Indications for
Although cardiography and a routine research method, it also has indications. To determine the cause of pain or discomfort in the chest area, the patient consults a therapist or cardiologist. The doctor initially collects anamnesis, examines, measures blood pressure and pulse, auscultates the heart, and then sends it for research in order to find out what the cardiogram shows.
Indications for ECG:
- chest pain (suspected angina pectoris or myocardial infarction);
- dyspnea;
- discomfort in the region of the heart after viral or bacterial infections;
- pathological palpitations, interruptions in the work of the heart muscle.
It is obligatory to conduct an ECG in such cases:
- when hospitalized in an inpatient department of any profile;
- before surgical interventions;
- during preventive examinations of adults;
- for schoolchildren when choosing a group of physical education classes.
An electrocardiogram of the heart is used both for the primary diagnosis of pathological conditions and for monitoring the dynamics of the disease. When prescribing drugs, the doctor relies on both the patient's subjective feelings and ECG data, which reflect actual changes in the cardiovascular system.
Execution technique
Carrying out cardiography does not require particularly complex skills, therefore, middle and junior medical personnel know how to do a cardiogram of the heart. A device for such manipulation is a cardiograph. It can be stationary and is constantly in a specially equipped office, which each polyclinic has, or mobile - for convenient ECG recording at the patient's bedside.
During the ECG, the patient lies on his back. The points where the electrodes are applied are freed from clothing and moistened with isotonic sodium chloride solution to improve conductivity. Electrodes in the form of plates cling to the limbs: red - on the right hand, yellow - on the left, green - on the left leg, and black on the right. Six electrodes in the form of suction cups are placed on the chest. They are called chest leads (V1-V6), and the limb electrodes are considered basic (I, II, III) and reinforced (aVL, aVR, aVF). Each of the leads is responsible for a specific area in the heart. Suspecting pathological processes along the posterior wall of the heart muscle, additional chest leads (V7-V9) are used.
It is important that before the planned electrocardiography the patient does not drink alcohol or coffee. When removing, it is undesirable to move, talk, as this leads to a distortion of the examination results.
The cardiogram is recorded as a graph on special paper or in electronic form. It is important to shoot at least four cardiac cycles to obtain objective data on the state of the heart. The film is signed with the name, gender (man, woman), the date of the study, the age of the patient, since the adult and the child have different values of the normal parameters. After that, the record is transferred to the doctor, who deciphers the ECG in detail.
Various techniques and indications for them
Classic ECG recording helps to see how the myocardium and the cardiac conduction system are behaving at the moment. In many cases (preventive examinations, normal pregnancy), a conventional ECG is sufficient. But situations arise when the patient complains of pain or shortness of breath only during stress or physical exertion, or at a certain time of the day, and the film does not show characteristic changes in rhythm or pathological teeth. In such episodes, additional types of cardiography are used.
With angina pectoris, it is not always possible to fix the changes on the ECG, so you have to use the stress ECG or treadmill test. This method involves doing physical activity (treadmill or bicycle ergometer) while recording an ECG.
Indications for performing a stress test:
- diagnostics of exertional angina and determination of its functional class;
- control of the effectiveness of treatment of ischemic disease and angina pectoris.
In addition, there are a number of contraindications to this procedure:
- acute period of myocardial infarction;
- unstable angina;
- arrhythmia, severe blockade;
- heart failure in the stage of decompensation.
Another specialized type of ECG is a holter (24-hour heart rate monitor). To perform this procedure, electrodes and the recorder itself are attached to the patient's body, which is small and measures electrical potentials around the clock. Read more about this type of cardiography in the article "The method of Holter ECG monitoring".
Decoding the results
Deciphering the electrocardiogram of the heart is an important and crucial stage in the diagnosis and prescription of treatment. For correct interpretation, it is necessary to understand the essence of the teeth and lines on the graph.
An ECG printout has three important elements:
- tooth - concavity or convexity of the line. Encrypted in Latin letters P, Q, R, S, T;
- the interval includes segments and teeth;
- segment - the distance between two teeth.
