How to treat streptococcus in the throat of a child? The features of therapy depend on what kind of infectious agent provoked the development of a particular disease.
How to treat streptococcus in the throat of a child? The features of therapy depend on what kind of infectious agent provoked the development of a particular disease.
To date, infectious disease specialists have identified at least 4 types of streptococcal infections.
However, the greatest danger to the health of the child is group A streptococci, which cause complications in the heart, kidneys, brain and joints.
Features of streptococci
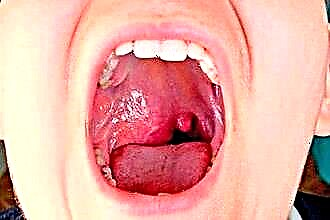
The development of a bacterial infection in children may be indicated by: purulent discharge from the nose, lack of appetite, sore throat, high fever, swelling and soreness of the lymph nodes, white plaque on the walls of the throat and tonsils. Beta-hemolytic streptococcus is among the most dangerous infectious agents. Pathogenic microorganisms provoke inflammation, which is accompanied by the accumulation of pus in the lesions.
The infection can spread to the paranasal sinuses - sphenoiditis, sinusitis, heart - endocarditis, pericarditis, brain - abscess, meningitis, or ears - otitis media, eustachitis.
Greening streptococcus is a conditionally pathogenic microorganism that does not cause diseases in the case of normal functioning of the immune system. However, hypothermia, lack of vitamins and minerals can weaken the defenses of the child's body. The subsequent active multiplication of gram-positive bacteria leads to poisoning of the body and the development of severe complications such as endocarditis or pericarditis.
Streptococcus is transmitted by airborne droplets and by household contact through toys, towels, dishes and other household items.
Diagnostics
How can you determine the development of streptococcus in the throat in children? It should be noted right away that it is impossible to identify the causative agent of the infection by clinical manifestations. Symptoms such as purulent sore throat, swelling of the mucous membrane, nasal congestion, enlargement of the submandibular lymph nodes and a severe runny nose indicate exclusively the development of a bacterial infection, but does not give any idea about the species of the causative agent of ENT disease.
To accurately determine the reason for the deterioration of the child's well-being, you need to undergo a hardware examination by a pediatrician and pass biomaterials (throat swab) for microbiological analysis. Only in this way will a specialist be able to accurately determine the nature of the causative agent of the disease and draw up a competent treatment regimen for the disease.
The waste products of streptococci cause severe allergic reactions, which can cause throat swelling and even asphyxiation.
The most difficult to treat is beta-hemolytic streptococcus, which quickly penetrates the tissues of the heart, compounds, kidneys, etc. To destroy pathogenic bacteria, antibiotics must be included in the conservative therapy regimen. If the disease is very severe, antimicrobials are given intramuscularly or intravenously.
Treatment methods
What drugs can eliminate streptococcus in the oropharynx in children? Treatment of a bacterial infection involves the use of drugs not only systemic, but also local. The simultaneous use of medications, inhalations and rinsing speeds up the child's recovery process.
To prevent drug poisoning, young patients are prescribed only those drugs that contain the minimum amount of toxic substances. In addition, it is very important to adhere to the dosage and duration of therapy, which can only be established by the attending physician. The basis of drug treatment is antibiotics, which must be supplemented with drugs of symptomatic action:
- antipyretic;
- antiallergic;
- immunostimulating;
- pain relievers;
- anti-inflammatory;
- vasoconstrictor.
If all measures of drug therapy are followed, after 4-5 days, the throat is completely cleared of purulent plaque, and the tonsils - from foci of inflammation.
It should be understood that streptococcal infection can recur, therefore, after the end of the antibacterial course, it is advisable to follow the preventive measures of ENT diseases. Weakened immunity is not able to cope with large infectious loads, therefore, within a month after recovery, try to limit the child's visit to public places - swimming pools, sports complexes, matinees, etc.
General recommendations
 With the development of ENT diseases, special attention should be paid to caring for a sick child. The waste products of streptococci create a considerable load on the heart, therefore it is very important that bed rest is strictly observed when the body temperature rises. In parallel with the passage of drug treatment, you need to monitor the implementation of the following rules:
With the development of ENT diseases, special attention should be paid to caring for a sick child. The waste products of streptococci create a considerable load on the heart, therefore it is very important that bed rest is strictly observed when the body temperature rises. In parallel with the passage of drug treatment, you need to monitor the implementation of the following rules:
- sparing diet - exclusion from the diet of sour, spicy, fatty and hot foods that irritate the laryngopharyngeal mucosa;
- drinking regimen - drinking at least 1.5 liters of warm drink per day, which accelerates the elimination of toxic substances from the body;
- throat treatment - rinsing a sore throat with antiseptic solutions that cleanse the mucous membrane of pathogens.
