Angina (acute tonsillitis) is an infectious disease characterized by inflammation of the main parts of the lymphatic pharyngeal ring (palatine and nasopharyngeal tonsils). Pathology arises due to the development of bacterial flora in the ENT organs, represented mainly by gram-positive microbes. A provocateur of inflammation can be staphylococcus or hemolytic streptococcus, less often a yeast-like fungus or virus.
 Why is angina dangerous? Untimely relief of pathological processes in the respiratory tract contributes to the spread of infection and damage to other organs and systems. The most formidable complication of tonsillitis is tonsillogenic sepsis, characterized by the formation of metastatic abscesses in the internal organs.
Why is angina dangerous? Untimely relief of pathological processes in the respiratory tract contributes to the spread of infection and damage to other organs and systems. The most formidable complication of tonsillitis is tonsillogenic sepsis, characterized by the formation of metastatic abscesses in the internal organs.
Pathogenesis
For what reason do complications arise after a sore throat? The penetration of pathogens into the respiratory tract is an impulse for the production of specific antibodies by the immune system. In turn, glycoprotein neoplasms identify foreign microorganisms in the blood and destroy them, neutralizing metabolites and poisons in tissues.
Streptococcus slopes to the number of facultative anaerobic bacteria, containing in its composition a whole complex of antigens, similar in structure to antigens of joints, muscle and kidney tissue. For this reason, the immune system can attack not only disease-causing bacteria, but also the tissues of its own organs. If the infection is not eliminated in time, the following types of complications may occur:
- systemic - pathological processes in the body resulting from the development of immunological disorders. The systemic consequences of angina are characterized by damage to the joints, heart muscle, kidneys and brain membranes;
- local - relatively mild complications of angina, localized only in certain areas of the respiratory tract. As a rule, they do not pose a particular threat to life, however, untimely elimination of local complications can lead to more serious consequences.
Important! Early termination of the course of drug treatment most often leads to the development of complications.
Etiology
Often the cause of severe complications after acute tonsillitis is untimely antibiotic therapy or early termination of the course. An apparent recovery forces many patients to stop drug treatment, as a result of which the foci of inflammation begin spread to adjacent organs and tissues. In addition, a complication can occur for the following reasons:
spread to adjacent organs and tissues. In addition, a complication can occur for the following reasons:
- antibiotic abuse;
- incorrect diagnosis and therapy;
- treatment exclusively with folk remedies;
- reduced body resistance;
- premature refusal of drug treatment.
If the doctor prescribes a course of treatment lasting 10-14 days, you cannot refuse to take medications ahead of schedule. The apparent improvement in well-being does not guarantee the absence of microbial agents in the affected tissues. Recurrence of tonsillitis leads to serious consequences, some of which can threaten a person's life.
When to see a doctor?
The symptoms of tonsillitis are very similar to the manifestations of most ENT diseases, accompanied by the formation of foci of inflammation in the airways. In the event of characteristic clinical manifestations of the disease, you should consult a specialist. Self-treatment of acute tonsillitis can lead to serious consequences, in particular the development of myocarditis or renal failure.
What are the main symptoms of a bacterial infection? Some of the most common signs of a sore throat include:
- febrile fever;
- discomfort in the throat;
- muscle weakness;
- headache;
- lack of appetite;
- enlarged lymph nodes;
- hyperemia of the tonsils.
A characteristic sign of the development of tonsillitis is a white coating on the mucous membrane of the throat, resulting from the formation of purulent foci in the ciliated epithelium.
Having discovered the first symptoms of an ENT disease, it is advisable to be examined by a specialist. As a rule, self-treatment does not contribute to recovery, which is due to the ineffectiveness of the drugs used. Confusing a sore throat with a cold, many patients try to stop the manifestations of the disease with antiviral agents. However, the bacterial flora is not sensitive to the effects of antiviral medications, which contributes to the unhindered spread of infection in the body.
Heart rheumatism
In most cases, complications after a sore throat make themselves felt 2-3 weeks after the elimination of inflammation in the ENT organs. Ineffective therapy can cause the development of rheumatism of the heart, characterized by the formation of scars on the heart muscle. Why it happens?
