that improves quality of life while reducing the risk of premature mortality. It is known that until 1950 they did not use medicines to resolve this issue. In the absence of an additional method of treating nervous hypertension among patients, there was a high risk of chronic diseases of the cardiovascular system, complications from other internal organs.
Basis of therapy
If nervous hypertension occurs, the first step is not to take medications. The basis for further successful treatment should be provided by:
- Limiting the use of table salt.
- Refusal to drink alcohol. It is noted that taking 80 g of the drink every day can increase the risk of hypertension several times.
- Weight loss.
- Active lifestyle.
It is enough to go in for sports for the prevention of nervous hypertension for 30-40 minutes, 3 times a week. Exercise is especially recommended for people with a sedentary lifestyle. The most favorable is the following pattern of activities: daily walking about 6 km and light jogging. Lessons in the pool effectively help to cope with high blood pressure levels. With constant training in combination with proper nutrition, blood pressure indicators in case of nervous hypertension decrease by 7-9 mm Hg.
In addition to playing sports, it is important to review your diet: add healthy foods, exclude harmful ones. Some are able to calm the nervous system and have a relaxing effect on the heart and blood vessels.
Arterial hypertension and hypertensive crisis can be prevented by potassium, B vitamins and calcium. These substances are rich in meat products, egg yolk, spinach, nuts, bananas and dried fruits. To maintain normal regulation of hormonal levels, iodine is needed. Therefore, patients should eat seaweed and seafood. It is recommended to limit fatty, smoked, salty foods.
Excessive consumption of alcoholic beverages reduces the effectiveness of antihypertensive drugs. When a desire to drink appears, it is allowed to take a drink (wine), without harm to health, in an amount not exceeding 140 ml.
It contains natural antioxidants (vitamins from groups A, C and E), substances that lower cholesterol levels. Therefore, natural wine helps to reduce excitement from the nervous system and the risk of high blood pressure or hypertensive crisis against a background of stress. At the first signs of arterial hypertension, it is necessary to start moving more, and not lie down. This will calm the nervous system and allow the high blood pressure to slowly return to normal.
Many patients with a tendency to nervous hypertension practice breathing exercises. Thanks to a special technique, it will be possible to reduce blood pressure by 10-15 mm Hg. Before you start breathing, you need to calm down. A slow deep exhalation is performed, the breath is held for a short time. Then a slow breath is taken. This technique has a calming and hypotensive effect within 10-15 minutes from the beginning of breathing exercises.
A warm bath is considered an effective and simple remedy for nervous hypertension.To do this, you need warm water with a temperature of 35-39˚С. You can add sea salt, essential oils to it. Additionally, after taking a warm sitz bath, you can do the same for your feet. The duration should not exceed 20 minutes.
 Home aromatherapy sessions are useful to help you relax after a stressful situation. It has a beneficial effect on blood vessels, which leads to a decrease in pressure in case of nervous hypertension. The following oils are suitable for the procedure:
Home aromatherapy sessions are useful to help you relax after a stressful situation. It has a beneficial effect on blood vessels, which leads to a decrease in pressure in case of nervous hypertension. The following oils are suitable for the procedure:
- lavender;
- ylang-ylang;
- the Rose;
- marjoram;
- bergamot;
- citrus.
Before aromatherapy, add no more than 3 drops of oil to the bathroom. If desired, they can be mixed to obtain different compositions of smells. During the procedure, you can lubricate the skin along the spine and the back of the neck with oils.
Ethnoscience
High blood pressure can be treated with traditional medicine. Chokeberry is considered one of these. It is recommended to eat 10-15 g of berries daily or drink juice based on them for up to 15-20 days. Garlic with vodka effectively helps with nervous hypertension. To obtain a solution, you will need 2 of its heads, which must first be crushed. Then it is mixed with 250 g of vodka and infused for 12 days and taken in 20 drops for 3 weeks. Mint can be added to enhance the palate.
One of the effective and tasty recipes for the treatment of nervous hypertension is a collection consisting of rose hips (2 tablespoons), juniper (2 tablespoons of cones), lemon balm (2 tablespoons) and dill (1 tablespoon). Mix all herbal ingredients and pour a liter of boiling water. The received collection is insisted within 4 hours. Then it is taken warm in 0.5 cups half an hour before meals.
Salt dressings help with nervous hypertension. The action is based on the phenomenon of osmosis - the tendency of water from a lower concentration to a higher one. Therefore, when a bandage is applied, excess fluid will be excreted from the body. This normalizes blood pressure readings. The bandage is applied to the lumbar region or the back of the head if a headache appears with nervous hypertension.
To obtain a saline solution, you will need 2 teaspoons of table salt and a glass of warm water. In it, a cotton cloth is abundantly moistened, lightly wrung out and applied to the skin. The same cloth is applied on top of the bandage, but dry. It must be kept for at least 4 hours. It is important to remember that a prerequisite is free air access through the tissue of the saline dressing.
Medicines
If a person is not hypertensive, you should not immediately start treatment with antihypertensive drugs. It is enough to calm down and take a sedative to relieve irritability. The best are herbal medicines (valerian, lemon balm, motherwort). Patients with high blood pressure on a nervous basis, in addition to sedatives, are prescribed additional groups of drugs. These include:
- beta blockers;
- diuretics;
- calcium channel blockers;
- ACE inhibitors;
- alpha blockers;
- drugs with a central mechanism of action (antagonists of imidazoline receptors).
Diuretics ("Furosemide", "Hypothiazide") lower blood pressure due to increased excretion of excess fluid and salts. This ultimately leads to relaxation of the walls of the blood vessels.
The principle of action is based on the acceleration of renal blood flow. With a sharp jump in pressure, provoked by stress, diuretics are injected through a vein. Preparations from the group of beta-blockers ("Carvedilol", "Nebivolol") reduce it by affecting the nervous system. They block the conduction of nerve impulses from prescriptions, which is manifested by a slowdown in the heart rate and normalization of blood pressure in case of nervous hypertension.
Calcium channel blockers (Flunarizin, Klentiazem) prevent the flow of calcium into the cell, slowing down its contraction. As a result, blood pressure decreases in hypertensive patients. ACE inhibitors ("Captopril", "Enalapril") reduce the vasoconstrictor response due to the weakening of the influence from the nervous system. The task of alpha-blockers ("Doxazosin", "Prazosin") is the same as that of drugs from the group of beta-blockers, but they affect other receptors. Under the action of drugs with a central mechanism of action ("Rilmenidine", "Moxonidine"), vascular spasm is eliminated, which leads to the normalization of blood pressure in case of nervous hypertension.
In every person's life, there are many situations associated with stress. For this reason, for some people, with emotional overstrain, temporary, and over time, persistent nervous hypertension occurs. To prevent such a condition from becoming permanent, timely treatment with drugs in combination with non-drug methods of therapy is necessary.
<