Angina (tonsillitis) refers to diseases of the ENT organs. It consists in the rapid development of the inflammatory process in the tonsil area, which progresses rapidly and causes severe complications. Timely treatment of angina in a nursing mother is a guarantee of the health of not only a woman, but also a child.
Colds, infectious processes, exacerbation of chronic diseases for women in the lactation period are considered almost the norm. This is due to a decrease in the protective properties of immunity, as a result of which the body becomes more susceptible to infections, it does not have enough strength to cope with diseases on its own.
 The postpartum recovery period implies a gradual strengthening of immunity, however, forces are still spent on feeding the child to ensure a sufficient supply of nutrients and components of immunity for its full growth and development.
The postpartum recovery period implies a gradual strengthening of immunity, however, forces are still spent on feeding the child to ensure a sufficient supply of nutrients and components of immunity for its full growth and development.
Primary tonsillitis
In most cases, the primary development of tonsillitis refers to an acute pathology of bacterial genesis, in particular, streptococcal infection. Among the symptoms, it is worth highlighting:
- increased sweating, fatigue, decreased appetite;
- feeling overwhelmed;
- fever;
- sore throat.
Inflammation is often localized in the palatine tonsils, but other tonsils (lingual, pharyngeal) may be affected. In addition, regional lymph nodes suffer, in which there is swelling, enlargement, soreness when palpating.
Angina is dangerous by the spread of streptococcal infection with the development of rheumatism, myocarditis, glomerulonephritis.
In addition to streptococcus, the causative agent of tonsillitis can be Haemophilus influenzae, corynebacteria. Infection occurs by airborne droplets or through food (minced meat, milk). Especially the risk of infection increases against the background of colds, hypothermia, overwork.
Depending on the type of inflammation, there are several main forms of tonsillitis:
- Catarrhal, when the tonsils increase due to infiltration, tissue edema. Against the background of therapy, the symptoms decrease already by 3 days, however, without treatment, a more severe form develops.
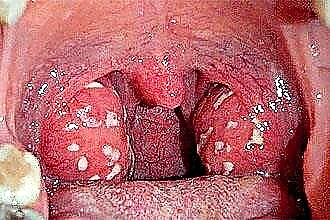 Follicular, in which purulent follicles are visible through the edematous tissues. After opening them, a film appears on the surface of the tonsils. Signs of intoxication are moderately expressed.
Follicular, in which purulent follicles are visible through the edematous tissues. After opening them, a film appears on the surface of the tonsils. Signs of intoxication are moderately expressed.- Lacunar. With this form, fibrinous-purulent masses accumulate in the lacunae, which lead to the development of severe intoxication, and the risk of abscess formation increases.
- Necrotic. On the surface of the tonsils, films of a gray shade are located, which spread to neighboring areas (arches, uvula, pharynx). When trying to remove plaque, ulcerative defects remain. Fever reaches 40 degrees, confusion, brain hypoxia is noted.
Symptoms
The disease develops rapidly with fever, body aches, severe weakness. Sore throat gradually increases, from which sleep is disturbed, mood and appetite deteriorate. An increase in the cervical, submandibular lymph nodes indicates the development of an inflammatory process.
With the formation of an abscess, fever reaches 40 degrees, it is difficult to swallow, open the mouth.
Hectic hyperthermia increases the risk of seizures, brain hypoxia, loss of consciousness, therefore, antipyretics are taken at temperatures above 38 degrees.
Specific sore throats
The most common types of tonsillitis are:
- Pharyngeal diphtheria, which has a locally localized, widespread, toxic form. A dense plaque is formed on the tonsils, the lashes are difficult to remove, after which a bleeding surface remains.

- Fungal type that is caused by yeast-like fungi. Intoxication syndrome is poorly expressed, “curdled” masses are recorded on the tonsils, after removal of which a smooth varnished surface remains.
- Simanovsky-Vincent is due to the combined activity of the fusiform bacillus, spirochete. Their disease-causing properties appear with non-observance of oral hygiene, smoking. On one amygdala, an ulcerative defect with a slight coating is observed. Without treatment, the process extends beyond the amygdala, but without affecting the other.
Secondary tonsillitis
The secondary origin of tonsillitis is observed with improper treatment of the underlying disease (influenza, measles, leukemia), when angina develops as a complication of untreated pathology. To distinguish the primary from the secondary genesis, it is enough to analyze the symptoms, to examine the patient.
Angina is observed in scarlet fever, syphilis, tularemia, enterovirus infection, infectious mononucleosis, agranulocytosis. Given this, we can conclude that the treatment of angina is not always the task of the otolaryngologist. For a comprehensive examination, you may need to consult a venereologist, infectious disease specialist, hematologist and other narrowly focused specialists.