When choosing medicines, you cannot rely on your own knowledge and experience in treating colds. Streptococcal infection progresses rapidly and, in case of irrational treatment, can cause formidable complications.
In addition, infectious diseases in children can proceed in an atypical form, so the symptoms of bacterial inflammation can be confused with the manifestations of viral pharyngitis, catarrhal sore throat, laryngitis, etc.
Antibiotics
Streptococcal sore throat, pharyngitis and scarlet fever in children can be cured only with the help of antibacterial drugs. It is they who destroy disease-causing microbes and help eliminate the symptoms of the disease. On average, the course of antibiotic therapy is 7-10 days, depending on the stage of development of the pathology and the dynamics of recovery.
For the treatment of young patients, only safe medications are used that do not have a toxic effect. In the absence of complications, streptococcal infection can be eliminated with the help of penicillins:
- "Ampicillin";
- "Benzylpenicillin";
- Oxacillin;
- "Hikontsil".
With the development of chronic tonsillitis, the treatment regimen includes penicillins resistant to beta-lactamase, a special enzyme secreted by streptococci to neutralize the action of antibiotics.
Many drugs of the penicillin series cause allergic reactions in children, therefore, if necessary, they are replaced with cephalosporins:
- Cefazolin;
- Ceftriaxone;
- "Suprax".
It is possible to eliminate the symptoms of scarlet fever and mild forms of sore throat with the help of macrolides. Antibiotics of this group are the least toxic, so they can be used to treat children aged 1-3 years. The most effective macrolide drugs include:
- "Spiramycin";
- Erythromycin;
- "Midecamycin".
It is very important to follow the recommendations for the use of medicines exactly.It is undesirable to skip taking antibiotics or completely abandon their use if the child's well-being improves.
Gargling
Eliminate local manifestations of streptococcal infection - pain, purulent inflammation and swelling can be done with rinsing. Sanitizing procedures allow you to clear the mucous membrane of the throat from more than 70% of pathogenic microbes. Regular irrigation of the tonsils and oropharynx with antiseptics has a beneficial effect on local immunity and accelerates tissue healing.
During rinsing, the active components of medications penetrate directly into the foci of infection, which allows you to quickly stop the development of streptococci. Reducing the intensity of inflammatory processes helps to reduce temperature, eliminate muscle weakness and drowsiness. In the treatment of bacterial sore throat in children, you can use the following antiseptic preparations for gargling:
- Betadine;
- "Povidone";
- Chlorhexidine;
- Eludril;
- Stopangin;
- Elekasol;
- "Furacilin".
Iodine medications such as Betadine, Lugs and Iodinol should be used with caution. They can provoke a burn of the mucous membrane and a deterioration in the well-being of the child.
It is not recommended to use drugs based on iodine for renal failure, Duhring's dermatitis, thyroid disease.
Preschool children are prone to allergic reactions, therefore, for their treatment, it is necessary to select drugs with a minimum content of synthetic components. It is recommended to use herbal remedies for rinsing the throat - Elekasol, Tantum Verde, Rotokan, etc.
Local antibiotics
Topical antibiotics are antimicrobial medicines that come in the form of sprays, rinses, and inhalers. They quickly penetrate the lesions and destroy streptococci, thereby improving the patient's well-being. It is important to understand that the role of topical drugs is secondary, so they cannot be used in place of systemic antibiotics.
 Eliminate the manifestations of streptococcal infection by taking the following medications:
Eliminate the manifestations of streptococcal infection by taking the following medications:
- "Fusafungin" - a medicinal solution for inhalation, which inhibits the reproduction of gram-positive bacteria;
- "Geksetidine" - a low-toxic solution for rinsing the oropharynx, which destroys up to 80% of pathogens in the foci of inflammation;
- Octenisept is a bacteriostatic aerosol preparation that is added to saline solutions for gargling.
To speed up recovery, physiotherapy procedures should be performed 3-4 times daily during the week. Systematic cleansing of the mucous membrane from bacterial plaque will accelerate tissue regeneration, which will help eliminate discomfort when swallowing.
Antipyretic
Fever, high fever, and pain are typical manifestations of a bacterial infection. Along with taking antibiotics, you can not refuse to use drugs of symptomatic action. Streptococcal sore throat and pharyngitis are often accompanied by high fever, sweating, chills, muscle weakness, etc.
To alleviate the child's condition and quickly eliminate the symptoms of intoxication, anti-inflammatory and antipyretic medicines can be used:
- Nurofen;
- "Paracetamol";
- Ibuprofen.
It is undesirable for children under 12 years of age to give pharmaceutical products containing acetylsalicylic acid, as this can cause the development of Reye's syndrome.