If antibiotics are not prescribed in time to destroy the bacterial flora, their own antibodies will continue to attack both pathogens and their own organs, in which antigens have a similar structure. As a result, the destruction of proteins occurs in the connective tissue, which is accompanied by rheumatic processes in the heart. Damage to heart valves can lead to heart defects, which can be fatal.
Important! Failure to comply with bed rest during the treatment of acute tonsillitis often leads to the development of heart complications.
Much less often, after the transfer of a bacterial infection, myocarditis occurs, i.e. inflammatory process in the heart muscle. With the development of pathology, symptoms such as acute pain in the region of the heart, shortness of breath, tachycardia, dizziness, etc. may appear.
Kidney disease
Violations of the genitourinary system are frequent complications after a sore throat. Long-term exposure to antibodies on kidney tissue contributes to the development of severe diseases such as:
- glamerulonephritis is an infectious-allergic lesion of glomeruli (renal tangles), which occurs due to changes in the morphology of the kidneys. If the pathology is not eliminated in time, the kidneys will cease to function, which will lead to an increase in the concentration of urea and toxins in the blood, the result of which is a uremic coma;
- pyelonephritis is an inflammatory process in the main parts of the tubular system of the kidneys: pelvis, parenchyma and renal cups. A bacterial infection can penetrate into the interstitial tissue, which is fraught with disruption of intercellular metabolism in tissues and, as a result, severe intoxication of the body.
If the therapy for sore throat has been unsuccessful, kidney complications may appear within 3-4 weeks after infection of the body. In this case, such characteristic symptoms as chills, febrile temperature, pain in the kidney area, swelling of the extremities, etc. occur.
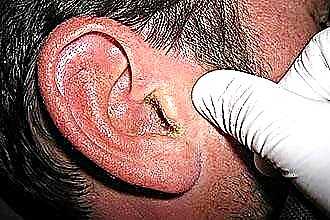
Ear infection
Otitis media is one of the most common complications after having a sore throat. As a result of inflammation of the upper respiratory tract, the risk of penetration of bacterial flora into the middle ear cavity through the Eustachian tube increases. The first few days, the infected ear practically does not hurt, which complicates the diagnosis and treatment.
An inflamed ear begins to hear poorly, which in most cases is associated with tissue edema and impaired conduction of sound signals. If foci of inflammation form in the mucous membrane of the tympanic cavity, average bacterial (purulent) otitis media is diagnosed.With the development of pathology, the following symptoms are most often manifested:
- congestion;
- decreased hearing acuity;
- shooting pains;
- dizziness;
- otorrhagia;
- purulent discharge;
- hyperemia of the ear membrane.
The ear is a sensitive organ, an infectious lesion of which is fraught with the development of hearing loss. Failure to eliminate bacterial infection in a timely manner can cause pathogens to enter the inner ear. The development of labyrinthitis can contribute to the onset of sensorineural hearing loss, which is virtually untreatable.
Important! If the ear is left untreated for a long time, it can be fraught with the development of meningitis or sepsis.
To prevent the development of otitis media, hearing loss, mastoiditis and other complications, antibacterial and anti-inflammatory drugs should be instilled into the sore ear. At the stage of regression of catarrhal processes, physiotherapeutic treatment can be prescribed. To cure the ear from purulent otitis media, it is more advisable to resort to electrocoagulation, phototherapy and magnetotherapy.
Chronic tonsillitis
Local complications after tonsillitis are most often characterized by chronic inflammation of the palatine and pharyngeal tonsils. If an infectious disease is not treated for a long period, a sluggish inflammation is likely to occur in the mucous membrane of the pharynx with a 90% probability. The provocateurs of the development of chronic tonsillitis are most often the coccal flora, represented by streptococci, staphylococci and pneumococci.
The development of focal infection is based on prolonged inflammation in the mucous membranes of the upper respiratory tract. If it is not possible to stop the manifestations of acute tonsillitis within 2-3 weeks, purulent foci form in the tonsils. Their appearance contributes to the loosening of the ciliated epithelium and changes in tissue morphology. With the development of chronic tonsillitis, a gradual poisoning of the body with bacterial metabolites occurs, which can lead to regional lymphadenitis.
If it is not possible to eliminate inflammation in the tonsils with the help of drug treatment, the patient is offered to undergo tonsillectomy, i.e. procedure to remove tonsils.




