With the defeat of the ENT organs, patients feel discomfort of varying intensity and localization. How to be treated if the throat in the Adam's apple region hurts and it hurts to swallow? Alarming clinical manifestations can signal dysfunction of the thyroid gland and its surrounding cartilage, cancer and infectious diseases, cervical osteochondrosis, and neuralgia.
 If pathological signs are found, you need to seek help from a therapist or otolaryngologist. If necessary, the doctor can refer the patient to an infectious disease specialist, traumatologist, oncologist, neurologist and specialists of a narrower specialization. It should be understood that throat discomfort is not always associated with the development of an infection.
If pathological signs are found, you need to seek help from a therapist or otolaryngologist. If necessary, the doctor can refer the patient to an infectious disease specialist, traumatologist, oncologist, neurologist and specialists of a narrower specialization. It should be understood that throat discomfort is not always associated with the development of an infection.
In some cases, an unpleasant symptom indicates the presence of benign and malignant tumors, impaired innervation of the pharyngeal muscles, thyroid dysfunction, etc.
What is Adam's apple?
Kadik are cartilaginous plates that are located in front of the thyroid gland. In men, they articulate at a lower angle, which makes the cartilage more visible than in women. Kadik performs several important functions, namely:
- protects the vocal cords and laryngeal tissue from injury;
- regulates the tension of the vocal cords during a conversation;
- prevents the penetration of liquid and food into the airways.
A pair of cartilaginous plates forms a barrier between the vocal cords, the tissues of the pharynx, and the endocrine gland. Due to the Adam's apple, the throat becomes less vulnerable to the negative effects of external factors. The cartilage seal reliably protects the thyroid gland from damage, which prevents the development of serious endocrine pathologies.
Pain in the larynx may indicate inflammation in the cartilage tissue, an enlarged endocrine gland, or the development of malignant neoplasms. In the event of an alarming symptom, it is undesirable to postpone a visit to a specialist. A timely visit to a doctor increases the chances of eliminating pathological processes using exclusively conservative methods of treatment.
Etiology of diseases
 Discomfort in the area of paired cartilage can occur due to the influence of various unfavorable factors. In more than 70% of cases, pain signals the development of septic inflammation in the tissues of the larynx.
Discomfort in the area of paired cartilage can occur due to the influence of various unfavorable factors. In more than 70% of cases, pain signals the development of septic inflammation in the tissues of the larynx.
Mechanical injuries play an important role in the manifestation of pain. Swelling of nearby tissues increases discomfort and can damage the thyroid gland.
The main causes of pain in the Adam's apple are:
- hypothyroidism;
- hyperthyroidism;
- thyroiditis;
- phlegmonous larynx;
- laryngitis;
- epiglottitis;
- throat cancer;
- cervical osteochondrosis.
Important! A prolonged dry cough can be a symptom of not only an infectious sore throat, but also the development of a cancerous tumor.
Oncological diseases pose the greatest danger to human health. As a rule, in the early stages of tumor development, patients do not feel pain and severe discomfort. From time to time, patients complain of a feeling of squeezing the pharynx while eating and swallowing saliva. Over time, a spastic cough occurs, while blood impurities are found in the sputum.
Laryngitis
Laryngitis is a catarrhal inflammation of the mucous membranes of the larynx, accompanied by soreness, pain and tissue edema. The development of ENT diseases can be provoked by pathogenic viruses or bacteria in the event of a sharp decrease in the reactivity of the body. In acute inflammation of the larynx, patients complain of the appearance of increasing pain in the area of the endocrine gland and Adam's apple.
 The clinical manifestations of laryngitis are:
The clinical manifestations of laryngitis are:
- spastic dry cough;
- hoarseness of voice;
- pain in the throat when swallowing;
- labored breathing; hyperthermia.
Important! Late treatment of laryngitis in children leads to the development of stenosis, i.e. false croup, which is fraught with hypoxia.
With the chronicization of pathological processes, the symptoms of the disease become less pronounced.
Ignoring the problem leads to the destruction of soft tissues in the airways and the development of local complications. To eliminate laryngitis, they resort to the use of antiviral or antibacterial agents, as well as antiallergic drugs that prevent the narrowing of the lumen in the airways.