General directions in treatment
In order to find out how and what of the drugs to treat a sore throat for a nursing mother with constant breastfeeding, you need to consult a doctor. Thanks to a complete examination and an individual integrated approach, it is possible to quickly cure the disease without harm to the health of the child.
It is recommended for a woman:
- bed rest, which allows you to maintain and restore strength to fight infection.
- Drinking plenty of warm drinks will speed up the release of toxins. Compote, fruit drink (cranberry, lingonberry), rosehip broth, herbal teas (chamomile, calendula) are especially useful. Fruit jelly, due to its viscous consistency, allows you to envelop the walls of the pharynx and activate regeneration.
- multivitamins;
- sparing nutrition, which excludes solid food to prevent trauma to swollen tonsils, the spread of infection throughout the body.
Gargling, throat irrigation
Starting from the first day when symptoms of the disease appear, it is recommended to start gargling. This makes it possible to stop the infectious process at an early stage, preventing its progression. At the stage of catarrhal sore throat, it is much easier to cure the disease than with advanced forms. Regular rinsing makes it possible to remove the infection from the oral cavity, as a result of which the pathogen does not penetrate deep into the tonsils.
Treatment of angina during lactation by rinsing is carried out with the following drugs: furacilin, chlorophyllipt, chlorhexidine, tincture of eucalyptus, calendula.
From folk remedies, some recipes should be distinguished:
- infusion of a mixture of sage, chamomile;
- infusion of garlic;
- aloe juice, kalahnoe;
- salt, soda;
- cranberry juice, honey.
Rinsing is carried out alternately with different means with an interval of 1-1.5 hours.
How to treat a sore throat for a nursing mother without antibiotics? If a woman manages to detect the inflammatory process in a timely manner, start therapy, the doctor may not prescribe antibiotics when confirming the regression of the disease based on the results of the diagnosis.
Lozenges, sprays
With gv in the intervals between rinses, it is recommended to dissolve lozenges, tablets with anti-inflammatory, antiseptic, analgesic effect. To reduce sore throat, the use of Trahisan, Strepsils, Lizobact is allowed.
Sprays are also used between rinses. Permitted sprays include Chlorophyllipt, Chlorhexidine, Ingalipt.
Antibacterial therapy
With the progression of the disease, the appearance of purulent masses, antibacterial agents are prescribed. Since it is quite difficult to treat angina while breastfeeding, the choice of approved medicines is carried out exclusively by the doctor, taking into account the type of pathogen, its sensitivity to antibacterial drugs.
Already on the 3rd day from the onset of the disease, without timely therapy, follicular, lacunar tonsillitis develops with a pronounced intoxication syndrome. When angina is diagnosed during breastfeeding, approved drugs include cephalosporin antibiotics, such as Cephalexin, macrolides (Sumamed, Azithromycin), protected penicillins (Amoxiclav, Flemoxin).
Prohibited antibacterial agents (fluoroquinolones, tetracyclines) lead to disruptions in the functioning of the child's organism systems, pathology of the hematopoietic organs.
 Experts are divided on the issue of stopping breastfeeding. Some doctors adhere to the tactic of short-term cessation of lactation for a period of up to 3 days, during which the woman takes the prescribed drugs in a therapeutic dosage. This allows an accelerated course to overcome the infection, eliminate the symptoms of the disease.
Experts are divided on the issue of stopping breastfeeding. Some doctors adhere to the tactic of short-term cessation of lactation for a period of up to 3 days, during which the woman takes the prescribed drugs in a therapeutic dosage. This allows an accelerated course to overcome the infection, eliminate the symptoms of the disease.
Other experts are confident that short-term intake of antibacterial agents from approved groups does not have a negative effect on the child, so feeding should not be stopped. During the course of the treatment, the child is prescribed probiotics.
Compliance with preventive measures is much easier than treating sore throats with breastfeeding. Thanks to the recommendations, it is possible to significantly reduce the risk of not only sore throat, but also other infectious diseases.
So, a woman needs:
- avoid crowds of people during a flu epidemic;
- dress warmly, avoid drafts;
- take multivitamins;
- devote enough time to sleep, rest;
- eat properly;
- avoid psycho-emotional overwork;
- often ventilate the room, do wet cleaning;
- use a humidifier.
All of the above tips allow you to increase the body's immune defenses, which is so necessary not only for a woman, but also for a child who receives everything necessary for the formation of good health with milk.

 Follicular, in which purulent follicles are visible through the edematous tissues. After opening them, a film appears on the surface of the tonsils. Signs of intoxication are moderately expressed.
Follicular, in which purulent follicles are visible through the edematous tissues. After opening them, a film appears on the surface of the tonsils. Signs of intoxication are moderately expressed.