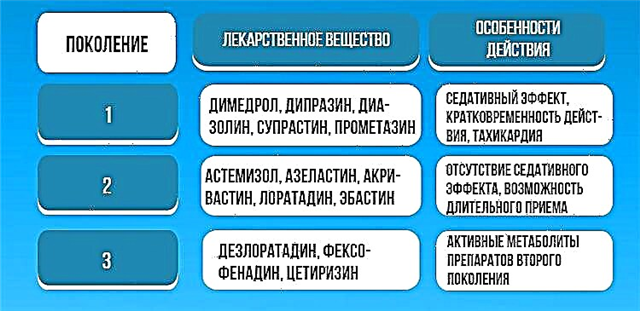
The use of antiviral and decongestant drugs for adults in pediatric practice is prohibited.
The use of antiviral and decongestant drugs for adults in pediatric practice is prohibited.
The fact is that young children are prone to allergic reactions, so even a slight overdose of drugs can cause severe swelling in the respiratory organs.
That is why children in infancy are treated mainly with folk remedies and safe drugs with a minimum concentration of synthetic substances.
Principles of therapy
The common cold is the most common cause of cough and nasal congestion in infants. The child's body is not able to effectively resist the onslaught of pathogenic viruses that quickly penetrate the mucous membranes of the ENT organs and cause inflammation. That is why babies get colds 3 times more often than teenagers and adults.
The main steps in the treatment of respiratory diseases in young patients include:
- restoration of patency of the nasal canals;
- exclusion of causal allergens;
- balanced diet;
- adherence to the therapeutic regimen (monitoring the degree of humidity and cleanliness in the room).
Before treating a newborn, you need to consult a pediatrician, since only a specialist can determine the true cause of rhinitis and cough syndrome in a child. It should be understood that not only viruses, but also bacteria can be provocateurs of inflammation in the respiratory tract. In this regard, in the process of treating infants, the following methods of therapy can be used:
Antiviral therapy
Antiviral treatment involves the use of drugs that suppress the development of viruses in the respiratory tract. Medicines contain components that not only destroy pathogens, but also stimulate the activity of protective cells in the body. In other words, most antiviral agents have a pronounced immunostimulating effect. The passage of pharmacotherapy allows you to stop inflammation in the nasal cavity and throat, as well as prevent the re-development of infection.
Some of the safest antiviral drugs for babies include:
- Anaferon;
- Orvirem;
- Relenza;
- "Vitaferon".
Irrational use of medications is fraught with nervous overexcitation and sleep disturbance in the child.
Antibacterial therapy
It is possible to treat a runny nose and cough with antibiotics only if, as a result of microbiological analysis, pathogenic microbes - staphylococci, pneumococci, Pseudomonas aeruginosa, etc. were found in a smear from the throat. Antimicrobial agents have a pronounced toxic effect, so they are used only in extreme cases. The safest antibiotics include drugs from the macrolide group, which almost never cause adverse reactions in babies:
- Erythromycin;
- Clarithromycin;
- Josamycin.
To prevent the development of dysbiosis, antimicrobial agents are best taken with probiotics.
Macrolide antibiotics are active against most intracellular and extracellular infections, therefore they are often used in the treatment of tonsillitis, pneumonia, bacterial laryngitis, etc.
Local therapy
At the initial stages of the development of acute respiratory infections, a runny nose and cough can be treated through physiotherapy procedures and local drugs. Unlike antiviral and antimicrobial drugs, they are not absorbed into the systemic circulation and therefore do not cause nausea, vomiting, dizziness, etc. in newborns. In pediatric practice, the treatment of respiratory diseases is often carried out in the following ways:
Sanitation of the nasal cavity
Cleansing the nasal passages from viscous secretions helps to restore normal nasal breathing and the healing of the mucous membrane. As a rule, nasal drops based on isotonic solutions are used to thin the mucus in the nose in a newborn. They additionally contain microelements and vitamins, which accelerate the regeneration of mucous membranes. The safest drugs include Physiomer, No-Salt, Humer, etc.
During the procedure, several important rules must be observed:
- lay the child on his back and drip 2-3 drops of the drug into the nasal passages;
- turn the baby on its side and insert the aspirator tube into the lower nostril;
- suck off the mucus and repeat the procedure for the second nostril.