Epiglottitis
Epiglottitis is called acute inflammation of the epiglottis, which provokes a violation of the patency of the airways. The epiglottis is a cartilaginous plate that serves as a distribution valve between the pharynx and the trachea. Due to the reflex closure of the inflamed epiglottis during the passage of mucus through the airway, patients with epiglottitis feel discomfort when swallowing saliva.
The following types of pathogens are provocateurs of inflammatory processes in the epiglottis and nearby tissues:
- pneumococci;
- varicellazoster;
- streptococci;
- fungi like Candida.
The development of epiglottitis is facilitated by a decrease in local immunity associated with mechanical damage and burns of the ENT organs.
The characteristic manifestations of pathology include increased salivation, shortness of breath, hoarseness of the voice, pain in the Adam's apple, cyanosis (blueness) of the lips, etc.
Larynx cancer
Cancer is one of the causes of discomfort at the level of the thyroid gland. At the stage of growth, malignant tumors do not cause pain and special discomfort. The presence of pathology is indicated by an enlarged thyroid gland, difficulty swallowing saliva, coughing and shortness of breath.
Cancer tumors are formed from the epithelium of the endocrine gland and are small nodules that increase in size over time. In the later stages of the development of cancer, patients complain of a feeling of squeezing of the pharynx, increasing pain and a spastic cough. The voice becomes hoarse, and the cervical lymph nodes increase in size.
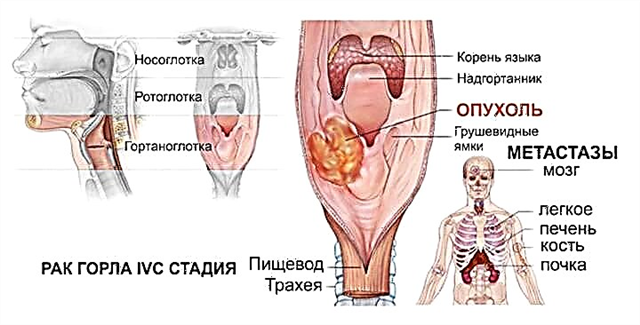
Of no small importance in the formation of cancerous tumors is the development of so-called precancerous pathologies, which include:
- pachyderma;
- leukoplasia of the laryngeal mucosa;
- chronic inflammation of the pharynx;
- papilloma formations;
- laryngeal ventricular cysts;
- dyskeratosis.
When contacting an oncologist, about a third of patients are diagnosed with stages 3 and 4 of the development of a cancerous tumor, in which neoplasms affect all three parts of the larynx. To prevent serious complications, a doctor should be consulted at the first signs of the disease.
Thyroiditis
Thyroiditis is an endocrine disease characterized by inflammation of the endocrine gland.
With the development of pathology, the patient has a feeling of squeezing the pharynx and Adam's apple. Visually, a thickening appears in the Adam's apple region, which indicates an increase in the size of the gland.
 Dysfunction of the thyroid gland inhibits the production of hormones, which can lead to the development of hypothyroidism.
Dysfunction of the thyroid gland inhibits the production of hormones, which can lead to the development of hypothyroidism.
The development of thyroiditis is evidenced by the following clinical manifestations:
- hyperthermia;
- headache;
- discomfort in the larynx;
- sensations of squeezing the Adam's apple;
- swelling of the throat;
- violation of the swallowing reflex.
The provocateurs of pathological processes in the thyroid gland are pathogenic viruses and bacteria that penetrate the tissues of the pharynx by a hematogenous route through the blood or lymph.
Disease therapy is carried out only in stationary conditions under the supervision of an endocrinologist and infectious disease specialist.
Phlegmon of the larynx
Phlegmon of the larynx is a diffuse purulent inflammation of the thyroid cartilage (Adam's apple), resulting from microbial damage to the ENT organs. The rapid development of pathology leads to the appearance of edema in the airways, which in some cases can lead to suffocation. In case of phlegmon, patients complain about:
- fever;
- painful swallowing;
- hoarseness of voice;
- shortness of breath;
- aphonia;
- enlarged lymph nodes;
- pain when turning the head;
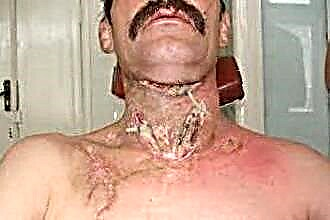 thickening of the tissues in the throat.
thickening of the tissues in the throat.
