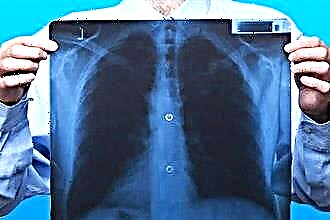
Chronic frontal sinusitis is an ailment in which the mucous membrane of the frontal sinus becomes inflamed. The illness usually lasts more than one month. Often the acute form of frontal sinusitis becomes chronic due to untimely access to a doctor or improper treatment. Such a disease is dangerous primarily because the affected frontal sinuses are located very close to the orbit and brain structures. This means that the inflammatory process can affect the soft tissues of the orbit and lead to various intracranial complications (even lethal outcome is possible).
Key causes of the disease
 Chronic frontal sinusitis is caused by pathogenic microbes such as streptococci, haemophilus influenzae and Staphylococcus aureus. Recent experimental studies using the polymerase chain reaction (PCR) method have also identified other causative agents of the disease - chlamydia, mycoplasma, and so on.
Chronic frontal sinusitis is caused by pathogenic microbes such as streptococci, haemophilus influenzae and Staphylococcus aureus. Recent experimental studies using the polymerase chain reaction (PCR) method have also identified other causative agents of the disease - chlamydia, mycoplasma, and so on.
Acute frontal sinusitis appears against the background of tonsillitis, acute respiratory viral infections or influenza and is complicated by various harmful microorganisms. The local immunity of the frontal sinus is noticeably weakened, which does not allow the body to cope with the infection on its own. Thus, the acute form of the disease is transformed into chronic frontal sinusitis.
One of the key risk factors in the formation of a chronic form of frontal sinusitis is the narrowing of the frontal pocket. This pathology blocks sinus drainage. Adenoids or changes in the structure of the shells contribute to the appearance of excess pressure in the nasal cavity. As a result, the mucous membrane is often injured. All this negatively affects the condition of the mouth of the frontal-nasal canal, which is constantly inflamed and edematous.
In addition to the above, there are several more factors that contribute to the appearance of chronic frontal sinusitis:
- ingress of a foreign body into the nasal cavity;
- mechanical injury to the nose;
- ozena (atrophy of the cartilaginous and bone structures of the nose);
- vasomotor or allergic rhinitis of the chronic type;
- deformation of the nasal septum;
- reduced immunity;
- general weakening of the body due to bad habits;
- excessive length or narrowness of the frontal-nasal canal;
- polyps and cysts in other paranasal sinuses;
- regular contact with allergens (dust, animal hair, etc.);
- frequent hypothermia.
Often, as the chronic form of frontal sinusitis develops, the tissues in the anterior cells of the ethmoid labyrinth become inflamed in parallel. In addition, chronic sinusitis can develop at the same time.
Symptoms and complications
 It should be noted right away that with an acute form of frontal sinusitis, the symptoms will always be brighter than with chronic. Despite this, the majority of patients suffering from chronic frontal sinusitis complain of constricting and aching headaches. This is the first and main symptom of an illness. With regular hypothermia or after a cold, swelling appears within the frontal sinus and a violation of the outflow of mucus occurs.
It should be noted right away that with an acute form of frontal sinusitis, the symptoms will always be brighter than with chronic. Despite this, the majority of patients suffering from chronic frontal sinusitis complain of constricting and aching headaches. This is the first and main symptom of an illness. With regular hypothermia or after a cold, swelling appears within the frontal sinus and a violation of the outflow of mucus occurs.
The result is an increase in pressure and an intensification of pain (especially when feeling the frontal region). In addition, the discomfort increases after drinking alcoholic beverages, coffee, mental exertion and insomnia.
In addition to headaches, chronic frontal sinusitis is also manifested by profuse nasal discharge (especially in the morning after sleep). They have an unpleasant odor and may include blood particles or casioid particles (dead cells). The mucus enters the mouth, flowing down the back of the nasopharynx. Therefore, the patient constantly tries to cough it up, suffers from bouts of nausea and even vomiting.
Chronic frontitis is accompanied by other symptoms:
- fear of bright light;
- frequent lacrimation;
- violation of the sense of smell;
- decreased visual acuity;
- increased eye pressure;
- nasal congestion;
- impossibility of nasal breathing;
- feeling of excess pressure in the frontal area;
- aching pain in the temples.
If the disease worsens, the clinical manifestations intensify. There are characteristic signs of body poisoning by the waste products of pathogenic bacteria (intoxication). The patient's temperature rises to subfebrile values (up to 39 degrees). Dizziness, general weakness and weakness are observed.
 Improper treatment or its complete absence can cause secondary dacryocystitis, polyps, mucocele and granulation within the frontal sinus. Such changes provoke depletion of the walls of the paranasal cavity. Therefore, the infection spreads to the bone and periosteum. In chronic frontal sinusitis, fistulas are often formed, which contribute to the appearance of open-type empyema. The disease becomes even more complicated if pathogenic microflora seeps through the lower wall of the sinus, and purulent masses enter the orbit.
Improper treatment or its complete absence can cause secondary dacryocystitis, polyps, mucocele and granulation within the frontal sinus. Such changes provoke depletion of the walls of the paranasal cavity. Therefore, the infection spreads to the bone and periosteum. In chronic frontal sinusitis, fistulas are often formed, which contribute to the appearance of open-type empyema. The disease becomes even more complicated if pathogenic microflora seeps through the lower wall of the sinus, and purulent masses enter the orbit.
In addition, pus can flow outside the sinus through the posterior cerebral wall. In this case, purulent meningitis, extradural abscess and some other dangerous complications occur. They can lead to early death, despite surgery.
