Tonsils - Oval-shaped lymphoid tissue glands are part of the immune system. In the human body, there are several types of glands, depending on the location: the palatine (first and second) and tubal (fifth and sixth) are paired organs, the pharyngeal (third) and lingual (fourth) are unpaired glands. The largest tonsils are palatine. They are the first to take a hit when the body is attacked by pathogenic microbes, therefore they become inflamed more often than others. Inflammation of these small glands brings a lot of trouble to the patient. What to do if the palatine glands hurt? How are tonsils treated?
Causes
 Pain in the tonsils is a characteristic sign of tonsillitis (acute tonsillitis). Frequent sore throats (4-6 times a year) are chronic tonsillitis. In a chronic process, the tonsils also hurt, but not nearly as intensely as in an acute one.
Pain in the tonsils is a characteristic sign of tonsillitis (acute tonsillitis). Frequent sore throats (4-6 times a year) are chronic tonsillitis. In a chronic process, the tonsils also hurt, but not nearly as intensely as in an acute one.
When microorganisms enter the oropharynx, the tonsils recognize them and, if viruses or bacteria dangerous to the human body are found, the glands begin to actively produce antibodies (macrophages). Macrophages fight the pathogenic microflora. This is how inflammation develops, which, in fact, is the body's immune response to the attack of the immune system by microorganisms.
The inflammatory process means that the microflora is violently destructive, and macrophages destroy the pathogenic microflora
Predisposing factors
But pathogenic bacteria and viruses alone are not enough for inflammation to begin. More predisposing factors are needed. Such factors include a long stay outside in damp windy weather, hypothermia, smoking, a tendency to allergies, chronic and acute infections of the ENT organs, blood diseases. The weaker a person's immunity, the more likely a person will get sore throat. People with strong immunity can also get sick with acute tonsillitis, but they tolerate the disease much easier. Chronic pathologies, constant stress, chronic fatigue greatly weaken the immune system.
The tonsils hurt not only with angina. The cause may be a pharyngeal abscess, an abscess in the tonsils themselves (one of the complications of acute tonsillitis). These are acute conditions that require urgent surgical care. Long-term exposure to allergens and dry air, foreign body in the pharynx, injury, fish bone in the tonsil, malignant tumor in the pharynx can cause pain. But if, with the above conditions, the tonsils may or may not hurt, then with angina the tonsils always hurt. This is the main feature that distinguishes this disease from other infectious diseases of the nasopharynx.
Clinical picture
- abrupt start and rapid development of the disease. Malaise, chills, weakness quickly give way to severe aches throughout the body, high fever, headache;
- pain in the throat and tonsils becomes quite unbearable when the patient tries to swallow. This makes it almost impossible to eat, and sometimes water;
- viral sore throat is always accompanied by a runny nose, cough, lacrimation, unlike bacterial;
Bacterial sore throat occurs much less often than viral (15% of all cases in adults), but the course is much more severe and longer
- The palatine glands and regional lymph nodes increase significantly in size, the mucous membrane turns red and swells. A serous or purulent plaque forms on the glands and mucous membrane of the pharynx, depending on the form of the disease.
Forms of acute tonsillitis
Typical forms:
- catarrhal;
- lacunar;
- follicular;
- fibrinous;
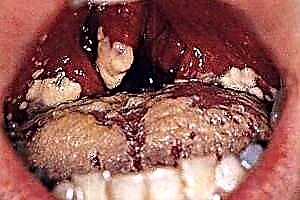
- phlegmonous.
Atypical forms:
- herpetic;
- fungal;
- syphilitic;
- laryngeal;
- monocytic;
- agranulocytic.
Diagnostics
The diagnosis of acute tonsillitis is made by an otolaryngologist based on a visual examination of the pharynx and the results of a smear from the throat mucosa. The pathogen is sown in the smear, its type is established, the sensitivity and susceptibility of the organism to antibiotics is determined. It is very important not to postpone a visit to a specialist when the first signs of illness appear. The success of therapy and the outcome of the disease depend on this. In the case of sore throat, self-medication is absolutely inappropriate. Only a doctor knows how to cure sore tonsils so that there are no complications.
Traditional therapy
Treatment of tonsils is carried out at home. Hospitalization is required in rare cases - for example, in case of complications requiring urgent surgical measures. It can be phlegmonous tonsillitis (paratonsillar abscess), in which an urgent opening of the abscess is necessary, laryngeal edema, and retropharyngeal abscess. Treatment should be comprehensive: this is the only way to expect a good therapeutic result. This means that at the same time, general therapy should be carried out, symptomatic, local, non-traditional. The patient himself must comply with certain regimes.
- Bed and dietary rest is an indispensable part of complex therapy. The body directs all its forces to fight the infection and the patient must help his body by temporarily limiting its activity. How quickly you can return to your normal lifestyle depends on the form of the disease, the type of pathogen, the state of immunity, the presence of bad habits and concomitant pathologies. Some patients need to be in bed for 1-3 days, others need a week or even two.
