Sore throat accompanies many diseases, both inflammatory and infectious. In some cases, you can observe that the pain in the throat when swallowing is given to the ear. This often indicates the spread of the inflammatory process to the ear. Otitis externa is characterized by pain in the ear area when talking, swallowing, chewing, which can spread to the neck and eyes. Otitis media is more common. Its development is due to the spread of infection, inflammation through the Eustachian tube, which runs between the tympanic cavity and the pharynx. Due to tissue edema, the ventilation function is impaired, and the secretion of inflammatory fluid increases in the tympanic cavity.
In addition, the infection can enter the ear in a hematogenous way (with blood flow). As a result, soreness appears, hearing decreases. With untimely treatment, purulent otitis media develops, due to the rapid multiplication of microbes. Accumulation of pus leads to increased pressure on the tympanic membrane, its perforation or infection of brain tissue, membranes with the development of abscesses and meningitis.
leads to increased pressure on the tympanic membrane, its perforation or infection of brain tissue, membranes with the development of abscesses and meningitis.
Especially often, complications from the ear are observed in children, which is associated with a smaller diameter of the Eustachian tube.
Otitis media does not often develop against the background of diseases of the pharynx. Usually it is a complication of meningitis, otitis media. Symptomatically, the disease manifests itself as severe dizziness, nausea, vomiting, tinnitus, and impairment of auditory function.
When your throat hurts, you should suspect:
- pharyngitis localized in the posterior pharyngeal wall;
- tonsillitis;
- ARVI.
Also, inflammation can be a consequence of the action of an allergic factor, overexertion of the vocal cords, trauma, including after surgery,
Complications
An untreated inflammatory process, especially of an infectious origin, leads to the generalization of the infection, provoking the appearance of severe complications:
- purulent inflammation (abscess in the tonsils, brain tissue), purulent otitis media, meningitis;
- mastoiditis, labyrinthitis;
- sepsis;
- cholestetoma (neoplasm consisting of dead cells of the epidermis), which leads to the destruction of the temporal bone;
- necrotic processes in the oropharynx;
- sinusitis;
- tracheitis, bronchitis.
Any warming up is contraindicated in the presence of pus. Heat speeds up the multiplication of microbes.
Diagnostic features
To make an accurate diagnosis, the doctor asks the symptoms of the disease, examines the anamnestic information. Further, laboratory and instrumental diagnostics are required.
Laboratory studies include virological, bacteriological analysis of smears from the pharynx, blood, bacterial culture of ear discharge.
From instrumental methods, pharyngoscopy is shown, which allows you to sightly examine the oropharynx, as well as otoscopy. In the case of a chronic course of otitis media, an X-ray of the temporal bone, tomography is recommended. In order to assess the severity of hearing impairment, audiometry is performed.
When it hurts to swallow, pain when swallowing depends on the severity of the pathological process. To eliminate symptoms, it is necessary to apply complex treatment aimed at combating the infectious pathogen, reducing swelling and the intensity of the inflammatory process in the oropharynx, Eustachian tube and ear sections.
Drug treatment
The main focus in the treatment of ear pain is ear drops. Consideration should be given to the integrity of the tympanic membrane. When suppuration occurs, it is worth suspecting its perforation.
Before the violation of the integrity of the tympanic membrane, it is recommended to use it with an analgesic component (Otipax, Otinum). After perforation, drops with an antibacterial component are prescribed (Otofa, Tsiprofarm). Antibiotics that have a negative effect on the hearing aid, such as gentamicin, neomycin, polymyxin B, are prohibited.
Candibiotic, Miramistin have antifungal effect. The hormonal component is part of Sofradex.