To prevent the formation of crusts inside the nasal passages, lubricate the mucous membrane with peach or sea buckthorn oil.
Rubbing your breasts
Warming procedures help to reduce the viscosity of phlegm in the bronchi and speed up its passage. Experts do not recommend using expectorants, as they often cause allergic reactions. But warming ointments for rubbing do not cause side effects and help to increase local immunity. To grind the back and chest of a newborn, you need to do the following:
- squeeze a small amount of warming ointment into the palm of your hand ("Doctor Mom", "Pulmex baby", "Doctor Theiss");
- massage the drug into the chest, excluding the heart area;
- turn the child over on his stomach and rub the warming ointment into the intercostal region.
Important! You cannot use warming ointments if the baby has a fever.
Newborns are poorly muscled and therefore cannot cough up mucus effectively. Massage facilitates the passage of mucus from the walls of the bronchi and its movement up the respiratory tract.
Nebulizer therapy
Ultrasonic and compression inhalers are absolutely safe, therefore they can be used to treat the smallest patients. To reduce the viscosity of mucus in the lower and upper respiratory tract, you can fill the nebulizer with alkaline solutions - mineral water (Borjomi, Essentuki) or Sodium chloride. Alkalinization of mucous membranes helps to restore the integrity of tissues in the lesions and, as a result, to eliminate local manifestations of the disease - rhinitis, cough, inflammation, etc.
Symptomatic medicines
A dry cough in a baby interferes with normal rest and sleep, so the baby becomes moody and restless. In addition, forced exhalation often injures the throat tissue, which subsequently leads to even greater inflammation of the mucous membranes. To alleviate the condition of the little patient and speed up his recovery, doctors recommend using the following symptomatic drugs in the treatment of respiratory diseases:
| Medication type | pharmachologic effect | Name |
|---|---|---|
| antitussives | prevent the appearance of spastic cough |
|
| antipyretic | eliminate the manifestations of fever - chills, sweating, weakness |
|
| antiseptic | liquefy mucus in the nasal cavity and relieve inflammation |
|
| moisturizing | moisturize and disinfect the nasal mucosa |
|
| antiviral | destroy viruses in the nasal cavity and eliminate inflammation |
|
Important! Only a qualified specialist can draw up an optimal drug therapy regimen for an infant.
Non-drug activities
 It is possible to eliminate rhinitis and cough faster only if a special therapeutic regimen is observed. According to practical observations, in 94% of cases, a decrease in immunity in infants is associated with a negative impact of external factors. To restore the normal functioning of the ENT organs, while undergoing pharmacotherapy, one should not forget about the following non-drug measures:
It is possible to eliminate rhinitis and cough faster only if a special therapeutic regimen is observed. According to practical observations, in 94% of cases, a decrease in immunity in infants is associated with a negative impact of external factors. To restore the normal functioning of the ENT organs, while undergoing pharmacotherapy, one should not forget about the following non-drug measures:
- regular ventilation of the room - improves tissue oxygenation and enhances local immunity;
- humidification of the air - accelerates the liquefaction of mucus in the bronchi and nasopharynx, prevents the formation of dry crusts in the nasal passages;
- laying out slices of onion and garlic in the room - contributes to the destruction of viruses in the respiratory tract due to the action of phytoncides contained in vegetables.
Parents should be aware that decreased immunity in babies is often associated with allergic reactions to complementary foods. Therefore, during the introduction of new products into the child's diet, all the above precautions must be observed.
Outcomes
Cough and runny nose are the main manifestations of respiratory disease, therefore, they can be eliminated only if the infection in the respiratory tract is destroyed. For the treatment of children under the age of 1 year, only the safest drugs based on isotonic solutions and natural ingredients are used. They rarely cause adverse reactions in children and even swelling of the mucous membranes of the nasopharynx.
Therapy for colds involves the use of physiotherapeutic procedures (inhalation, rubbing, sanitation of the nasopharynx), as well as topical preparations. Most of them are aimed at removing mucus from the respiratory tract and healing tissues directly in the foci of inflammation.