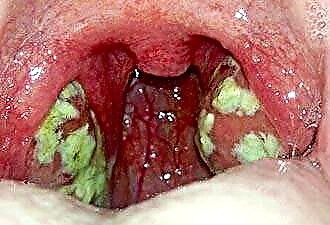
In most cases, the appearance of a pain syndrome in the throat indicates the development of an inflammatory reaction, which is characterized by hyperemia of the posterior pharyngeal wall and swelling of the mucous membrane. However, there are cases when the throat hurts, but not red.
 First, let us list when, most often, when examining the throat, redness may not be detected:
First, let us list when, most often, when examining the throat, redness may not be detected:
- chronic tonsillitis;
- chronic pharyngitis;
- atrophic, hyperplastic laryngitis;
- oncological processes in the throat;
- sexually transmitted diseases (gonorrhea, syphilis).
In addition, a similar picture is found in pathology such as:
- osteochondrosis in the cervical vertebral region develops as a result of pathological changes in the structure of the vertebrae, as well as intervertebral discs. As a result of this, compression of the nerve endings occurs, followed by the appearance of pain in the throat. In addition, a person may feel headache, discomfort, the presence of a foreign object in the oropharynx, or perspiration.
- spasm of the larynx against a background of nervous overstrain, panic attack leads to pain and sensation of a foreign object (coma) in the oropharynx.
- overstrain of the vocal apparatus during prolonged conversation, screaming;
- irritation of the mucous membrane of the oropharynx with polluted / cold air, smoke, as well as after inhalation of chemical vapors;
- allergic pharyngopathy can cause soreness in the throat due to tissue edema, but not inflammation and hyperemia of the mucous membrane;
- traumatic injury, for example, solid food (crackers), due to which small cuts form on the mucous membrane;
- gastroesophageal reflux disease in rare cases can provoke sore throat;
- diseases of the thyroid gland, when the glandular tissue grows, squeezing the nerve endings;
- severe vitamin deficiency;
- varicose veins of the esophagus.
Chronic tonsillitis
Chronic inflammation in the tonsils is characterized by frequent exacerbations in the form of acute tonsillitis.
Often, it is the palatine tonsils that are affected, however, children can be diagnosed with chronic adenoiditis, when the inflammation is localized in the pharyngeal tonsil.
The disease occupies up to 10% of cases among the entire population, therefore it is considered quite common. Among children, the figure rises to 15%.
The reasons that predispose the development of chronic tonsillitis include the activation of hemolytic, greening streptococcus, staphylococcus and adenoviruses. Under certain conditions, the development of pathology is possible against the background of the activation of opportunistic microorganisms. Incomplete recovery after acute tonsillitis leads to the chronicity of the disease.
The symptomatology of the disease depends on the form:
- for a simple form, periods of exacerbation are characteristic, in the intervals between which a person feels good. There is no intoxication syndrome. Tonsillitis aggravates the course of comorbidities such as hypertension, diabetes, thyroid dysfunction, epilepsy, and diseases of the digestive tract.
- toxic-allergic - depending on the severity of clinical signs, it is divided into two degrees. The first degree is characterized by subfebrile hyperthermia, malaise, cardiac arrhythmias, arthralgia, body aches. In laboratory tests, an increased ESR, leukocytosis and a violation of the ratio of protein fractions are detected. In the second degree, the clinical picture is more diverse, including dysfunction of the cardiac, urinary and osteoarticular systems.
The chronic form cannot be established during an exacerbation of the disease. During remission, pharyngoscopy is the main diagnostic method. Signs that indicate a long-term current autoimmune process include:
- the presence of purulent discharge in the crypts, which indicates frequent tonsillitis. Pus can be in the form of plugs, have an unpleasant odor;
- cohesion of the arches with the tonsils;
- swelling of the junction of the arches;
- overgrowth of tissue of the palatine arches;
- hyperemia of the arches is recorded quite rarely.
On examination by an ENT doctor, a regional enlargement of the lymph nodes is revealed, which also indicates chronic inflammation. The frequency of sore throats during the year is 2-3 times, rarely, when exacerbations are observed more often.
Treatment of the disease involves the use of conservative or surgical tactics. Evaluation of the effectiveness of conservative treatment is carried out on the basis of the following data:
- reducing the number of exacerbations;
- the disappearance of signs of a chronic process with pharyngoscopy;
- decrease in the severity of symptoms during exacerbations.