Drug therapy for the appearance of pain in the ear also provides for the appointment:
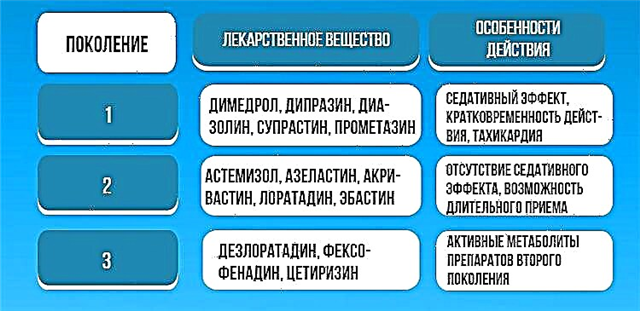
- antihistamines (Suprastin, Erius), due to which tissue swelling decreases, the airway function of the Eustachian tube improves, the middle ear is sanitized;
- antiemetic drugs (metoclopramide) for damage to the structures of the inner ear to reduce nausea;
- hormonal medications (Methylprednisolone) are prescribed in the absence of purulent discharge, in the case of severe inflammation, exudation of a serous nature;
- sedatives (Glycine);
- antibiotic therapy is carried out when the presence of bacterial pathogens is confirmed. Cephalosporins (Zinnat), macrolides (Azitrox), penicillins (Amoxiclav, Flemoklav) are widely prescribed;
- antipyretics (Nimesil) are used at elevated temperatures.
For local therapeutic effects, scopolamine patches are used, physiotherapy procedures (after the end of the acute phase of inflammation), for example, UHF, sollux, warming compresses.
 According to the indications, surgical intervention is prescribed, for example, dissection of the tympanic cavity, labyrinthotomy, opening of the temporal pyramid. Proteolytic enzymes can be injected directly into the tympanic cavity.
According to the indications, surgical intervention is prescribed, for example, dissection of the tympanic cavity, labyrinthotomy, opening of the temporal pyramid. Proteolytic enzymes can be injected directly into the tympanic cavity.
When there is a pain syndrome radiating to the ear zone, attention should be paid to the treatment of the main inflammatory focus. For analgesia, reducing tissue swelling, sputum, gargling is recommended:
- Miramistin is used in undiluted form. For a child, the drug is diluted in half with water.
- Givalex is popular for its strong antimicrobial, anti-inflammatory, analgesic effect. It is widely used in otolaryngology for sore throat for patients over 6 years old. Before the rinsing procedure, dilute 10 ml of the medication in 50 water.
- Furasol has an antimicrobial effect and is indicated for patients from 4 years of age. The contents of the package are dissolved in 180 ml of water.
- Stopagnin has a long-term antimicrobial effect, which lasts up to 10 hours. It is allowed for rinsing in undiluted form for patients over 6 years old (consumption - 15 ml per session).
- Furacilin in tablet form is used after thorough crushing of the tablet, dissolving in 0.5 liters of water at a temperature of about 70 degrees. Then the solution is cooled to 40 degrees. In order to enhance the therapeutic effect, furacilin can be diluted with 70% alcohol (1500: 1) or mixed with 3 drops of calendula alcohol tincture.
- Rotokan is indicated for patients over 12 years old, has a powerful antimicrobial, anti-inflammatory effect, reduces the severity of edema, strengthens the vascular wall, which prevents the release of the liquid plasma component into the tissue, activates local blood flow, and stimulates tissue regeneration. A healing solution is prepared by dissolving 5 ml of the drug in 180 ml of water.
- Chlorophyllipt is effective against staphylococci and other infectious pathogens, especially in the presence of purulent discharge. The solution is applied after diluting 5 ml of the drug in 180 ml of water.
Rinsing is prohibited for children under 5 years old if they do not have the skills to carry out the procedure. When the solution enters the respiratory tract, severe bronchospasm and respiratory failure develop.
The rinsing procedure is repeated up to 6 times a day. During the day, after 1.5-2 hours, it is advisable to use different medicines to ensure a good result. The temperature of the solution should not exceed 40 degrees in order to avoid burns of the mucous membrane of the oropharynx.
After the procedure, it is not recommended to drink liquid, smoke, go out into the cold, or eat for half an hour. Thanks to this, it is possible to provide the maximum therapeutic effect. When rinsing, you should tilt your head back, pronounce the sound "Y" to increase the area of the mucous membrane in contact with the drug.