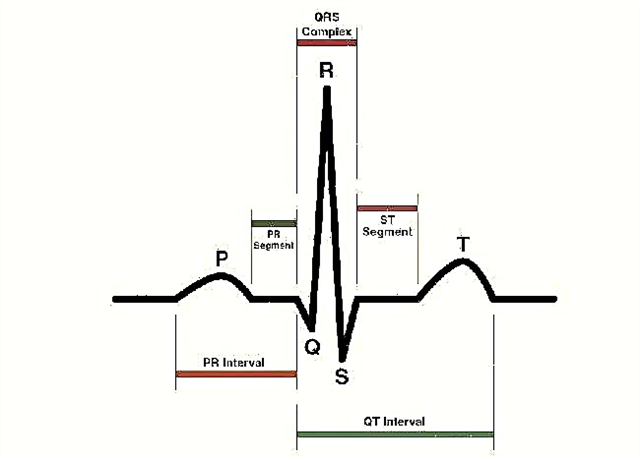
When describing the cardiogram, the duration of the intervals, the height of the teeth, the position and shape of the segments are taken into account. Important factors are the recording speed of the tape with which the electrocardiograph works (usually 25 or 50 mmsec) and artifacts (patient movement during the procedure, baseline drift):
- P wave - displays processes in the atrium, normally positive, up to 2.5 mm high and 0.1 s duration.
- Q wave - shows impulses in the interventricular septum, duration - 0.03 s.
- The R wave - the highest, displays the impulses of the ventricles themselves.
- The S wave - negative and shallow, indicates the completion of the passage of the impulse in the ventricles.
- T wave - reflects the repolarization of the ventricles.
The next important indicator of a normal ECG is sinus heart rate. Criteria: the P wave is in front of all QRS, equal to PQ (0.12-0.2 s) in all leads and the heartbeat is 60-80 beats / min.
Next, the electrical axis of the heart (EOS) is determined, which characterizes the conductive and fiber organization of the organ. It can be vertical (+70 +90 degrees), horizontal (0 +30) and normal (+30 +60).
Who is doing
A doctor of any specialty has at least a minimal idea of how to read a cardiogram of the heart, to be able to recognize the signs of severe conditions. Most often, cardiograms are deciphered by therapists or cardiologists, because they prescribe this study. Paramedics and emergency doctors read tapes to quickly make decisions about medical support or hospitalization in a cardiac hospital. In many polyclinics there are doctors who do only decoding of cardiograms (functional diagnostics doctor) and write a conclusion to the study performed.
At the end of the recording, modern cardiographs provide a preliminary study result indicating the sizes of intervals and teeth, heart rate, the position of the electrical axis of the heart and signs of such pathologies: blockade, arrhythmias, hypertrophy of the myocardial walls. This makes it easier for the doctor to count and measure the segments, but it happens that the program will misinterpret the results. The doctor checks the pathological signs on the ECG and makes the correct conclusion.
In some cases, the conclusion of an electrocardiogram of the heart does not completely solve the problem of diagnosis. The doctor may ask to see previous tapes and conclusions of other examinations. When making a diagnosis, take into account the data of anamnesis, the course of the disease, and taking medications.
Is it possible to independently interpret the results
Many patients want to know how to independently decipher the cardiogram of the heart, because they often want to find out the result of the study as soon as possible in order to calm themselves. But it is better to entrust this task to the doctor, having received competent advice, although some ECG data are easy to interpret even for beginners. The procedure is easier if the recording is of high quality and there are no artifacts on the tape.
To understand how to read a cardiogram of the heart, you need to know about the parameters of the rhythm and heart rate. To determine the number of contractions, the number of large squares on the film between the two nearest R teeth is counted. At a speed of 50 mm s, 600 is divided by the number of squares, and at 25 mm s, 300 is divided by the number of squares.