Conservative tactics include the appointment of medications and physiotherapy procedures. The course of treatment lasts 10 days three times a year. The most effective are the washing of the lacunae of the tonsils with an antiseptic solution. The procedures are repeated 10-15 times, every other day. From physiotherapy, UV radiation, UHF, ozokerite, as well as ultrasonic aerosols are prescribed. A special place in therapy is given to vitamins and immunomodulators.
If conservative methods are ineffective, surgical removal is performed - tonsillectomy. The indications include the toxic-allergic form of the second degree and the presence of paratonsillar abscesses.
With prolonged preservation of infected tonsils, tonsilogenic sepsis develops.
In the first days of the postoperative period, the patient is prohibited from drinking, talking and eating. Further, the diet gradually expands, however, the temperature regime of the dishes, as well as their consistency, should be controlled.
Chronic pharyngitis
Chronization of the inflammatory process in the oropharynx is observed with improper therapy for acute pharyngitis. There are several forms of the disease: catarrhal, hypertrophic, and atrophic, however, redness of the throat is not diagnosed only with the latter form of the disease.
The atrophic type of pharyngitis is characterized by thinning and severe dryness of the mucous membrane. It becomes shiny, varnished, and the number and size of the glands decreases.
Clinical symptoms are represented by dryness, soreness, some soreness in the pharynx, which makes it difficult to swallow and causes a putrid odor and mouth cavity. When talking, a person often becomes thirsty.
 Diagnostics includes pharyngoscopy. During the examination, thinning of the mucous membrane is revealed. It is shiny, pale pink in color; mucus of a viscous consistency and crust is localized on the surface.
Diagnostics includes pharyngoscopy. During the examination, thinning of the mucous membrane is revealed. It is shiny, pale pink in color; mucus of a viscous consistency and crust is localized on the surface.
Treatment of the disease is aimed at eliminating the cause of the pathology (sinusitis, dust, smoking), as well as reducing the severity of clinical symptoms. It is especially important to sanitize the oral cavity and remove crusts and mucus.
In the treatment, 1% sodium chloride solution is used, to which iodine is added in a volume of 5 drops per 190 ml. The prepared solution is used for daily washing of the tonsils, which removes the discharge and superficial plaque in the form of serous-purulent crusts. This solution is also used to regularly irrigate the mucous membrane of the oropharynx, thereby reducing irritation and the intensity of symptoms.
Periodically, lubrication of the posterior pharyngeal wall with Lugolev solution is required. With atrophic pharyngitis, the use of drugs, the action of which is aimed at suppressing the glandular secretion, is not allowed. This applies to sodium bicarbonate solutions, eucalyptus oils, sea buckthorn, which have a drying property.
A good effect is noted with the use of novocaine blockades, which are performed in the area of the posterior pharyngeal wall. For blockade, a combination of novocaine with biostimulants (aloe) is shown. The procedure is repeated 9 times at intervals of 6 days.
Chronic laryngitis
A sore throat can be with the hypertrophic type, which is characterized by the proliferation of the mucous membrane. The process can be local or widespread.
Symptomatically, the disease is manifested by persistent voice hoarseness, soreness, soreness, rare cough, as well as the sensation of a foreign object when swallowing.
In diagnostics, indirect laryngoscopy is used, as well as stroboscopy. If in the diffuse type, hyperemia is well visualized, then in the case of a limited process, the mucous membrane is slightly pink.
In differential diagnosis, it is necessary to distinguish the limited form from specific infectious granulomas and cancers. Serological methods and biopsy followed by histology are used to confirm the diagnosis.
 Treatment areas include the elimination of provoking factors and the provision of rest for the vocal cords. With hyperplasia of the mucous membrane, point quenching is performed with a lapis solution. The procedure is performed repeatedly at intervals of 2-3 days. The full course is 2 weeks.
Treatment areas include the elimination of provoking factors and the provision of rest for the vocal cords. With hyperplasia of the mucous membrane, point quenching is performed with a lapis solution. The procedure is performed repeatedly at intervals of 2-3 days. The full course is 2 weeks.
With a limited form, endolaryngeal removal is shown, after which the material is sent for histological analysis. The operation is performed using endoscopic techniques.
With the atrophic form of laryngitis, a person is worried about severe dryness of the mucous membrane, perspiration, soreness and a feeling of a foreign object. Blood streaks may be observed in the sputum, indicating damage to the mucous membrane during the coughing process.