Traditional treatment
In addition to the main therapy, traditional medicine is prescribed. In order to combat fever, to accelerate the elimination of toxins from the bloodstream, an abundant drink is prescribed. A decoction of chamomile, rose hips, sage, linden is suitable for this.
If the eardrum is not injured, instillation of the ear with warm boric acid is allowed. The ear canal should be closed with a cotton swab to prevent the medicine from leaking out.
- salt is used for warming. The procedure is carried out as follows. The heated salt should be poured into a handkerchief / sock, after which it should be applied behind the ear. The duration of the procedure is 5 minutes, while the temperature of the salt and the force of pressure should be controlled in order to avoid burns. To enhance the therapeutic effect, salt can be mixed with chopped garlic (2-3 cloves) boiled for 5 minutes.
- when confirming a fungal infection, lotions with apple cider vinegar are shown. To do this, mix it 1: 1 with alcohol, moisten a cotton swab in the resulting solution, insert into the ear canal. The duration of the procedure is 5 minutes.
- essential oil. The healing agent is a mixture of tea tree (3 drops), olive oil in a volume of 30 ml, colloidal silver and apple cider vinegar in a volume of 5 ml. The mixture is slightly warmed up, the mixture is instilled into the ear canal with a pipette. After 5 minutes, you need to lie down on your healthy ear so that the medicine is completely drained out.
- the ear will not hurt if you apply a cotton swab dipped in 0.5% hydrogen peroxide into the ear canal.
- a few drops of white vinegar are diluted with water (1:10). The swab is moistened with the medicine and placed in the ear canal.
- the garlic is chopped with a grater, poured with olive oil, left overnight. Then you should filter, warm up the mixture a little, bury the ear in 2 drops.
 Alcohol drops are used exclusively for intact tympanic membrane
Alcohol drops are used exclusively for intact tympanic membrane
To eliminate sore throat, folk remedies can be used, such as:
- salt, soda. The solution is prepared by mixing the ingredients in a volume of 5 g in 180 ml of warm water. You can add a couple of drops of iodine to increase efficiency.
- sage has a pronounced antimicrobial, anti-inflammatory effect, activates regenerative processes. It is enough to brew 5 g of herbs in 180 ml of boiling water under a lid. After filtering out the broth, you can start gargling.
- Chamomile is known for its powerful anti-inflammatory effects. You can prepare a broth by brewing 15 g of herbs with 180 ml of boiling water under a lid.
- dry raspberry leaves should be brewed in a thermos.
The pain will cease to be given to the ear when the inflammatory process decreases, and the infection will no longer be present.
Prophylaxis
To prevent the spread of infection and inflammation from the oropharynx into the ear structures and nasopharynx, it is necessary to adhere to simple rules:
- do not overcool, get wet in the rain;
- water procedures with wetting of the ear canal are prohibited (pool, sea);
- after taking a shower, remove the remaining water from the ear canal;
- regular ventilation of the room;
- crowds of people should be avoided during an epidemic;
- taking vitamins;
- a complete nutritious diet;
- bed rest;
- plentifully warm drink with raspberries, honey, lemon.
 To increase the body's immune forces, it is recommended to take a medicinal product based on honey. To prepare it, combine one dessert spoon of liquid honey, cocoa, olive oil, mix thoroughly. Take three times 10 g.
To increase the body's immune forces, it is recommended to take a medicinal product based on honey. To prepare it, combine one dessert spoon of liquid honey, cocoa, olive oil, mix thoroughly. Take three times 10 g.
If you are not allergic to dairy products, you can drink warm milk with honey. Ginger is also helpful. Its root can be brewed with boiling water, drunk like tea.
If you have a sore throat when swallowing, you should immediately start gargling. If there is no effect after 2 days, as well as if there is pain in the ear area, you should consult a doctor. Examination and diagnosis by a doctor allows you to establish the severity of the disease, the risk of complications. Based on the results of the diagnosis, the doctor determines the tactics of treatment, selects drugs and selects the dosage.