Angina is an inflammatory disease that, probably, almost every child has managed to get to know. In many cases, it is caused by a bacterial infection. Therefore, the use of children's antibiotics for angina is simply necessary. They effectively fight against pathogenic microorganisms that harm the body, and also prevent the further development of complications.
Some parents strongly discourage the use of antibacterial drugs. The main argument is that they reduce immunity and adversely affect the intestines. At the same time, antibiotics for children with angina allow you to quickly and completely recover. Let's try to figure out which antibiotic is better for a child's angina.
Categories of antibiotics for sore throat
 Antibacterial drugs are divided into several groups. Each of them fights "their" bacteria. The following categories of antibiotics are considered the most effective for angina for children:
Antibacterial drugs are divided into several groups. Each of them fights "their" bacteria. The following categories of antibiotics are considered the most effective for angina for children:
- Penicillins. Most popular. They are most often prescribed to children with angina. They are very effective against streptococci, staphylococci and meningococci. Works well for follicular tonsillitis. If drugs from this group are prescribed and taken correctly, recovery occurs in 90% of all cases. Their names are “Amoxiclav”, “Amoxil”, “Amoxicillin”, “Ampiox”, “Augmentin”, “Benzylpenicillin”, “Bitsillin”, “Gramox”, “Flemoklav”, “Flemoxin Solutab”, “Hikontsil”. Local treatment of sore throat is performed using "Bioparox", which the manufacturer produces in aerosol form (recommended for children from 3 years old).
- Cephalosporins. This category includes antibiotics, which are an order of magnitude stronger than penicillins. They are able to eliminate almost any pathogen. An experienced doctor prescribes them if the child cannot take penicillins and macrolides due to allergies to them. In addition, such antibiotics are prescribed for purulent sore throat and in young children in the most extreme case. Their names are Cephalexin, Cefotaxime and Ceftriaxone.
- Macrolides. Drugs from this group have also worked well. They are characterized by a softened effect. Such medicines are prescribed for angina in a child, when an intolerance to penicillins is found. Their names are "Azithromycin", "Clarithromycin", "Lincomycin", "Midecamycin", "Roxithromycin", "Spiramycin", "Sumamed", "Chemocin", "Erythromycin".
- Fluoroquinols. Despite the fact that medicines from this category have an antibacterial effect, they are conventionally referred to as antibiotics. These drugs have no natural counterparts. This is one hundred percent pharmaceutical development. Such drugs are prescribed only when all other antibiotics are rejected for various reasons. Since they are completely synthetic, they can be taken from the age of 12. Here are some examples of these medicines: "Lomefloxacin", "Moxivloxacin", "Ofloxacin", "Ciprolet", "Ciprofloxacin".
It is not possible to determine which of the above drugs is the best antibiotic for angina. Each of them has its own advantages and disadvantages.
 Cephalosporins are the most powerful, but they also have many side effects.
Cephalosporins are the most powerful, but they also have many side effects.- Macrolides are distinguished by a gentle effect on the child's body, but they do not always help as needed.
- Penicillin drugs lead in the number of allergic reactions.
- Fluoroquinols are 100% "chemical" agents.
Therefore, the appointment of this or that drug should be strictly individual - it should correspond to the type of pathogen detected and the characteristics of the child's body.
What drugs are prescribed most often
It is impossible to determine by eye which antibiotic is better than the rest to cope with a sore throat in a child. You can learn all the names of drugs, compare the positive and negative aspects of each of them. However, the treatment of angina in children with a specific remedy can be started only after the result of a bacteriological examination of a smear taken from the tonsils is ready.
As for statistics, most often doctors prescribe Amoxicillin, Flemoxin and Sumamed to children. Let's tell you more about them.
- "Amoxicillin". This antibiotic for children has managed to positively recommend itself thanks to the successful elimination of all pathogenic microorganisms. It has a significant advantage that distinguishes it favorably from other drugs - low toxicity. "Amoxicillin" is the active substance of several drugs of the penicillin group. Most often, doctors prescribe Amoxiclav for children, as its effect is enhanced by clavulanic acid. It is produced in granular form for suspension preparation. It is very convenient to use for babies literally from the first months after birth and up to 6 years. And children of primary school age can already take pills that have a higher power.