Diagnostics
After the symptoms are found, it is necessary to perform instrumental diagnostics. For this, a rhinoscopic examination is carried out, which allows to detect the presence of pus.
 X-rays are often prescribed by doctors. It makes it possible to determine the current state of the frontal sinuses (their size, shape, interaction of one sinus with another) and the presence / absence of mucus in them. Neoplasms in the form of polyps are detected by unevenness or partial darkening of the lumen of the sinus. Also, in the diagnostic process, diaphanoscopy (non-invasive screening method) is used.
X-rays are often prescribed by doctors. It makes it possible to determine the current state of the frontal sinuses (their size, shape, interaction of one sinus with another) and the presence / absence of mucus in them. Neoplasms in the form of polyps are detected by unevenness or partial darkening of the lumen of the sinus. Also, in the diagnostic process, diaphanoscopy (non-invasive screening method) is used.
As an addition, laser flowmetry, ultrasound, direct joulemetry can be performed. To confirm or deny the presence of intracranial complications, MRI, CT and scintigraphy are used. Invasive diagnostic methods are used - resistometry and mucosal biopsy. A new method of examination - endoscopy (visual examination of the affected area) - is distinguished by high accuracy.
Consultations with a neurologist or ophthalmologist are prescribed immediately before surgery or when symptoms of possible complications are present.
Treatment directions
- Mucus tests are taken immediately before therapy. The type of pathogenic microflora is determined, the optimal methods of influencing it are selected.
- Prolonged chronic frontal sinusitis, the treatment of which consists in eliminating the inflammatory process, involves the use of antibiotics and other drugs. The outflow of mucus from the affected frontal sinus is necessarily restored. In addition, the doctor prescribes anti-inflammatory drugs and drugs to relieve swelling of the mucous membrane. If chronic frontal sinusitis is of an allergic nature, antihistamines are used.
- In parallel, infectious foci in other paranasal sinuses (if any) are detected and eliminated. This is extremely important, since the constant circulation of microbes in the nasal cavity does not effectively fight chronic frontal sinusitis. This condition can be called the key to the successful treatment of the disease.
 Additionally, the sinuses are washed and their cavity is irrigated with antiseptic and antibacterial solutions. Due to the use of funds for vasoconstriction, it is possible to quickly eliminate puffiness and activate the outflow of mucus.If purulent accumulations are not detected during frontalitis of the chronic type, warming up in the form of dry warm compresses on the frontal and nasal regions is prescribed.
Additionally, the sinuses are washed and their cavity is irrigated with antiseptic and antibacterial solutions. Due to the use of funds for vasoconstriction, it is possible to quickly eliminate puffiness and activate the outflow of mucus.If purulent accumulations are not detected during frontalitis of the chronic type, warming up in the form of dry warm compresses on the frontal and nasal regions is prescribed.- When medication therapy does not bring the expected result, surgical intervention is necessary. The operation is indicated if the inflammation has spread to the periosteum and frontal bones, polyps and cysts have appeared. The surgical method of treatment involves the creation of a small hole in the sinus and the regular introduction of antibacterial agents, hormonal and some other drugs through it.
Medicines from the arsenal of traditional medicine
As for folk remedies, the most effective are inhalations, massage and breathing exercises. The anatomical location of the frontal sinuses does not allow for effective use of sprays and drops. The drugs simply cannot penetrate the affected area. Therefore, inhalation comes to the rescue.
Moist air containing extracts of medicinal plants, vapors of essential oils or herbal infusions easily penetrates absolutely all parts and sinuses of the nose. Pour clean water into an enamel container, bring it to a boil, and then add one of the following:
 Healing herbs - St. John's wort, oak bark, burdock, calendula, chamomile and so on.
Healing herbs - St. John's wort, oak bark, burdock, calendula, chamomile and so on.- Essential oils of black cumin, sea buckthorn, thuja, fir.
- Bay leaf, propolis, horse chestnut, honey, garlic.
Feel free to cover yourself with a towel or blanket so that the steam does not dissipate. Inhale it for 10-15 minutes.
Also pay attention to the massage of the soles and facial area. It is effective against chronic frontal sinusitis. The massage should be carried out until complete recovery. The duration of each session is about 15 minutes. Do not forget about daily breathing exercises. It will accelerate recovery and normalize the general condition of the body.
Chronic frontitis is a dangerous disease that is fraught with serious complications, up to and including death. Timely access to a doctor, full diagnosis and subsequent comprehensive treatment will help avoid sad consequences.
Do not forget about the prevention of frontal sinusitis. Make sure your nose is breathing normally at all times. Any anatomical defects in the nose must be corrected immediately.
It is extremely important to properly and to the end treat seasonal colds (rhinitis, colds, SARS, and so on). Improve immunity with contrast showers and cold rubdowns, introduce foods high in vitamins into the diet. Eat vitamin and mineral complexes from time to time. Your health and quality of life depends on it.

 Additionally, the sinuses are washed and their cavity is irrigated with antiseptic and antibacterial solutions. Due to the use of funds for vasoconstriction, it is possible to quickly eliminate puffiness and activate the outflow of mucus.If purulent accumulations are not detected during frontalitis of the chronic type, warming up in the form of dry warm compresses on the frontal and nasal regions is prescribed.
Additionally, the sinuses are washed and their cavity is irrigated with antiseptic and antibacterial solutions. Due to the use of funds for vasoconstriction, it is possible to quickly eliminate puffiness and activate the outflow of mucus.If purulent accumulations are not detected during frontalitis of the chronic type, warming up in the form of dry warm compresses on the frontal and nasal regions is prescribed. Healing herbs - St. John's wort, oak bark, burdock, calendula, chamomile and so on.
Healing herbs - St. John's wort, oak bark, burdock, calendula, chamomile and so on.