Antipyretics (antipyretic drugs) should only be given to children when the temperature is over 38 ° C. The presence of subfebrile fever indicates that the body is trying to independently suppress the development of streptococci, whose cellular structures are destroyed when the temperature rises. If you bring down the temperature, this will only contribute to the spread of infection and, accordingly, a deterioration in health.
Throat lozenges
The advantage of lozenges and lozenges for resorption is the uniform distribution of the active components of the drug along the mucous membrane of the throat.
They usually include anti-inflammatory, analgesic and disinfecting substances that quickly clear the larynx from purulent foci of inflammation.
It is undesirable to give lollipops to children under 3 years old, they can swallow them or choke.
If you dissolve the lozenges every 2-3 hours, the pain, swelling and discomfort in the throat will go away within 3-4 days. For the treatment of streptococcal sore throat and pharyngitis, the following are usually used:
- Faringosept;
- Septolete;
- Flurbiprofen;
- Stopangin;
- Strepsils;
- Grammidin.
Most lozenges contain phenol, which destroys microbes and accelerates mucosal epithelialization. Components such as hexetidine, ambazone and benzalkonium chloride have a similar effect. To enhance the effect of drugs, it is recommended to pre-gargle with saline solutions. This will clear the laryngopharynx of mucus that prevents the absorption of active ingredients.
Inhalation with saline
Inhalation helps to soften the throat and eliminate inflammation, which has a beneficial effect on the patient's well-being. To prevent burns of the mucous membrane, it is recommended to perform the procedure using a nebulizer. The compact device converts medicinal solutions into an aerosol, which is quickly absorbed by the affected mucosa. In addition, nebulizer therapy is indicated for the treatment of even infants, since it does not cause side reactions and aspiration of fluid.
Strep throat infections can be treated with these nebulizer medications:
- Interferon;
- Tonsilgon;
- "Lazolvan";
- Ambrobene;
- Furacilin;
- Ingalipt;
- Chlorophyllipt.
In most cases, drugs are pre-diluted with mineral water (Borjomi, Essentuki) or saline in a 1: 1 ratio. This allows you to slightly reduce the concentration of active components in the drug, thereby reducing the likelihood of allergic reactions.
To achieve the desired results, during inhalation with a nebulizer, you need to take into account the following nuances:
- the therapy session should be carried out only in a sitting position;
- the duration of one procedure can vary from 7 to 15 minutes;
- only room temperature solutions can be poured into the nebulizer chamber;
- in case of sore throat, a special mask or mouthpiece is used for inhalation;
- on average, the course of nebulizer therapy is 10-15 days (at least 3-4 procedures should be performed per day).
Do not dilute medicines with herbal decoctions, as they contain sediment that can clog the filter or spray mesh, which will damage the device.
Folk remedies
 Many parents are skeptical about the use of drugs because they see them as pure "chemistry." Alternative medicine methods seem to them to be more effective and safer. In fact, folk remedies can be used in the treatment of ENT diseases, but only in combination with antibiotics.
Many parents are skeptical about the use of drugs because they see them as pure "chemistry." Alternative medicine methods seem to them to be more effective and safer. In fact, folk remedies can be used in the treatment of ENT diseases, but only in combination with antibiotics.
Gargling with solutions based on natural remedies is considered the most effective. Such folk remedies have a pronounced antibacterial and wound-healing effect:
- infusion of kombucha;
- a decoction of medicinal chamomile;
- infusion of oak bark;
- saline solution;
- tincture of propolis (diluted with water in a ratio of 1:10).
Too concentrated rinsing solutions dehydrate the mucous membranes and cause allergic reactions.
Do not forget that alternative medicine is only an addition to the main therapy. With a complete rejection of traditional medicine, the disease can become chronic and cause complications.
Prophylaxis
Beta-hemolytic streptococcus is a rheumatogenic strain of bacteria that can provoke disturbances in the work of the musculoskeletal and cardiovascular systems. Within 2-3 weeks after the complete disappearance of the symptoms of bacterial inflammation, the risk of developing rheumatism remains - a serious disease characterized by damage to the joints and heart muscle. How can complications be prevented?
Within 10 days after the end of the course of pharmacotherapy, children with a tendency to develop rheumatoid fever are prescribed benzylpenicillins and immunostimulating agents. The former prevent the reproduction of streptococci, and the latter increase the activity of immune cells that protect the body from the penetration of pathogenic viruses and microbes.
Some patients are prescribed drugs that normalize the biocenosis, i.e. qualitative composition of microflora in the oral cavity. If all recommendations are followed, the risk of complications is reduced to almost zero. To convince you of the absence of side diseases, it is advisable to be examined by a specialist at least twice within 2-3 weeks after elimination of the streptococcal infection.