 "Flemoxin" - is an analogue of the drug "Amoxiclav", since it also contains the active ingredient amoxicillin. However, this is a more advanced drug. When it is taken, allergic reactions and side effects occur much less frequently. "Flemoxin" is excellent for treating tonsillitis and bacterial infections affecting the lower respiratory tract. The course of treatment with this remedy lasts from 5 to 7 days. If the child's well-being does not improve, the doctor should be notified.
"Flemoxin" - is an analogue of the drug "Amoxiclav", since it also contains the active ingredient amoxicillin. However, this is a more advanced drug. When it is taken, allergic reactions and side effects occur much less frequently. "Flemoxin" is excellent for treating tonsillitis and bacterial infections affecting the lower respiratory tract. The course of treatment with this remedy lasts from 5 to 7 days. If the child's well-being does not improve, the doctor should be notified.- Sumamed. It is a good macrolide antibiotic. Its use makes it possible to significantly speed up recovery. You will have to be treated not 7-10 days, as with other drugs, but only 3 or even 2 days. Such a reduction in the course of treatment is extremely important for the child's body. After all, we know that antibiotics kill not only harmful bacteria, but also useful ones, as a result of which the intestines suffer. One of the advantages of Sumamed is its ability to accumulate in the body.
When a doctor prescribes this or that antibiotic for sore throat, he must specify in what form it should be purchased. Also, the doctor indicates the required dosage, based on the age of the small patient and his body weight.
For a baby at 6 months, at 1 year, at 3 years old and for a 9-year-old child, the form of the drug and its dosage will, of course, be different.
What form of medication is optimal for the child
The most comfortable form of antibiotic for a child with angina is suspension. First, it is very easy to prepare. Secondly, it is much more convenient to select the dosage with it. Thirdly, it is much easier for the baby to take it (especially if the tonsils are severely inflamed and it is very problematic to swallow something).
Up to 5 years of age with angina, the antibiotic must be given only in the form of a suspension. If you cannot find such a medicine, then it is permissible to use tablets crushed into powder.
 A child who turns 6 years old is considered old enough to take antibacterial drugs in pill form. Moreover, the assortment of drugs in this form is much wider. But this is on condition that he learned to swallow them. If he still does not know how, it's okay - you can take a suspension.
A child who turns 6 years old is considered old enough to take antibacterial drugs in pill form. Moreover, the assortment of drugs in this form is much wider. But this is on condition that he learned to swallow them. If he still does not know how, it's okay - you can take a suspension.
From the age of 9, with angina, antibiotics can be used in any form - be it tablets, capsules, or the same suspension. In terms of safety and effectiveness, these forms are exactly the same.The choice is often due to the financial ability of the parents (suspensions, as a rule, are an order of magnitude more expensive than tablets or capsules) and the presence of the desired form in the pharmacy.
As for intramuscular injections of antibacterial drugs, they can be given to children regardless of age. However, this is the worst option because the antibiotic shot:
- very painful;
- in most cases, it is guilty of the development of the baby's fear of any injections;
- leaves a severe infiltrate in the place where the medicine was injected;
- requires stationary conditions - hospital stay.
Fortunately, modern drugs produced in the form of tablets and suspensions are not inferior to injectable drugs in terms of speed of action and effectiveness. Thus, with angina, antibiotics in the form of injections are rarely prescribed to children.
When and how to take
The doctor needs to make sure that it is warranted before giving an antibiotic to a child. To treat angina with antibacterial drugs is required when:
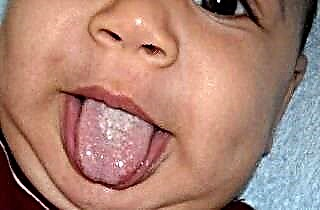
- the appearance on the tonsils of a purulent plaque of white color ();
- high temperatures reaching 40 ° C;
- enlarged and painful regional lymph nodes;
- sore throat combined with a sluggish state of the child.
 Before starting the treatment of children with antibiotics, it is necessary to take into account the test results (you will need to donate blood, urine and a smear - it is taken from the throat). Bacterial research allows you to determine the specific type of pathogen. Knowing what kind of bacteria triggered the disease, you can understand which group of antibacterial drugs can eliminate it. Thus, it becomes clear which antibiotics should be used.