Septic inflammation progresses rapidly and affects the deeper tissues of the pharynx.
Failure to undergo therapy leads to cyanosis of the skin, severe pain in the throat, radiating to the back of the head and ears, etc.
A spastic cough increases pain and can bring the patient to painful shock, accompanied by hypoxia, impaired consciousness, and malfunctioning of the heart muscle.
Hypothyroidism
Hypothyroidism is a disease in which there is insufficient production of thyroid hormones. Pathology is most often preceded by inflammation and trauma of the endocrine gland. The key reason for the development of hypothyroidism is autoimmune thyroiditis. Most often, the disease occurs in the elderly and women during the period of hormonal changes in the body.
The clinical manifestations of the disease are nonspecific, so most patients are unaware of the development of hypothyroidism. Against the background of a lack of hormones in the body, disruptions in metabolic processes are observed, which becomes the cause of the development of myxedema. The disease is characterized by an increase in the amount of mucin in the intercellular space. The development of myxedema is evidenced by:
- dryness and pallor of the skin;
- swelling of the limbs;
- decrease in body temperature;
- hair loss;
- smoothing the contours of the face.
The disease can be eliminated through the passage of hormone replacement therapy, in which patients are prescribed drugs such as Triiodothyronine, Thyroidin, etc.
Cervical osteochondrosis
 Why is it painful to swallow in the Adam's apple, but the throat does not hurt? Painful swallowing of saliva may be a consequence of the development of cervical osteochondrosis. The disease is characterized by compression of blood vessels and nerve roots located between the vertebrae. Dislocation of the vertebrae leads to damage to the neural endings, which leads to pain in the muscles and ligaments.
Why is it painful to swallow in the Adam's apple, but the throat does not hurt? Painful swallowing of saliva may be a consequence of the development of cervical osteochondrosis. The disease is characterized by compression of blood vessels and nerve roots located between the vertebrae. Dislocation of the vertebrae leads to damage to the neural endings, which leads to pain in the muscles and ligaments.
The protrusion of the intervertebral discs provokes inflammation of the membranes of the spinal canal. Subsequent tissue edema leads to stagnation of blood in the cervical spine, resulting in stenosis.
Compression of the vertebral arteries, nerve bundles and nearby tissues causes discomfort, which is magnified by the tension of the muscles of the larynx.
The development of cervical osteochondrosis is evidenced by the following clinical manifestations:
- painful swallowing;
- discomfort in the Adam's apple;
- dry cough;
- a feeling of constriction in the throat;
- coughing up bloody discharge.
Late treatment of cervical osteochondrosis can lead to the development of a spinal stroke.
Other reasons
Unpleasant sensations in the region of the endocrine gland and Adam's apple cannot be called specific. The symptom may indicate the development of pharyngeal neurosis, infectious diseases, mental disorders and gastrointestinal dysfunction. When examining patients with characteristic complaints, the following are often diagnosed:
- paratonsillar abscess;
- angina of Ludwig;
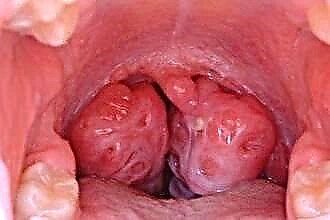 Infectious mononucleosis;
Infectious mononucleosis;- diphtheria;
- aphthous stomatitis;
- gastroduodenitis;
- enterocolitis;
- gastrointestinal reflux;
- cholecystitis;
- stomach ulcer.
Allergies to food, drugs, animal dander, etc. can provoke discomfort in the throat.
In addition, a lump in the throat in the Adam's apple can be a manifestation of neurosis. Constant stress, psycho-emotional overstrain and depressive conditions negatively affect the functioning of the autonomic nervous system. As a result of impaired conduction of nerve impulses, a spasm of the pharyngeal muscles occurs, as a result of which pain appears when swallowing saliva.

 thickening of the tissues in the throat.
thickening of the tissues in the throat. Infectious mononucleosis;
Infectious mononucleosis;