After that, the EOS value is indicated. As mentioned earlier, the axis position can be normal, horizontal, or vertical. Norm: vertical in thin people, horizontal - in hypersthenics (stocky, with a wide chest). Deviation of EOS is deciphered as hypertrophy of the myocardial walls, blockage of the pathways or other pathologies.
What does the conclusion of electrocardiography look like?
There is a generally accepted norm for the wording of the ECG conclusions, which all doctors adhere to. At the beginning of the description, write a complete description of the teeth, segments and intervals, indicating their size, amplitude and duration. Then note the type of rhythm (variant of the norm - sinus) and the direction of the axis of the heart. If the indicators are in order, then the doctor makes a note that no violations were found on the cardiogram.
If deviations from the norm are recorded, the doctor enters them into the conclusion: which tooth or segment is changed and what problem is he talking about. A high and pointed P wave is a sign of an enlargement of the right atrium (cor pulmonale), and a bifurcated two-humped P wave interprets an enlargement of the left atrium.
If the PQ interval (the norm is 0.12-0.2 seconds) is increased, then the characteristics of atrioventricular blockade and its degree are included in the ECG description:
- I - only lengthening of the interval without other changes;
- II - lengthening Р-Q;
- III - there is no connection between the QRS and the P wave.
One of the important diagnostic keys is the ST segment, because it reflects a decrease in oxygen supply to the myocardium.
The QRS complex shows the processes in the ventricles, and its changes or various deformations indicate a blockade of the bundle of His, ventricular extrasystole.
Changes in the T wave reflect pathological processes during the restoration of the heart after contraction. Biphasic T appears with hypercalcemia, intoxication with cardiac glycosides; a reduced T wave says that the endocrine system is suffering (hypothyroidism, dyshormonal cardiomyopathy).
With a pathological rhythm, indicate which segment of the conducting system generated it. Allocate:
- atrial rhythm with a heart rate of 45-60 beats / min. (P-negative in II and III leads before the ventricular complex);
- atrioventricular - the P wave appears after the QRS;
- ventricular - the QRS is wide, there is no connection with the P wave, the heart rate is less than 40 beats / min.
For clarity, let's look at an example of decoding a normal electrocardiogram: “PQ - 0.11 s. 2. QRS - 0.05 s. 3. QT - 0.3 s. 4.RR - 0.61 - 0.65 - 0.6. Sinus rhythm, regular. Heart rate 74 beats per minute. Normal position of EOS ".
An example of a normal ECG

ECG diagnostic value
The method of cardiography appeared a long time ago and does not lose its relevance in our time. Since then, it has improved and changed, but it still remains an irreplaceable study of diseases of the cardiovascular system.
Most accurately, the cardiogram determines the cause of the rhythm pathology. The ECG successfully records the appearance of para-impulses, and indicates the location of the focus, the type of arrhythmia. Often on the film, blockage of the pathways (sinoatrial, AV-node, bundle branch) is manifested. In addition to identifying pathologies, the cardiogram helps the doctor decide on further treatment tactics.
But with the diagnosis of coronary artery disease, the method of conventional electrocardiography sometimes does not cope. After all, it is important to record a sign of ischemia during a seizure, which does not always happen at a doctor's appointment. But in such cases, a cardiogram is removed during exercise, or with the help of a holter, angina attacks are determined.
The cardiogram clearly displays myocardial infarction, which greatly facilitates its diagnosis, and due to the simplicity and speed of the procedure, the procedure helps to start treatment on time. In addition, an ECG study acts as an indicator of the prescription of coronary syndrome.
The method of electrocardiography is used for the diagnosis of diseases of the cardiovascular system, and in endocrinological practice. Diabetes mellitus increases the risk of developing atherosclerosis and coronary artery disease. With pheochromocytoma, rhythm disturbance and cardiomyopathy are possible. Diffuse toxic goiter is a common cause of atrial fibrillation.
In modern medical practice, electrocardiography remains one of the simplest, fastest and most affordable diagnostic methods. With its help, a number of diseases are determined in the early stages and many complications are prevented.