Before starting the treatment of children with antibiotics, it is necessary to take into account the test results (you will need to donate blood, urine and a smear - it is taken from the throat). Bacterial research allows you to determine the specific type of pathogen. Knowing what kind of bacteria triggered the disease, you can understand which group of antibacterial drugs can eliminate it. Thus, it becomes clear which antibiotics should be used.
In some cases, sore throat is provoked by bacteria of the genus Candida. Such tonsillitis is treated with antifungal drugs. In addition, sore throat can be viral (for example, herpetic variety). It cannot be treated with an antibiotic - it will be completely useless.
It is very important to determine the specific pathogen so as not to overload the child's body with unnecessary drugs, especially such serious ones.
Often, streptococci are to blame for the occurrence of tonsillitis in a child. Penicillin group agents successfully cope with these bacteria. To increase the effectiveness, drugs are prescribed not only internally, but also locally ("Bioparox"). They immediately enter the respiratory tract and eliminate bacteria on their surface.
It is better not to take the antibiotic with food, because its effectiveness may decrease. It is best to drink the drug before meals or 2, and even better - 3 hours after meals. Compliance is very important for proper treatment.
The duration of antibacterial therapy is usually 5-10 days. If the child has become much better, for example, on the 2nd day, in no case should you stop taking medications. Otherwise, there is a risk of complications.
Side effects and contraindications
The occurrence of any side effects usually occurs due to the incorrect dosage of the medicine or the individual characteristics of the organism of a particular child. Common adverse effects include:
 problems of the functioning of the digestive system;
problems of the functioning of the digestive system;- nausea;
- diarrhea;
- jaundice;
- defeat of oral candidiasis;
- dermatitis.
If the child develops at least one of these side effects, the antibiotic treatment should be stopped immediately. Give him an activated charcoal drink and flush the stomach. If the state of health continues to deteriorate, do not waste time and immediately go to the doctor.
The main contraindication to the use of an antibacterial drug for angina in children is individual intolerance. In addition, if a child suffers from liver or kidney problems, a large number of antibiotics will be prohibited. And those medications that are still prescribed must be taken only under medical supervision. Uncontrolled intake can cause allergic reactions or exacerbate the disease.
Many antibiotics are not prescribed for young people. Therefore, before starting treatment for children under 3 years old, it is imperative to consult with an experienced specialist.
Parents are strictly forbidden to choose a drug at their own discretion and to arbitrarily set the timing of the course of treatment. Such actions can cripple the not yet strengthened immunity.
Let's summarize
With tonsillitis, antibiotics are prescribed for children only after an accurate diagnosis has been made. This can only be done by a doctor.
 Parents, seeing a reddened throat, call angina viral pharyngitis and laryngitis, as well as a fungal infection of the pharynx. In such cases, the use of antibacterial drugs is not only not beneficial, but can also be harmful.
Parents, seeing a reddened throat, call angina viral pharyngitis and laryngitis, as well as a fungal infection of the pharynx. In such cases, the use of antibacterial drugs is not only not beneficial, but can also be harmful.
The decision to prescribe antibiotics should be made exclusively by a doctor after examining a small patient. If the disease is relatively easy, the symptoms are gradually relieved by conventional cold medications, the doctor has time to wait until the results of a general blood test are ready. But if the child is ill and the clinical picture clearly indicates an acute form of streptococcal tonsillitis, the antibiotic should be used immediately.

 Cephalosporins are the most powerful, but they also have many side effects.
Cephalosporins are the most powerful, but they also have many side effects. "Flemoxin" - is an analogue of the drug "Amoxiclav", since it also contains the active ingredient amoxicillin. However, this is a more advanced drug. When it is taken, allergic reactions and side effects occur much less frequently. "Flemoxin" is excellent for treating tonsillitis and bacterial infections affecting the lower respiratory tract. The course of treatment with this remedy lasts from 5 to 7 days. If the child's well-being does not improve, the doctor should be notified.
"Flemoxin" - is an analogue of the drug "Amoxiclav", since it also contains the active ingredient amoxicillin. However, this is a more advanced drug. When it is taken, allergic reactions and side effects occur much less frequently. "Flemoxin" is excellent for treating tonsillitis and bacterial infections affecting the lower respiratory tract. The course of treatment with this remedy lasts from 5 to 7 days. If the child's well-being does not improve, the doctor should be notified. problems of the functioning of the digestive system;
problems of the functioning of the digestive system;