Diagnosis is carried out using laryngoscopy, in which thinned, shiny mucous membranes are visualized. In some areas, it is covered with mucus of a viscous consistency and crusts.
Treatment is aimed at eliminating the provoking factor and reducing symptoms. To facilitate the discharge of sputum, medications are used to reduce its viscosity. For irrigation and inhalation, it is recommended to use an isotonic solution with iodine (5 drops per 190 ml). The procedure is repeated twice a day for a month.
Inhalation with oil and menthol is periodically required. Potassium iodide is used to stimulate the glandular function. It is taken orally 8 drops three times a day.
Before using iodine-containing preparations, it is necessary to establish the presence of possible allergic reactions.
With atrophy, injections into the posterior pharyngeal wall of novocaine with aloe are shown. The procedure is repeated 8 times at intervals of 6 days.
Oncological diseases
Depending on the localization of the malignant process, the features of the course of the disease are distinguished, as well as the prognosis:
- a tumor in the supra-ligamentous region is diagnosed in 65% of cases. Cancer is characterized by rapid progression, metastasis and poor prognosis.
- the ligamentous section occurs in 32% of cases. It can be diagnosed at an early stage.
- subglottic localization is found in 3%, usually in the later stages.
Laryngeal cancer in 98% is manifested by a squamous cell tumor. It is quite difficult to identify the oncological process at the first stage of development, since there are no clinical signs. As the disease progresses, the patient notices a decrease in body weight, malaise, decreased appetite and subfebrile hyperthermia. In laboratory tests, anemia is recorded.
With an increase in the formation in the throat, a person notes the appearance of soreness, a feeling of a foreign lump, impaired swallowing, difficulty in passing solid food, dry cough in the form of seizures, unpleasant taste sensations and putrid breath.
In addition, there is voice hoarseness, blood impurity in saliva, phlegm, shortness of breath, ear pain and numbness in areas of the face. Regional lymph nodes become enlarged, dense, lumpy, welded together and adjacent tissues. They form a motionless conglomerate.
In most cases, the cause of death is:
- bleeding that cannot be stopped. Its development is due to a violation of the integrity of the blood vessels against the background of the progression of the disease and the decay of the tumor;
- secondary infection with the development of sepsis;
- suffocation due to blood entering the respiratory tract.
Diagnosis of oncological diseases is based on palpation of regional lymph nodes, examination of the pharynx, larynx with  laryngoscopy, fibrolaryngoscopy, as well as the study of smears and material taken during the puncture of the altered area of the mucous membrane.
laryngoscopy, fibrolaryngoscopy, as well as the study of smears and material taken during the puncture of the altered area of the mucous membrane.
Suspicion is caused by areas with an uncharacteristic shade, ulceration, raids, elevating above the rest of the areas. Lymph nodes are examined using ultrasound. The tracheoscope helps to establish the prevalence of the malignant process and assess the degree of airway obstruction.
To detect metastases, radiography, bronchoscopy, computed and magnetic resonance imaging are prescribed.
Treatment of oncological diseases is based on the results of diagnostics. Depending on the stage, surgery can be performed to remove the tumor, altered lymph nodes, radiation and chemotherapy.
The prognosis for a five-year survival rate in the first stage reaches 80%, in the second - 70%, in the third - 55%, in the fourth - no more than 30%.
Syphilis
There are several forms of venereal disease:
- angular, the symptomatology of which resembles acute tonsillitis with the defeat of one amygdala. The disease is characterized by soreness when swallowing, febrile hyperthermia, reddening of the mucous membrane and enlarged lymph nodes.
- ulcerative - accompanied by the appearance of an ulcerative defect on the surface of the amygdala. Also, there are gray films, hectic hyperthermia, pain when swallowing, increased salivation and impaired motor ability of the jaw.
- erosive - manifested by erosion on the tonsil, the appearance of serous discharge.
- the gangrenous form is characterized by a sharp deterioration, fever up to 40 degrees, malaise and increased sweating.
Diagnostics consists in the analysis of anamnestic information, endoscopy and serological tests.
As you can see, there are a huge number of reasons for the appearance of pain in the oropharynx area. To determine the correct treatment tactics, you must consult a doctor. A complete examination will allow you to establish the severity of the disease, as well as diagnose concomitant pathology. When pain appears, treatment should be started with rinsing the throat with antiseptic solutions. However, in the absence of effect and increased pain already on the third day, you should consult a specialist.