- In the treatment of tonsils, diet is of great importance. In acute tonsillitis, the mucous membrane of the tonsils and throat becomes hypersensitive and vulnerable, therefore, all foods that can damage the mucous membrane should be excluded during the acute phase. This is not only solid food, but also sour, spicy, too sweet. Solid food injures the mucous membrane, acidic and spicy - irritates, sweet foods contribute to the rapid reproduction of pathogenic microflora. It is also necessary to exclude foods that need additional energy.
 for digestion. This meat, except for chicken and rabbit, fatty fish, all fatty and smoked foods. The patient must adhere to a drinking regimen, the main principle of which is: the more often the better. You can drink teas, jelly, fruit drinks (except for cranberry), juices diluted in half with water, low-fat fermented milk and dairy products. Do not drink pure citrus juices.
for digestion. This meat, except for chicken and rabbit, fatty fish, all fatty and smoked foods. The patient must adhere to a drinking regimen, the main principle of which is: the more often the better. You can drink teas, jelly, fruit drinks (except for cranberry), juices diluted in half with water, low-fat fermented milk and dairy products. Do not drink pure citrus juices. - Bacterial sore throat is treated with broad-spectrum antibiotics. This is the foundation of therapy. In order to prevent beneficial bacteria in the intestines from dying, probiotics are prescribed simultaneously with antibacterial drugs. How to treat tonsils with viral sore throat? If the causative agent of the disease is a virus, then antibiotics are not prescribed. In this case, they not only will not be beneficial, but can also harm the body. This fact proves once again that it is imperative to consult a doctor to determine the etiology of the disease.
- The therapeutic complex includes symptomatic drugs to lower the temperature, eliminate edema, relieve painful sensations, vitamins to strengthen the immune system.
- What to do if purulent plugs appear in the lacunae of the tonsils? It is better to see a doctor and not touch the plugs yourself. Inexperienced cleansing of lacunae from plugs can provoke bleeding from the glands, which will generally aggravate the course of the disease. It is allowed to independently lubricate the mucous membrane of the throat and glands with antiseptic solutions. It is necessary to irrigate the throat with sprays and do regular gargling with saline.
- From the moment the temperature normalizes, warming procedures can be carried out: mustard plasters and mustard wraps, inhalations, warming compresses on the throat.
Alternative therapy
Folk remedies will help to quickly cure a sore throat:
- do frequent gargling with water and lemon juice, or garlic, onions, beets;
For sore throat, do not eat pure fresh garlic, onion and lemon
- take honey, propolis tincture, water 1: 1: 1, use for rinsing;
- mix a tablespoon of propolis oil with milk, take three times a day before meals;
- at the very beginning of the disease, as soon as a sore throat appears, it is useful to chew propolis until a slight burning sensation appears in the mouth. With severe pain and hyperemia, this remedy is not recommended;
- twice a day for 10 minutes to carry out inhalations with propolis ointment. To do this, take propolis and petroleum jelly 1: 1 and melt in a water bath. Store in a dark container;
- drink teas with raspberry jam, with pureed black
 currants, with lemon and honey;
currants, with lemon and honey; - gargling with a solution of apple cider vinegar is effective for treating sore tonsils: 10ml to 200ml of warm water;
- make vodka compresses on the throat, compresses with ash from the stove;
- in folk medicine, the treatment of tonsils with kerosene is considered effective. This oily liquid penetrates deep into tissues, dilates blood vessels, dulls pain, kills parasites, and has an antiseptic and anti-inflammatory effect. Pure kerosene is not used for therapeutic purposes. The composition is applied: refined kerosene, water, baking soda, sunflower oil. The mixture is lubricated with tonsils. Since kerosene is an aggressive substance, it can only be used after testing. It is necessary to lubricate the skin behind the ear with kerosene. If there are no rashes, redness, edema, then the product is suitable for use.
Official medicine considers such rinsing to be inappropriate.
Kerosene causes chemical burns, so you cannot use it for rinsing, especially for people who have too sensitive mucous membranes.
Complications, prevention
What to do to avoid complications? Angina, like no other infectious disease, has a lot of unpleasant consequences. These are local complications: abscess of the tonsils and pharynx, laryngeal edema, ulceration of the mucous membrane. Common complications: rheumatism, myocarditis, endocarditis, pericarditis, heart defects, arrhythmia, sepsis, brain abscess. In all cases, urgent care and long-term expensive treatment are required.
Complications can be avoided by timely contacting a specialist, following all recommendations, and going through the treatment process from start to finish. It is no secret that many people quit treatment when they feel the first improvement. You can't do that. In these cases, the disease either returns or complications develop.
Great importance should be attached to preventive measures. For tonsillitis, prevention is the same as for other infectious diseases: hardening the body, strengthening immunity, avoiding contact with sick people, avoiding crowded places at the peak of morbidity. You need to try not to expose yourself to stress, not to overcool, treat chronic pathologies on time, and eat well.


 for digestion. This meat, except for chicken and rabbit, fatty fish, all fatty and smoked foods. The patient must adhere to a drinking regimen, the main principle of which is: the more often the better. You can drink teas, jelly, fruit drinks (except for cranberry), juices diluted in half with water, low-fat fermented milk and dairy products. Do not drink pure citrus juices.
for digestion. This meat, except for chicken and rabbit, fatty fish, all fatty and smoked foods. The patient must adhere to a drinking regimen, the main principle of which is: the more often the better. You can drink teas, jelly, fruit drinks (except for cranberry), juices diluted in half with water, low-fat fermented milk and dairy products. Do not drink pure citrus juices. currants, with lemon and honey;
currants, with lemon and honey;