Why is the course of VSD often accompanied by a headache and what is its mechanism?
 At the heart of the development of headache in VSD is several mechanisms (spasm or vasodilation of the brain). With autonomic dysfunction, the innervation of the vascular wall of the sympathetic and parasympathetic parts of the nervous system (NS) is disturbed with a predominance of one of them. In addition, biologically active substances and hormones released into the bloodstream in response to autonomic stimulation affect the tone of the vascular wall.
At the heart of the development of headache in VSD is several mechanisms (spasm or vasodilation of the brain). With autonomic dysfunction, the innervation of the vascular wall of the sympathetic and parasympathetic parts of the nervous system (NS) is disturbed with a predominance of one of them. In addition, biologically active substances and hormones released into the bloodstream in response to autonomic stimulation affect the tone of the vascular wall.
Due to the violation of the tone of the vascular wall, vasodilation occurs, which causes a discrepancy between the total peripheral resistance of the vessels to the tensile force of the pulse blood volume. Prolonged overflow of the venous bed provokes a violation of the permeability of the vascular wall and its edema, and over time, edema of nearby tissues.
Spasm of arterioles (with excessive sympathetic stimulation) causes transient local hypoxia of the brain tissue, which also causes headaches.
Overflow of intracranial veins provokes the opening of the emissary ducts to redirect blood to the extracranial venous plexuses. At the junction of the veins, most of the nociceptors are located, the irritation of which increases pain.
The nature of the pain
Patients with dystonia have a so-called "chronic recurrent headache".
For cephalalgia with VSD, the following are characteristic:
- Vascular type of headache;
- Localization - temporal, frontal, temporo-parietal regions, occasionally with irradiation to the back of the head;
- Character - dull, aching in the temples, bursting, pulsating;
- Occurs at any time of the day;
- Provoked by excessive stress, emotional or physical stress;
- Amplified by bright lighting, loud noises, strong odors;
- In dynamics, the pulsating character of cephalalgia is replaced by a dull, bursting one;
- Additionally, there is pallor of the skin, non-systemic vertigo, nausea, asthenia, rarely - transient neurological symptoms;
- In the interictal period, the patient feels good, occasionally there is a feeling of a "heavy head".
How to stop and treat an attack?
Headache with VSD is caused by impaired vascular tone and perifocal edema.
To reduce pain symptoms, you can take one of the following drugs:
- Paracetamol, Panadol;
- Migrenol;
- Solpadein;
- Pentalgin;
- Sedalgin;
 Askofen;
Askofen;- Tempalgin;
- Ibuprofen, Nurofen.
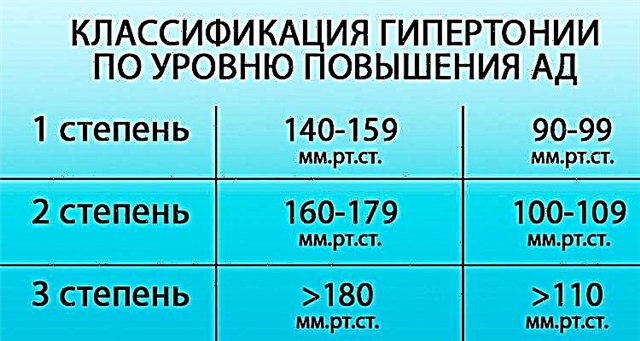
It is important to determine the level of blood pressure (BP) - normalizing this indicator can often eliminate the headache. It is also worth trying to provide the patient with physical, mental and sensory peace.
To prevent repeated attacks of cephalalgia, you need to adhere to a healthy lifestyle, eat well, dose work and rest.
With hypotension, additional treatment with tincture of Eleutherococcus, ginseng, caffeine-containing preparations is possible.
In the case of a hypertensive variant of the VVD, antihypertensive drugs (ACE inhibitors, SA blockers2+-channels, β-blockers, mild diuretics, sartans).
What is the reason for dizziness with vascular dystonia?
Dizziness is one of the most common symptoms of neurological dysfunction.
Vertigo with VSD is caused by a violation of the blood supply to the cerebellum and the vestibular analyzer in the brain. Also, the occurrence of this symptom is facilitated by proprioceptive impulses from the cervical muscles. Vertigo is often accompanied by a hypotonic type of VSD.
Vertigo with autonomic dysfunction belongs to the class of non-systemic and is characterized by the absence of a sense of rotation of oneself or objects in space.
Basic sensations:
 Light-headedness (sometimes loss of consciousness) with sweating, nausea, a feeling of fear, severe weakness, dark flies before the eyes, numbness;
Light-headedness (sometimes loss of consciousness) with sweating, nausea, a feeling of fear, severe weakness, dark flies before the eyes, numbness;- Imbalance of the type: "swaying", "swaying", "it is difficult to stand on your feet";
- Uncertain feelings: "fog in the head", "as if drunk", "the soil is leaving from under your feet"
As a rule, dizziness with VSD of a paroxysmal nature. Often, the patient can associate the appearance of a symptom with the influence of external factors (stressful situations, stuffy transport, a quick change in body position.
The patient, waiting for the next attack, becomes nervous, irritable, the general emotional background is reduced.
The use of antispasmodics, venotonics, neurometabolites and lifestyle correction will help get rid of dizziness with VSD.
Noise in the head: why does it appear and how to deal with it?
Impaired autoregulation of vascular tone reduces the adaptive potential of the circulatory system.
Noise in the head appears in patients with a combination of VSD and other organic pathology (atherosclerosis, osteochondrosis of the cervical spine, chronic cerebral blood flow disorder).
In the case of atherosclerosis, the noise occurs due to turbulent blood flow through the altered vessels (a rigid wall with many atherosclerotic plaques).
 In patients with concomitant osteochondrosis, there is compression of the vertebral artery and impaired blood flow in the vertebro-basilar basin, which reduces the nutrition of the brain structures.
In patients with concomitant osteochondrosis, there is compression of the vertebral artery and impaired blood flow in the vertebro-basilar basin, which reduces the nutrition of the brain structures.
Chronic hypoxia of parts of the brain causes dysfunction of the auditory analyzer, which is the reason for the "phantom" noise in the head.
Only therapy of the underlying disease can eliminate noise in the head with VSD.
Additionally use:
- Cinnarizine, Cavinton, Vinpocentin;
- Vasodilators (Nicotinic acid, Thionicol);
- Sermion.
A burning sensation is one of the leading symptoms of vascular dystonia
Burning head pains occur in patients with concomitant osteochondrosis of the cervical spine, psychotic disorders and hypertensive type of VSD, especially in women against the background of hormonal changes.
A burning sensation in the head occurs at the site of paretic vasodilation and, as a result, tissue hyperemia. In addition to this, there may be facial redness, a local increase in temperature, palpitations, anxiety, and throbbing in the head. Also, burning pains can be caused by local hypoxia of the head tissues.
First of all, you need to measure blood pressure and, if necessary, take an antihypertensive drug. Also, the use of non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs or antispasmodics will help to cope with a headache.
Severity and ambiguity: how to get rid of such manifestations of VSD?
Feelings of a "heavy head" and "ambiguity of thoughts" are a rather subjective description of the symptoms, which allows one to suspect the development of a neurotic state in the patient.
Together with the manifestations of VSD, neurosis significantly worsens the patient's well-being, quality of life and reduces the ability to work.
 These symptoms can also be explained by impaired blood circulation in the brain caused by autonomic dysfunction, act as an "aura" before a sympathoadrenal crisis "and residual effects after a headache attack, have a psychogenic nature.
These symptoms can also be explained by impaired blood circulation in the brain caused by autonomic dysfunction, act as an "aura" before a sympathoadrenal crisis "and residual effects after a headache attack, have a psychogenic nature.
To eliminate the feeling of a heavy and unclear head with VSD, you need to approach in a complex way:
- Normalize blood circulation in the brain - Stugeron, Cinnarizin, Cavinton;
- Use nootropic drugs - Nootropil, Piracetam;
- Prescribe herbal adaptogens - eleutherococcus, ginseng, ginkgo biloba;
- If necessary, use antidepressants - Amitriptyline, Fluoxetine;
- Take a course of psychotherapy;
- Give up bad habits, lead a healthy lifestyle.
Are there reliable ways to normalize the outflow of blood from the brain?
The regulatory mechanisms of the circulatory system have a complex organization. The outflow of blood from the cranial cavity is influenced by many factors (tension of the vascular wall, blood flow velocity, the state of the structures of the brain and spine, rheological properties of blood).
There are no drugs that can regulate the outflow of blood from the cranium apart from the treatment of the underlying pathology.
This situation requires an integrated approach with a combination of the following methods:
 Venotonics - Diosmin, Detralex, Troxerutin, Pentoxifylline;
Venotonics - Diosmin, Detralex, Troxerutin, Pentoxifylline;- Antiplatelet agents - ASK, Clopidogrel;
- Neurocorrectors - Cinnarizine, Vinpocentin, Cavinton;
- Diuretics - Furosemide;
- Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory - Meloxicam, Ksefokam;
- Neck and collar zone massage;
- Acupuncture of the head and neck area;
- Adequate physical activity, morning exercises, if necessary, a complex of exercise therapy;
- Rational nutrition, smoking cessation and alcohol consumption;
- A good rest.
- Mandatory treatment of the underlying pathology.
Conclusions
The diagnosis of vascular dystonia can be made only by excluding organic pathology with similar symptoms. VSD makes its debut in childhood and adolescence under the influence of external factors and hormonal changes during puberty. In the adult population, dystonia, as an isolated condition, occurs in pregnant women. In other cases, it is worth conducting a thorough diagnostic search for the root cause of the headache or dizziness. An indispensable component of the treatment of autonomic dysfunction is psychotherapy.

 Askofen;
Askofen; Light-headedness (sometimes loss of consciousness) with sweating, nausea, a feeling of fear, severe weakness, dark flies before the eyes, numbness;
Light-headedness (sometimes loss of consciousness) with sweating, nausea, a feeling of fear, severe weakness, dark flies before the eyes, numbness; Venotonics - Diosmin, Detralex, Troxerutin, Pentoxifylline;
Venotonics - Diosmin, Detralex, Troxerutin, Pentoxifylline;